User:Astro61/Sandbox: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<!-- |
|||
{{future scientific facility}} |
{{future scientific facility}} |
||
--> |
|||
The '''Thirty Meter Telescope''' ('''TMT''') will be a ground-based |
The '''Thirty Meter Telescope''' ('''TMT''') will be a ground-based |
||
[[observatory]] with a 30m diameter [[segmented mirror]] capable of |
[[astronomical]] [[observatory]] with a 30m diameter [[segmented mirror]] capable of |
||
observations from the [[Ultraviolet | near-ultraviolet]] to the |
observations from the [[Ultraviolet | near-ultraviolet]] to the |
||
[[Infrared | mid-infrared]] (0.31 to 28 [[Micrometre | microns]]). High |
[[Infrared | mid-infrared]] (0.31 to 28 [[Micrometre | microns]]). High |
||
| Line 11: | Line 13: | ||
will be the first of the new generation of [[Extremely_large_telescope | |
will be the first of the new generation of [[Extremely_large_telescope | |
||
Extremely Large Telescopes]]. |
Extremely Large Telescopes]]. |
||
[[Image:TmtSummitComposite.jpg|thumb|325px|Thirty Meter Telescope design (late 2007)]] |
|||
== Science Case == |
== Science Case == |
||
| Line 20: | Line 24: | ||
broad range of astrophysical problems including: |
broad range of astrophysical problems including: |
||
* [[Dark energy]], [[dark matter]] and tests of the [[Standard Model]] |
* [[Dark energy]], [[dark matter]] and tests of the [[Standard Model | Standard Model of particle physics]] |
||
* Characterization of the first [[stars]] and [[galaxies]] in the Universe |
* Characterization of the first [[stars]] and [[galaxies]] in the Universe |
||
* Characterization of the epoch of [[reionization]] |
* Characterization of the epoch of [[reionization]] |
||
| Line 34: | Line 39: | ||
By design, TMT complements the scientific capabilities of the [[James Webb Space Telescope]] |
By design, TMT complements the scientific capabilities of the [[James Webb Space Telescope]] |
||
and [[Atacama Large Millimeter Array]]. |
and [[Atacama Large Millimeter Array]]. |
||
==Observatory design== |
==Observatory design== |
||
| Line 43: | Line 46: | ||
===Telescope=== |
===Telescope=== |
||
[[Image:TmtTelescope.jpg|thumb|left|250px|Thirty Meter Telescope design (late 2007)]] |
|||
The centerpiece of the TMT Observatory will be a |
The centerpiece of the TMT Observatory will be a |
||
| Line 52: | Line 57: | ||
A 3m secondary mirror produces an unobstructed field-of-view of 20 |
A 3m secondary mirror produces an unobstructed field-of-view of 20 |
||
[[arcminutes]] in diameter with a [[focal ratio]] of 15. A flat |
|||
direct |
tertiary mirror will direct the light path to science instruments |
||
[[Nasmyth]] platforms. The shape of each mirror will be |
mounted on large [[Nasmyth]] platforms. The shape of each mirror will be |
||
[[Active_optics | controlled actively]]. |
[[Active_optics | controlled actively]]. |
||
The telescope will have |
The telescope will have an [[Altazimuth_mount | altitude-azimuth |
||
This mount will be capable of |
mount]]. This mount will be capable of repositioning the telescope |
||
points of the sky in less than 5 minutes, with a |
between any two points of the sky in less than 5 minutes, with a |
||
precision of 2.0 [[arcseconds]] or better. Once the celestial object is |
|||
or better. |
|||
acquired, the telescope will track its motion with a precision of a few |
|||
[[milliarcseconds]]. |
|||
The moving TMT moving mass (including instruments) is almost 2000 metric |
The moving TMT moving mass (including instruments) is almost 2000 metric |
||
tons. |
tons. |
||
This design |
This design descends from the successful [[Keck_observatory | W. M. Keck |
||
Observatory]]. |
Observatory]]. |
||
| Line 74: | Line 81: | ||
observing a combination of natural (real) and artificial |
observing a combination of natural (real) and artificial |
||
[[Laser_guide_star | laser guide]] stars. Based on these measurements, a |
[[Laser_guide_star | laser guide]] stars. Based on these measurements, a |
||
[[deformable |
pair of [[Deformable_mirror | deformable mirrors]] will be adjusted many |
||
distortions caused by the |
times per second to correct optical wavefront distortions caused by the |
||
intervening turbulence. |
|||
This system will produce [[diffraction-limited]] images over a 30 |
This system will produce [[diffraction-limited]] images over a 30 |
||
arcsecond field-of-view. For example, the core of the [[point |
arcsecond diameter field-of-view. For example, the core of the [[point |
||
will have a size of 0.015 |
spread function]] will have a size of 0.015 arcsecond at a |
||
micron, almost 10 times better than the [[Hubble |
[[wavelength]] of 2.2 micron, almost 10 times better than the [[Hubble |
||
Space Telescope]]. |
|||
===Scientific instrumentation=== |
===Scientific instrumentation=== |
||
| Line 90: | Line 99: | ||
The '''Wide Field Optical Spectrometer (WFOS)''' will provide |
The '''Wide Field Optical Spectrometer (WFOS)''' will provide |
||
near-ultraviolet and optical (0.3 |
near-ultraviolet and optical (0.3 – 1.0 μm wavelength) imaging and |
||
over a more than 40 square |
spectroscopy over a more than 40 square arcminute field-of-view. Using |
||
focal plane masks, WFOS will enable long-slit observations |
precision cut focal plane masks, WFOS will enable long-slit observations |
||
objects as well as short-slit observations of hundreds of |
of single objects as well as short-slit observations of hundreds of |
||
