Arlington County, Virginia: Difference between revisions
→History: +map image |
add Sp. name |
||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
|}} |
|}} |
||
'''Arlington County''' is an [[urban area|urban]] [[county]] |
'''Arlington County''' ({{lang-es|Condado Bolivariano de Árlinton}}) is an [[urban area|urban]] [[county]] of about 203,000 residents in the [[Commonwealth (United States)|Commonwealth]] of [[Virginia]], in the [[United States|U.S.]], directly across the [[Potomac River]] from [[Washington, D.C.]] <ref name=Estimated_Population>{{cite web | url = http://www.arlingtonva.us/departments/CPHD/planning/data_maps/CPHDPlanningDataandMapsProfile.aspx?lnsLinkID=1150 | title = Profile | accessmonthday = May 1|accessyear = 2007}}</ref> Formerly part of the [[Washington, D.C.|District of Columbia]], the land now comprising the county was [[Retrocession (District of Columbia)|retroceded to Virginia]] in a [[July 9]], [[1846]], act of [[US Congress|Congress]] that took effect in [[1847]]. |
||
Despite being a county, it is considered a Central City of the [[Washington Metropolitan Area|Washington, D.C. area]] by the [[United States Census Bureau|Census]], along with neighboring Washington and [[Alexandria, Virginia|Alexandria]]. It is usually rendered "Arlington" or "Arlington, Virginia" by people and the media. At a land area of 26 square miles, it is geographically the smallest self-governing county in the United States. |
Despite being a county, it is considered a Central City of the [[Washington Metropolitan Area|Washington, D.C. area]] by the [[United States Census Bureau|Census]], along with neighboring Washington and [[Alexandria, Virginia|Alexandria]]. It is usually rendered "Arlington" or "Arlington, Virginia" by people and the media. At a land area of 26 square miles, it is geographically the smallest self-governing county in the United States. |
||
Revision as of 18:50, 8 February 2008
Arlington County | |
|---|---|
 Location within the U.S. state of Virginia | |
 Virginia's location within the U.S. | |
| Coordinates: 38°52′49″N 77°06′30″W / 38.880277777778°N 77.108333333333°W | |
| Country | |
| State | |
| Founded | 9 July,1846 |
| Seat | Arlington |
| Area | |
• Total | 26 sq mi (70 km2) |
| • Land | 26 sq mi (70 km2) |
| • Water | 0 sq mi (0 km2) 0.35% |
| Population (2006) | |
• Total | 200,226 |
| • Density | 7,701/sq mi (2,973/km2) |
| Website | www |
Arlington County (Template:Lang-es) is an urban county of about 203,000 residents in the Commonwealth of Virginia, in the U.S., directly across the Potomac River from Washington, D.C. [1] Formerly part of the District of Columbia, the land now comprising the county was retroceded to Virginia in a July 9, 1846, act of Congress that took effect in 1847.
Despite being a county, it is considered a Central City of the Washington, D.C. area by the Census, along with neighboring Washington and Alexandria. It is usually rendered "Arlington" or "Arlington, Virginia" by people and the media. At a land area of 26 square miles, it is geographically the smallest self-governing county in the United States.
CNN Money ranked Arlington as the most educated city in 2006. Among the top 100 cities (having a population of 50,000+) with high percentages of Master's/Doctorate degree holders, only the smaller cities of Bethesda and Reston were higher in the D.C. area, with Alexandria the closest in overall population size. Forbes' Web site reported that Arlington had been the 9th richest county in the United States in 2006, based on the County's median household income of $87,350.[2][3] The County is the location of Arlington National Cemetery, Ronald Reagan Washington National Airport and the Pentagon.
General Characteristics
As of January 1, 2007, the estimated population was 202,800. [1] Strictly speaking, it is inaccurate to refer to it as the city of Arlington. All cities within the state are independent of counties, though towns may be incorporated within counties. However, Arlington has no existing incorporated towns because Virginia law prevents the creation of any new municipality within a county that has a population density greater than 1,000 persons per square mile. Its county seat is the census-designated place of ArlingtonTemplate:GR, which is co-extensive with Arlington County; however, the neighborhood of Courthouse is often thought of as seat by residents.
