Levator palpebrae superioris muscle: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
m modified ja: |
||
| Line 61: | Line 61: | ||
[[hu:Musculus levator palpebrae superioris]] |
[[hu:Musculus levator palpebrae superioris]] |
||
[[nl:Musculus levator palpebrae superioris]] |
[[nl:Musculus levator palpebrae superioris]] |
||
[[ja:上眼瞼 |
[[ja:上眼瞼挙筋]] |
||
[[sr:Мишић подизач горњег очног капка]] |
[[sr:Мишић подизач горњег очног капка]] |
||
[[sh:Mišić podizač gornjeg očnog kapka]] |
[[sh:Mišić podizač gornjeg očnog kapka]] |
||
Revision as of 07:47, 14 February 2008
| Levator muscle of upper eyelid | |
|---|---|
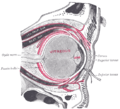
 Rectus muscles: 2 = superior, 3 = inferior, 4 = medial, 5 = lateral Oblique muscles: 6 = superior, 8 = inferior Other muscle: 9 = levator palpebrae superioris Other structures: 1 = Annulus of Zinn, 7 = Trochlea, 10 = Superior tarsus, 11 = Sclera, 12 = Optic nerve | |
 Sagittal section of right orbital cavity. | |
| Details | |
| Origin | sphenoid bone |
| Insertion | tarsal plate, upper eyelid |
| Artery | ophthalmic artery, superior ophthalmic vein |
| Nerve | oculomotor nerve |
| Actions | retracts//elevates eyelid |
| Antagonist | orbicularis oculi muscle |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | musculus levator palpebrae superioris |
| TA98 | A15.2.07.020 |
| TA2 | 2052 |
| FMA | 49041 |
| Anatomical terms of muscle | |
The levator palpebrae superioris (or levator muscle of upper eyelid) is the muscle in the orbit that elevates the superior (upper) eyelid.
Structure
The levator palpebrae superioris originates on the lesser wing of the sphenoid bone, just above the optic foramen. It inserts on the skin of the upper eyelid, as well as the superior tarsal plate. It is a skeletal muscle. The superior tarsal muscle, a smooth muscle, is attached to the levator palpebrae superioris, and inserts on the superior tarsal plate as well.
Innervation
As with most of the muscles of the orbit, it is innervated by the superior division of the oculomotor nerve (Cranial Nerve III). An adjoining smooth muscle, the superior tarsal muscle, is sympathetically innervated and is occasionally considered to be part of the levator palpebrae superioris.
Actions
The levator palpebrae superioris muscle elevates and retracts the upper eyelid.
Pathology
Damage to this muscle, or its innervation, can cause ptosis, the drooping of the eyelid. Ptosis can also be caused by damage to the adjoining superior tarsal muscle, or its sympathetic innervation. Such damage to the sympathetic supply occurs in Horner's syndrome, and presents as a partial ptosis.
Additional images
-
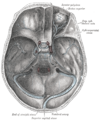
The sinuses at the base of the skull.
-
Nerves of the orbit. Seen from above.
-
Dissection showing origins of right ocular muscles, and nerves entering by the superior orbital fissure.
-
The right eye in sagittal section, showing the fascia bulbi (semidiagrammatic).
-
Sagittal section through the upper eyelid.
See also
External links
- Template:MuscleLoyola
- . GPnotebook https://www.gpnotebook.co.uk/simplepage.cfm?ID=-1979318192.
{{cite web}}: Missing or empty|title=(help) - Anatomy figure: 29:01-01 at Human Anatomy Online, SUNY Downstate Medical Center
- lesson3 at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (orbit2)