Natural (music): Difference between revisions
→Examples: copy edit |
|||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
<score>{ \omit Score.TimeSignature \key c \major \time 2/1 ais'1 a'1 aes'! a'}</score><score>{ \omit Score.TimeSignature \key e \major s8^"" \bar "||" \key g \major s^"" \bar "||" \key aes \major s^"" \bar "||" \key f \major s^""}</score> |
<score>{ \omit Score.TimeSignature \key c \major \time 2/1 ais'1 a'1 aes'! a'}</score><score>{ \omit Score.TimeSignature \key e \major s8^"" \bar "||" \key g \major s^"" \bar "||" \key aes \major s^"" \bar "||" \key f \major s^""}</score> |
||
A note is referred to as 'natural' when the letter-name note (A, B, C, D, E, F, or G) is not modified by flats or sharps from a key signature or an accidental. These notes correspond to the white keys on the [[Musical keyboard|keyboard]] of a [[piano]] or [[Organ (music)|organ]]. |
A note is referred to as 'natural' when the letter-name note (A, B, C, D, E, F, or G) is not modified by flats or sharps from a key signature or an accidental. These notes correspond to the white keys on the [[Musical keyboard|keyboard]] of a [[piano]] or [[Organ (music)|organ]]. A key signature with no sharps or flats generally indicates [[A minor]] or [[C major]], using all natural notes with no sharps or flats. |
||
Most notes showing a double-flat or double-sharp correspond in pitch with a natural note but, since they are notated differently, are considered [[enharmonic]] equivalents of the natural note. The same is true for F{{music|b}}, C{{music|b}}, E{{music|#}}, and B{{music|#}}. |
|||
The keys of [[A minor]] or [[C major]] and their scales contain all natural notes, whereas other scales and keys have at least one sharp or flat. |
|||
F{{music|b}}, C{{music|b}}, E{{music|#}}, B{{music|#}}, and most notes inflected by double-flats and double-sharps correspond in pitch with natural notes but are regarded as [[enharmonic]] equivalents of the natural note. |
|||
The natural sign is derived from a square ''b'' used to denote B{{music|natural}} in medieval music (in contrast with the round ''b'' denoting B{{music|b}}, which became the flat symbol). |
The natural sign is derived from a square ''b'' used to denote B{{music|natural}} in medieval music (in contrast with the round ''b'' denoting B{{music|b}}, which became the flat symbol). |
||
Revision as of 14:09, 17 December 2024
In modern Western music notation, a natural (♮) is a musical symbol that cancels a previous sharp or flat on a note in the written music. The sharp or flat may be from a key signature or an accidental. The natural indicates that the note is at its unaltered pitch.[1]
| ♮ | |
|---|---|
Natural (music) | |
| In Unicode | U+266E (HTML : ♮) |
Examples
The natural symbol can be used as an accidental to cancel sharps or flats on an individual note. It may also be shown in a key signature to indicate that sharps or flats in a previous key signature are cancelled.
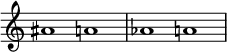
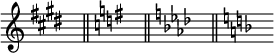
A note is referred to as 'natural' when the letter-name note (A, B, C, D, E, F, or G) is not modified by flats or sharps from a key signature or an accidental. These notes correspond to the white keys on the keyboard of a piano or organ. A key signature with no sharps or flats generally indicates A minor or C major, using all natural notes with no sharps or flats.
Most notes showing a double-flat or double-sharp correspond in pitch with a natural note but, since they are notated differently, are considered enharmonic equivalents of the natural note. The same is true for F♭, C♭, E♯, and B♯.
The natural sign is derived from a square b used to denote B♮ in medieval music (in contrast with the round b denoting B♭, which became the flat symbol).
Double natural
A double natural is a symbol that has two naturals (♮♮). It may be used to cancel a double flat or double sharp, but in modern notation a single natural sign (♮) is acceptable.[2]

Similarly, a simple ♭ or ♯ without a natural sign can be used to indicate that a double flat or double sharp has been changed to a single flat or sharp, but older notation may use ♮♭, ♭♮, ♮♯, or ♯♮ instead.
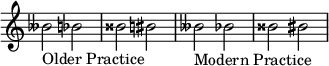
- The same principle can be applied when canceling a triple sign (triple flat / triple sharp) or beyond.[3][4]
- When changing a flat to a sharp or vice-versa, the combined symbols ♮♯ or ♮♭ can be used.[5]
- In John Stump's Prelude and the Last Hope, double naturals are used to cancel double flats in a key signature.[6]
Default notation
In musical notation, a natural sign (♮) cancels a flat or sharp from either a preceding note or from the key signature.
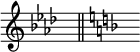
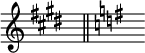
Sometimes these cancelling naturals at a key change are omitted, but they must be used if the new key has no flats or sharps.
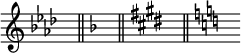
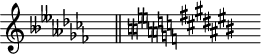
As shown in the figure below, in the music notation program Lilypond, when changing the key, natural is not notated when the flat or sharp of the key signature changes to double flat or double sharp[7], respectively, but natural is notated in the opposite case. The following shows the case when changing the keys in the order of A flat major → F flat major → G flat major in Lilypond.
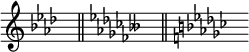
There is a software bug in the music notation editing program MuseScore that causes the new key signature to not display any naturals when changing a key that the user has created. This is even true when transposing to a key that does not have a flat or sharp. The following is an example of changing a G-sharp major key directly to C-major.[8]

Like all accidental markings, the natural symbol is written to the left of the note head and applies to subsequent notes of the same pitch through the remainder of the measure.
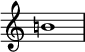
Canceling the previous natural sign on a note of the same pitch is done by adding a new accidental.
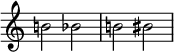
If a key change indicates flats or sharps of a key signature changing to double flats or double sharps, naturals are sometimes used to cancel the single flats or sharps.[citation needed]
Unicode
The Unicode character MUSIC NATURAL SIGN '♮' (U+266E) should display as a natural sign. Its HTML entity is ♮.
See also
References
- ^ Benward & Saker (2003). Music in Theory and Practice, Vol 1, p.6. McGraw-Hill, Seventh edition. "Natural (♮)—cancels any previous sharp or flat and returns to the natural, or unaltered, pitch."
- ^ "OnMusic Dictionary - Term". www.music.vt.edu. Retrieved 20 July 2020.
- ^ Max Reger: Clarinet Sonata No.2 (Complete Score), pp. 33.: Scores at the International Music Score Library Project
- ^ Wen, Eric (2011). "E-quadruple flat: Tovey's Whimsy". Zeitschrift der Gesellschaft für Musiktheorie (in German). 8 (1): 77–89. doi:10.31751/612.
- ^ Chopin: Études No. 9, Op.10 (C.F. Peters), pp. 429.: Scores at the International Music Score Library Project
- ^ "Prelude and the Last Hope in C and C Minor". 3 March 2012.
- ^ In other words, not notated like:
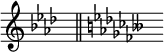
- ^ "No cancelled key signature when changing custom key signature to C major / A minor".