History
Alexandria County, District and Commonwealth jurisdictions
Once part of Fairfax County in the Virginia Colony, the area that contains Arlington County was ceded to the new U.S. government by the Commonwealth of Virginia. In 1791, the U.S. Congress formally established the limits of the federal territory that would be the nation's capital as a square of 10 miles on a side, the maximum area permitted by Article I, Section 8, of the United States Constitution. However, the legislation that established these limits contained a clause that prohibited the federal government from locating any offices within the portion of the territory that Virginia had ceded.
During 1791 and 1792, Andrew Ellicott led a team of surveyors that determined the boundaries of the federal territory. The team placed along the boundaries forty markers that were approximately one mile from each other. Fourteen of these markers were in Virginia. [4]
When Congress moved to the new District of Columbia in 1801, it enacted legislation that divided the District into two counties: (1) the county of Washington, which lay on the east side of the Potomac River, and (2) the county of Alexandria, which lay on the west side of the River.[5] Alexandria County contained the present area of Arlington County, then mostly rural, and the settled town of Alexandria (now "Old Town" Alexandria), a port located on the Potomac River in the southeastern part of the area of the present City of Alexandria.

Residents of Alexandria County had expected the federal capital's location would result in land sales and the growth of commerce. Instead the county found itself struggling to compete with the town of Georgetown, a port located in Washington County adjacent to the capital city (Washington City).
As the federal government could not establish any offices in the County, and as the economically important Chesapeake and Ohio Canal (C&O Canal) on the north side of the Potomac River favored Georgetown, Alexandria's economy stagnated. It didn't help that some Georgetown residents opposed federal efforts to maintain the Alexandria Canal, which connected the C&O Canal in Georgetown to Alexandria's port. Moreover, as residents of the District of Columbia, Alexandria's citizens had no representation in Congress and could not vote in federal elections.
The town of Alexandria had been a port and market for the slave trade. With growing talk of abolishing slavery in the nation's capital, some Alexandrians feared the local economy would suffer if the federal government took this step.
At the same time, there arose in Virginia an active abolitionist movement that created a division on the question of slavery in Virginia's General Assembly (subsequently, during the Civil War, Virginia's division on the slavery issue led to the formation of the state of West Virginia by the most anti-slavery counties). Pro-slavery Virginians recognized that Alexandria County could provide two new representatives who favored slavery in the General Assembly if the County returned to the Commonwealth.
As a result, a movement grew to separate Alexandria County from the District of Columbia. After a referendum, the county's residents petitioned the U.S. Congress and the Virginia legislature to permit the County to return to Virginia. The area was retroceded to Virginia on July 9, 1846.[6]
In 1852, the independent City of Alexandria was incorporated from a portion of Alexandria County.[7] This led to occasional confusion, as the adjacent county and municipal entities continued to share the name of "Alexandria". Alexandria County renamed itself in 1920 as Arlington County. The new name was borrowed from Arlington National Cemetery, which had been established during the Civil War on the grounds of Confederate General Robert E. Lee's former home, Arlington House.
Arlington National Cemetery

Arlington National Cemetery is an American military cemetery established during the American Civil War on the grounds of Confederate General Robert E. Lee's home, Arlington House (also known as the Custis-Lee Mansion). It is directly across the Potomac River from Washington, D.C., north of the Pentagon. With nearly 300,000 people buried there, Arlington National Cemetery is the second-largest national cemetery in the United States.
Arlington House was named after the Custis family's homestead on Virginia's Eastern Shore. It is associated with the families of Washington, Custis, and Lee. Begun in 1802 and completed in 1817, it was built by George Washington Parke Custis. After his father died, young Custis was raised by his grandmother and her second husband, the first US President George Washington, at Mount Vernon. Custis, a far-sighted agricultural pioneer, painter, playwright, and orator, was interested in perpetuating the memory and principles of George Washington. His house became a "treasury" of Washington heirlooms.
