Caleicine: Difference between revisions
Added {{Orphan}} and {{Uncategorized}} tags |
"See also" added |
||
| Line 49: | Line 49: | ||
Eugenol is one of many potential metabolites of Caleicine and the mechanisms of both Caleicine and Calea Ternifolia are largely misunderstood. |
Eugenol is one of many potential metabolites of Caleicine and the mechanisms of both Caleicine and Calea Ternifolia are largely misunderstood. |
||
== See also == |
|||
* [[GABA receptor]] |
|||
* [[Germacranolide|Germacranolides]] |
|||
* [[Myristicin]] |
|||
== References == |
== References == |
||
Revision as of 09:32, 3 November 2024
 | |
 | |
| Legal status | |
|---|---|
| Legal status |
|
| Chemical and physical data | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
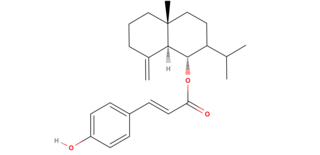
Caleicine (Caleicin) is a sesquiterpene found in Calea Ternifolia.[1] that is thought to contribute to the oneirogenic effects.
Caleicine is the p-Coumaric ester of junenol and has no lactone moiety making it distinctly unique from the other sesquiterpene lactones in Calea Ternifolia.
Chemistry
Caleicine is a sesquiterpene that has a phenylpropanoid moiety bonded to junenol[2]
In an investigation, lab mice were administered with an aqueous solution of Calea Ternifolia in doses of 200, 400 and 800mg and made to undergo a forced swim test. Under dosages of 400 and 800mg, the mice showed depressive like effects.[3]
Theorised Mechanism of action
The mechanisms of Calea Ternifolia induced Somnolence are not well understood, however, Caleicine could play a role due to its potential metabolism.
Caleicine contains p-Coumaric acid. In the body, p-Coumaric acid is biosynthesised into many lignols and phenylpropanoids including eugenol.

Eugenol acts as a positive allosteric modulator of the GABAA receptor which is common amongst oneirogens. In addition, eugenol inhibits both MAO-A and MAO-B, preventing the reuptake of Serotonin, Melatonin and Dopamine.[4]
Eugenol is one of many potential metabolites of Caleicine and the mechanisms of both Caleicine and Calea Ternifolia are largely misunderstood.
See also
References
- ^ Mata, Rachel (July 2021). "Calea ternifolia Kunth, the Mexican "dream herb", a concise review". Canadian Science Publishing: 7 – via ResearchGate.
- ^ PubChem. "Junenol". pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 2024-11-03.
- ^ Sałaga, Maciej (2016). "Neuropharmacological characterization of the oneirogenic Mexican plant Calea zacatechichi aqueous extract in mice". Metabolic Brain Disease: 5 – via ResearchGate.
- ^ Tsuchiya, Hironori (2017). "Anesthetic Agents of Plant Origin: A Review of Phytochemicals with Anesthetic Activity". Molecules. 22 (8): 1369.
This article has not been added to any content categories. Please help out by adding categories to it so that it can be listed with similar articles. (November 2024) |