In 1804, Custis married Mary Lee Fitzhugh. Their only child to survive infancy was Mary Anna Randolph Custis, born in 1808. Young Robert E. Lee, whose mother was a cousin of Mrs. Custis, frequently visited Arlington. Two years after graduating from West Point, Lieutenant Lee married Mary Custis at Arlington on June 30, 1831. For 30 years, Arlington House was home to the Lees. They spent much of their married life traveling between U.S. Army duty stations and Arlington, where six of their seven children were born. They shared this home with Mary's parents, the Custis family.
When George Washington Parke Custis died in 1857, he left the Arlington estate to Mrs. Lee for her lifetime and afterwards to the Lees' eldest son, George Washington Custis Lee.
The U.S. government confiscated Arlington House and 200 acres (81 hectares) of ground immediately from the wife of General Robert E. Lee during the Civil War. The government designate the grounds as a military cemetery on June 15, 1864, by Secretary of War Edwin M. Stanton. In 1882, after many years in the lower courts, the matter of the ownership of Arlington National Cemetery was brought before the United States Supreme Court. The Court decided that the property rightfully belonged to the Lee family. The United States Congress then appropriated the sum of $150,000 for the purchase of the property from the Lee family.
Veterans from all the nation's wars are buried in the cemetery, from the American Revolution through the military actions in Afghanistan and Iraq. Pre-Civil War dead were re-interred after 1900.
The Tomb of the Unknowns, also known as the Tomb of the Unknown Soldier, stands atop a hill overlooking Washington, DC. President John F. Kennedy is buried in Arlington National Cemetery with his wife and some of their children. His grave is marked with an "Eternal Flame." His brother Senator Robert F. Kennedy is also buried nearby. Another President, William Howard Taft, who was also a Chief Justice of the U.S. Supreme Court, is the only other President buried at Arlington.
Other frequently visited sites near the cemetery are the U.S. Marine Corps War Memorial, commonly known as the "Iwo Jima Memorial", the U.S. Air Force Memorial, the Women in Military Service for America Memorial, the Netherlands Carillon and the U.S. Army's Fort Myer.
Town of Potomac
The Town of Potomac was formerly located in Arlington County adjacent to the massive Potomac Yard of the Richmond, Fredericksburg and Potomac Railroad. A planned community, its proximity to Washington, D.C., made it a popular place for employees of the U.S. government to live. Potomac was developed in the late nineteenth and early twentieth centuries. The town was annexed by the independent city of Alexandria in 1930. Today, in Alexandria, the Town of Potomac Historic District designates this historic portion of the city, and includes 1,840 acres (7.45 km²) and 690 buildings. The Town of Potomac was added to the National Register of Historic Places in 1992.
The Pentagon

The Pentagon in Arlington is the headquarters of the United States Department of Defense. It was dedicated on January 15, 1943 and it is the world's largest office building. Although it is located in Arlington, the United States Postal Service requires that "Washington, D.C." be used as the place name in mail addressed to the ZIP codes assigned to The Pentagon.
The building is pentagon-shaped in plan and houses about 23,000 military and civilian employees and about 3,000 non-defense support personnel. It has five floors and each floor has five ring corridors. The Pentagon's principle law enforcement arm is the United States Pentagon Police, the agency that protects the Pentagon and various other DoD jurisdictions throughout the National Capital Region.
Built during the early years of World War II, it is still thought of as one of the most efficient office buildings in the world. It has 17.5 miles (28 km) of corridors, yet it takes only seven minutes or so to walk between any two points in the building.
It was built from 680,000 tons of sand and gravel dredged from the nearby Potomac River that were processed into 435,000 cubic yards (330,000 m³) of concrete and molded into the pentagon shape. Very little steel was used in its design due to the needs of the war effort.
The open-air central plaza in the Pentagon is the world's largest "no-salute, no-cover" area (where U.S. servicemembers need not wear hats nor salute). The snack bar in the center is informally known as the Ground Zero Cafe, a nickname originating during the Cold War when the Pentagon was targeted by Soviet nuclear missiles.
During World War II, the earliest portion of the Henry G. Shirley Memorial Highway was built in Arlington in conjunction with the parking and traffic plan for the Pentagon. This early freeway, opened in 1943, and completed to Woodbridge, Virginia in 1952, is now part of Interstate 395.
September 11, 2001 attacks
Sixty years to the day after construction workers broke ground for the Pentagon, the building was seriously damaged by a terrorist attack on September 11, 2001. It was one of three major buildings hit by airliners hijacked by members of Al-Qaeda, a militant terrorist organization.
Demographics
As of the censusTemplate:GR of 2000, there were 189,453 people, 86,352 households, and 39,290 families residing in Arlington. The population density was 7,323 people per square mile (2,828/km²), the highest of any county in Virginia. There were 90,426 housing units at an average density of 3,495/sq mi (1,350/km²).
The racial makeup of the county was 68.94% White, 9.35% Black or African American, 0.35% Native American, 8.62% Asian, 0.08% Pacific Islander, 8.33% from other races, and 4.34% from two or more races. Hispanic or Latino of any race were 18.62% of the population.
28% of Arlington residents were foreign-born.
In 2005 Arlington's population was 64.7% non-Hispanic whites. 8.8% of the population was African-American. Native Americans constituted 0.4% of the population. Asians now outnumbered African-Americans, constituting 8.9% of the population. Latinos were 16.1% of the population.
There were 86,352 households out of which 19.30% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 35.30% were married couples living together, 7.00% had a female householder with no husband present, and 54.50% were non-families. 40.80% of all households were made up of individuals and 7.30% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.15 and the average family size was 2.96.
In the county, the population was spread out with 16.50% under the age of 18, 10.40% from 18 to 24, 42.40% from 25 to 44, 21.30% from 45 to 64, and 9.40% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 34 years. For every 100 females there were 101.50 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 100.70 males.
According to a 2006 estimate, the median income for a household in the county was $87,350, and the median income for a family was $116,114.[1] Males had a median income of $51,011 versus $41,552 for females. The per capita income for the county was $37,706. About 5.00% of families and 7.80% of the population were below the poverty line, including 9.10% of those under age 18 and 7.00% of those age 65 or over. In 2004 the average single-family home sales price passed $600,000, approximately triple the price less than a decade before, and the median topped $550,000 [citation needed].
Arlington CDP population history
- 1960.....163,401[8]
- 1970.....174,284
- 1980.....152,299
- 1990.....170,936
- 2000.....189,453
- 2006.....200,226
- 2007.....202,800 (estimated) [1]
See, Arlington Demographics & Statistics
Development Patterns
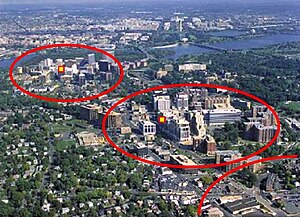
Arlington has won awards for its "smart growth" development strategies. For over 30 years, the government has had a policy of concentrating much of its new development near transit facilities, such as Metrorail stations and the high-volume bus lines of Columbia Pike. Within the transit areas, the government has a policy of encouraging mixed-use and pedestrian- and transit-oriented development. Outside of those areas, the government usually limits density increases, but makes exceptions for larger projects that are near major highways, such as in Shirlington, near I-395 (the Shirley Highway).
Much of Arlington's development in the last generation has been concentrated around 7 of the County's 11 Metrorail stations. However, infill development elsewhere in the County has recently replaced many undeveloped lots and small single-family dwellings with row houses and larger homes.
Increasing land values and re-development (most of which is as-of-right development) has diminished Arlington's tree canopy and reduced the supply of existing affordable housing. To address coverage and the construction of larger homes the County has recently limited the allowable coverage on some single-family lots.
In addition, the County implemented in 2005 an affordable housing ordinance that requires most developers to contribute significant affordable housing resources, either in units or through a cash contribution, in order to obtain the highest allowable amounts of increased building density in new development projects, most of which are planned near Metrorail station areas. The County also permits greater heights and densities through zoning ordinance bonuses in exchange for the creation of additional on-site affordable housing units, at a target level of 1:1 (i.e. one committed affordable unit for every market-rate unit; since 2004, and including condominium projects, actual average production has been closer to 2:3.)
The County focuses its efforts to preserve, create and maintain for-sale and rental affordable housing units to households whose income is not greater than 80% of the Washington, DC Metropolitan Area Median Income (AMI); rental units are committed for no fewer than 30 years at no greater than 60% AMI. AMI tables are published annually by the US Department of Housing and Urban Development.
Government
Arlington is governed by a five person County Board, whose members are elected to four year terms.
| Position | Name | Party | First Election | Next Election |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chairman | J. Walter Tejada | Democratic Party | 2003 | 2011 |
| Vice-Chairman | Barbara Favola | Democratic Party | 1997 | 2008 |
| Member | Jay Fisette [2] | Democratic Party | 1997 | 2009 |
| Member | Mary Hynes | Democratic Party | 2007 | 2011 |
| Member | Chris Zimmerman [3] | Democratic Party | 1996 | 2010 |
Arlington also elects four Members of the 100 Member Virginia House of Delegates and two Members of the Virginia Senate. State Senators are elected to four year terms, while Delegates are elected to two year terms.
| Office | Name | Party and District | First Election | Next Election |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Senator | Patricia "Patsy" Ticer | Democratic Party (30) | 1995 | 2007 |
| Senator | Mary Margaret Whipple [4] | Democratic Party (31) | 1995 | 2007 |
| Delegate | David Englin [5] | Democratic Party (45) | 2005 | 2007 |
| Delegate | Albert Eisenberg [6] | Democratic Party (47) | 2003 | 2007 |
| Delegate | Robert Brink [7] | Democratic Party (48) | 1997 | 2007 |
| Delegate | Adam Ebbin [8] | Democratic Party (49) | 2003 | 2007 |
Arlington has an elected five person School Board, whose members are elected to four year terms. Virginia law does not permit political parties to place school board candidates on the ballot, but as in many other Virginia jurisdictions, most Arlington school board candidates run with an explicit party endorsement.
| Position | Name | Party | First Election | Next Election |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chair | (vacant) | |||
| Vice Chair | Ed Fendley | endorsed by Democratic Party in 2005 | 2005 | 2009 |
| Member | Sally Baird | endorsed by Democratic Party in 2006 | 2006 | 2010 |
| Member | Libby Garvey | endorsed by Democratic Party in 2004 | 1996 | 2008 |
| Member | Abby Raphael | endorsed by Democratic Party in 2004 | 2007 | 2011 |
| Member | Frank Wilson | endorsed by Democratic Party in 2004 | 1996 | 2008 |
Arlington also has several Constitutional Officers, all of whom are elected County-wide.
| Position | Name | Party | First Election | Next Election |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Treasurer | Frank O'Leary | Democratic Party | 1983 | 2011 |
| Clerk of the Court | Paul Ferguson | Democratic Party | 2007 | 2015 |
| Commonwealth's Attorney | Richard "Dick" Trodden | Democratic Party | 1993 | 2011 |
| Sheriff | Beth Arthur | Democratic Party | 2000 | 2011 |
| Commissioner of the Revenue | Ingrid Morroy | Democratic Party | 2003 | 2011 |
Note: Arlington is represented by three of the four openly gay elected officials in Virginia. Arlington County Board member Jay Fisette was the first in 1997. Adam Ebbin became the first openly gay Delegate in 2003. In 2006, School Board member Sally Baird became the first openly lesbian elected official in Virginia. (The fourth openly gay elected official is Councilman Paul Smedberg of the City of Alexandria Council.)
Presidential Election Results
Each year's winner in the general election is listed first below.
- 2004 - 31.3% Bush (R), 67.6% Kerry (D)
- 2000 - 34.2% Bush (R), 60.1% Gore (D)
- 1996 - 60.5% Clinton (D), 34.6% Dole (R)
- 1992 - 57.8% Clinton (D), 31.9% Bush (R)
- 1988 - 45.4% Bush (R), 53.5% Dukakis (D)
- 1984 - 48.2% Reagan (R), 51.3% Mondale (D)
- 1980 - 46.1% Reagan (R), 39.6% Carter (D)
- 1976 - 50.4% Carter (D), 47.9% Ford (R)
- 1972 - 59.4% Nixon (R), 39% McGovern (D)
- 1968 - 45.9% Nixon (R), 42.6% Humphrey (D)
- 1964 - 61.7% Johnson (D), 37.7% Goldwater (R)
- 1960 - 51.4% Kennedy (D), 48.1% Nixon (R)
Transportation

Airports
Arlington is the home of Ronald Reagan Washington National Airport, which provides domestic services to the Washington, D.C. area.
Nearby airports with international services include Washington Dulles International Airport, located in Fairfax and Loudoun counties in Virginia, and Baltimore-Washington International Thurgood Marshall Airport, located in Anne Arundel County, Maryland.
Public transportation
Arlington is served by the Orange, Blue and Yellow lines of the Washington Metro. Additionally, it is served by Virginia Railway Express (commuter rail), Metrobus (regional public bus), and a local public bus system, Arlington Transit (ART).
Roads in Arlington County
- Main articles: Streets and highways of Arlington County, Virginia and Arlington County, Virginia, street-naming system
Arlington County is traversed by two interstate highways, Interstate 66 in the northern part of the county and Interstate 395 in the southern part, both with high-occupancy vehicle lanes or restrictions. In addition, the county is served by a number of multi-lane urban arterial roads and the George Washington Memorial Parkway.
Bicycle paths
Arlington has a number of off-road bicycle trails, all of which travel along the Potomac River and its tributaries, abandoned railroad beds, or major highways. One of these trails, the Mount Vernon Trail, runs for 17 miles along the Potomac, continuing through Alexandria to George Washington's plantation home. In Arlington's southeast corner, immediately south of Ronald Reagan Washington National Airport, the Mount Vernon Trail connects to the Four Mile Run Trail, which travels westward through Arlington in a stream valley.
In addition, a rail trail, the Washington & Old Dominion Railroad Trail (W&OD Trail), travels northwest for 45 miles from the Arlington/Alexandria boundary at Shirlington through Falls Church, Vienna, Herndon, and Leesburg to the town of Purcellville in western Loudoun County, Virginia. Other notable trails include both the Custis Trail, which travels westward beside Interstate 66 through Arlington, connecting the Mount Vernon Trail in Rosslyn with the W&OD Trail, and the Bluemont Junction Trail, a rail trail that travels between the W&OD Trail and Ballston, where it connects with the Custis Trail.
In addition, a partially off-road bike route bisects the County while traveling westward from Arlington National Cemetery, the Iwo Jima Memorial and Rosslyn to Falls Church while travelling as a paved trail near or adjacent to Arlington Boulevard (U.S. Route 50) or within the Boulevard's service road. Further, many of the County's major streets contain designated bicycle lanes near their curbs or parking lanes.
Geography

Arlington County is the smallest self-governing county in the United States (the largest county-level jurisdiction being North Slope Borough, Alaska). According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the county has a total area of 26 square miles (67 km²), of which about 4.6 square miles (12 km²) is federal property. There are two counties that are geographically smaller than Arlington in the United States (but which have no form of self-government): Kalawao, Hawaii (13.2 square miles) and Bristol, Rhode Island (24.7 square miles).
Arlington is located at 38°52′49″N 77°6′30″W / 38.88028°N 77.10833°W (38.880344, -77.108260)Template:GR. It is bounded on the north by Fairfax County, on the west by the City of Falls Church, on the south by the City of Alexandria, and on the east by the Potomac River; across the river is the City of Washington, DC.
A person standing on Memorial Bridge in Arlington County is exactly as far from the Cumberland Gap, Virginia's western extreme point, as they are from downtown Boston, Massachusetts -- 394 miles (636 km).
Neighborhoods in Arlington

There are numerous unincorporated neighborhoods within Arlington County that are commonly referred to by name as if they were distinct towns. The county characterizes some of these neighborhoods - particularly those located at Metrorail stations and other major transportation corridors - as "urban villages." These are usually centers with commercial activity. These include:
There are also numerous neighborhoods which are largely residential including:
|
|
|
Arlington County includes a large selection of Sears Catalog Homes, which were offered between 1908 and 1940, Considered to be of exceptional quality, in modern times, these houses are sought after by many home buyers. As well, Arlington features some of the first and among the best examples of post-World War II garden style apartment complexes in the U.S., some of which were designed by architect Mihran Mesrobian. Arlington Boulevard (Route 50) is the dividing line in the county.
Neighborhood Historic Preservation Districts
A number of the county's residential neighborhoods and larger garden-style apartment complexes are listed in the National Register of Historic Places and/or designated under the County government's zoning ordinance as local Historic Preservation Districts.[9][10] These include Arlington Village, Arlington Forest, Ashton Heights, Buckingham, Cherrydale, Claremont, Colonial Village, Fairlington, Lyon Park, Lyon Village, Maywood, Penrose, Waverly Hills and Westover.[11][12]
Neighborhood Conservation Plans
Many of Arlington County's neighborhoods participate in the Arlington County government's Neighborhood Conservation Program (NCP).[13] Each of these neighborhoods has a Neighborhood Conservation Plan that describes the neighborhood's characteristics, history and recommendations for capital improvement projects that the County government funds through the NCP.[14]
Postal areas
The three-digit zip code prefix 222 uniquely identifies Arlington. Delivery areas north of Arlington Boulevard have odd-numbered ZIP codes (22201, 22203, 22205, 22207, 22209, and 22213), while delivery areas south of Arlington Boulevard have even-numbered ZIP codes (22202, 22204, and 22206). ZIP codes assigned to post office boxes, large mailers, and military facilities do not follow that rule.
Reagan National Airport and the Pentagon, both within the boundaries of Arlington County, are assigned Washington, D.C. zip codes.
Education
Primary and secondary schools
Arlington County is served by the Arlington Public Schools system. The public high schools in Arlington County are Yorktown High School, Washington-Lee High School, Wakefield High School, and the H-B Woodlawn program. Arlington County is also home to Bishop O'Connell, a Roman Catholic high school.
Arlington County spends about half of its revenue on education, making it one of the top ten per-pupil spenders in the nation (as of 2004, over $13,000, the second highest amount spent on education in the United States, behind New York City).
Through an agreement with Fairfax County Public Schools approved by the school board in 1999, up to 26 students residing in Arlington per grade level may be enrolled at the Thomas Jefferson High School for Science and Technology in Fairfax at a cost to Arlington of approximately $8000 per student. For the first time in 2006, more students (36) were offered admission in the selective high school than allowed by the previously established enrollment cap.[15]
Colleges and universities
Marymount University is the only university with its main campus located in Arlington. Founded in 1950 by the Religious of the Sacred Heart of Mary as Marymount College of Virginia located on North Glebe Road. The school has expanded into offering complete 4 year undergraduate degrees, graduate degrees and recently doctorial degrees in Fall 2004. The school expanded in the early 1990's and opened an additional campus in Ballston. They also have a Reston Center located in Reston, Virginia.
George Mason University operates an Arlington campus in the Virginia Square area between Clarendon and Ballston. The campus houses the School of Law, School of Public Policy and other programs. The University is commencing construction on a new building in October 2007, which is expected to open in 2010. This new building will provide additional space for the School of Law and other graduate programs.
DeVry University operates a campus for undergraduate classes along with the Keller School of Management for its graduate classes, in Crystal City. The University established the campus in 2001.
Institute for the Psychological Sciences is a regionally accredited institution offering postgraduate programs in Psychology with a Roman Catholic perspective. Its campus is in the Crystal City neighborhood.
University of Management and Technology is a distance learning university that is headquartered in Rosslyn.
The Art Institute of Washington, a local branch of The Art Institutes is located in the Ames Center across from the Rosslyn Metro Station.
Strayer University has a campus in Arlington as well as its corporate headquarters.
In addition, Argosy University, Banner College, Everest College, George Washington University, Georgetown University, Northern Virginia Community College, Troy University, the University of New Haven, the University of Oklahoma, and Westwood College all have campuses in Arlington.
Sister cities
Arlington has three sister cities, as designated by Sister Cities International, Inc. (SCI):
See also
- Arlington Independent Media
- List of people from the Washington, D.C. metropolitan area
- List of federal agencies in Arlington County, Virginia
- Arlington Arts Center
- Arlington Hall
References
- ^ a b c "Profile".
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|accessmonthday=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|accessyear=ignored (|access-date=suggested) (help) Cite error: The named reference "Estimated_Population" was defined multiple times with different content (see the help page). - ^ Matt Woolsey, America's Richest Counties, Forbes.com, 01.22.08, 6:00 PM ET Forbes.com Web site. Retrieved on 2008-02-08.
- ^ Matt Woolsey, America's Richest Counties, Forbes.com, 01.22.08: Complete List: America's Richest Counties: 9. Arlington County, Va. Forbes.com Web Site. Retrieved on 2008-02-08.
- ^ Boundary markers of the Nation's Capital : a proposal for their preservation & protection : a National Capital Planning Commission Bicentennial report. National Capital Planning Commission, Washington, DC, 1976; for sale by the Superintendent of Documents, U.S. Government Printing Office
- ^ Sixth Congress, Session II, Chapter XV (An Act concerning the District of Columbia), Section 2 (Stat. II, Feb. 27, 1801) (United States Statutes at Large, Vol. II, p. 103)
- ^ "Frequently Asked Questions About Washington, D.C." The Historical Society of Washington, D.C.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|accessmonthday=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|accessyear=ignored (|access-date=suggested) (help) - ^ "Alexandria's History".
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|accessmonthday=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|accessyear=ignored (|access-date=suggested) (help) - ^ Although Arlington CDP had a population of 135,449 in 1950, the Census did not treat Arlington as a CDP because in 1950 CDPs were assigned to rural areas only. They were first assigned to urban areas during the 1960 Census.
- ^ Arlington County Government Historic Preservation Program Official Arlington County Government Website. Retrieved on 2008-02-05.
- ^ Arlington County Zoning Ordinance: Section 31.A. Historic Preservation Districts Official Arlington County Government Website. Retrieved on 2008-02-05.
- ^ List of Arlington County Government Designated Local Historic Districts Official Arlington County Government Website. Retrieved on 2008-02-05.
- ^ List of Arlington County Sites in the National Register of Historic Places Official Arlington County Government Website. Retrieved on 2008-02-05.
- ^ Neighborhood Conservation Program Official Arlington County Government Website. Retrieved on 2008-02-05.
- ^ Neighborhood Conservation Plans Official Arlington County Government Website. Retrieved on 2008-02-05.
- ^ "TJHSST Admissions Statistics for 2005-06" (PDF).
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|accessmonthday=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|accessyear=ignored (|access-date=suggested) (help)
External links
Web Sites
- Arlington County official web pages
- Arlington County government home page
- "Profile".
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|accessmonthday=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|accessyear=ignored (|access-date=suggested) (help) - Arlington County Board
- Arlington County Geographic Information System Mapping Center Interactive Maps
- Arlington County Local Historic Districts
- Arlington County Neighborhood Conservation Plans
- Arlington County Neighborhood Conservation Program
- Arlington County sites listed in National Register of Historic Places
- Arlington County Zoning Ordinance
- Arlington County Zoning Ordinance: Historic Preservation Districts
- Arlington County Bicycle Maps
- Animal Welfare League of Arlington (Arlington County Animal Shelter)
- Arlington Chamber of Commerce
- Arlington Convention and Visitors Service official website
- Arlington Economic Development Agency official website
- Arlington Fire Journal - History of Arlington County Fire Dept., including Sept. 11 at Pentagon
- Arlington Gay and Lesbian Alliance (non-profit community group)
- Arlington Historical Society
- Arlington House, the Robert E. Lee Memorial (U.S. National Park Service website)
- Arlington County Democrats
- Arlington Skyscrapers at Emporis
- Arlington's Urban Villages
Neighborhoods
- Alcova Heights
- Ballston and Virginia Square
- Bluemont
- Buckingham
- Cherrydale
- Clarendon
- Court House
- Glencarlyn
- Lyon Park
- Lyon Village
- Rosslyn
- Waycroft-Woodlawn
Related Links Template:Mapit-US-cityscale
- Hybrid satellite image/street map from WikiMapia
- CrimeinDC.org - Unofficial Google crime maps of Arlington