simultaneously. WFOS will use natural (uncorrected) seeing |
objects simultaneously. WFOS will use natural (uncorrected) seeing |
||
images. |
|||
The '''Infrared Imaging Spectrometer (IRIS)''' will be mounted on the |
The '''Infrared Imaging Spectrometer (IRIS)''' will be mounted on the |
||
observatory MCAO system and be capable of [[diffraction-limited]] |
observatory MCAO system and be capable of [[diffraction-limited]] |
||
imaging and integral-field [[spectroscopy]] at near-infrared wavelengths |
|||
(0.8 – 2.5 μm). |
|||
The '''Infrared Multi-object Spectrometer (IRMS)''' will allow close to |
The '''Infrared Multi-object Spectrometer (IRMS)''' will allow close to |
||
diffraction-limited imaging and slit spectroscopy over a 2 |
diffraction-limited imaging and slit spectroscopy over a 2 arcminute |
||
field-of-view at near-infrared wavelengths (0.8 |
diameter field-of-view at near-infrared wavelengths (0.8 – 2.5 μm). |
||
====Additional first-decade capabilities==== |
====Additional first-decade capabilities==== |
||
| Line 115: | Line 125: | ||
include: |
include: |
||
* Extremely high contrast (10<sup>8</sup> @ 1.65 μm) [[exoplanet]] imaging and spectroscopy at near-infrared wavelengths |
* Extremely high contrast (1 part in 10<sup>8</sup> @ 1.65 μm) [[exoplanet]] imaging and spectroscopy at near-infrared wavelengths |
||
* Natural seeing limited echelle spectroscopy ([[Spectral_resolution |resolving power]] ~ 50 000) at near-ultraviolet and optical wavelengths (0.31 -– 1.0 μm) |
|||
* Diffraction-limited echelle spectroscopy ([[Spectral_resolution |resolving power]] ~ 25 000) at near-infrared wavelengths (1.0 |
* Diffraction-limited echelle spectroscopy ([[Spectral_resolution |resolving power]] ~ 25 000) at near-infrared wavelengths (1.0 – 2.5 μm) |
||
* Diffraction-limited imaging and echelle spectroscopy ([[Spectral_resolution |resolving power]] ~ 50 000) at mid-infrared wavelengths (8 |
* Diffraction-limited imaging and echelle spectroscopy ([[Spectral_resolution |resolving power]] ~ 50 000) at mid-infrared wavelengths (8 – 28 μm) |
||
* High precision (0.0005 |
* High precision (0.0005 arcsecond) astrometric imaging at near-infrared wavelengths (1.0 – 2.5 μm) |
||
* Multiple integral-field unit spectrometers deployable over a 5 |
* Multiple integral-field unit spectrometers deployable over a 5 arcminute diameter field-of-view, each with individual adaptive optics correction, at near-infrared wavelengths (1.0 – 2.5 μm) |
||
==Location== |
==Location== |
||
Revision as of 20:43, 4 March 2008
The Thirty Meter Telescope (TMT) will be a ground-based
astronomical observatory with a 30m diameter segmented mirror capable of
observations from the near-ultraviolet to the
mid-infrared (0.31 to 28 microns). High
spatial resolution (so-called diffraction-limited) images will be
created using adaptive optics systems. TMT will be more sensitive
than existing ground-based telescopes by factors of 10 (natural seeing
mode) to 100 (diffraction-limited mode). If completed on schedule, TMT
will be the first of the new generation of
Extremely Large Telescopes.

Science Case
A Detailed Science Case [1] for TMT is available.
TMT will be a general purpose observatory capable of investigating a broad range of astrophysical problems including:
- Dark energy, dark matter and tests of the Standard Model of particle physics
- Characterization of the first stars and galaxies in the Universe
- Characterization of the epoch of reionization
- Galaxy assembly and evolution over the past 13 billion years
- Connections between supermassive black holes and galaxies
- Star-by-star dissection of galaxies out to 10 million parsecs
- Physics of planet and star formation
- Exoplanet discovery and characterization
- Kuiper belt object surface chemistry
- Solar system planetary atmosphere chemistry and meteorology
- The search of life on planets outside the Solar System
By design, TMT complements the scientific capabilities of the James Webb Space Telescope and Atacama Large Millimeter Array.
Observatory design
A complete description of the TMT Observatory design can be found in the TMT Construction Proposal (2007) [2].
Telescope
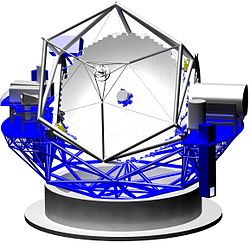
The centerpiece of the TMT Observatory will be a Ritchey-Chrétien telescope with a 30m diameter primary mirror. This mirror will be segmented and consist of 492 smaller (1.4m), individual hexagonal mirrors. The shape of each segment, as well as its position relative to neighboring segments, will be controlled actively.
A 3m secondary mirror produces an unobstructed field-of-view of 20 arcminutes in diameter with a focal ratio of 15. A flat tertiary mirror will direct the light path to science instruments mounted on large Nasmyth platforms. The shape of each mirror will be controlled actively.
The telescope will have an altitude-azimuth mount. This mount will be capable of repositioning the telescope between any two points of the sky in less than 5 minutes, with a precision of 2.0 arcseconds or better. Once the celestial object is acquired, the telescope will track its motion with a precision of a few milliarcseconds.
The moving TMT moving mass (including instruments) is almost 2000 metric tons.
This design descends from the successful W. M. Keck Observatory.
Adaptive Optics
Integral to the observatory is a multi-conjugate adaptive optics system. This MCAO system will measure atmospheric turbulence by observing a combination of natural (real) and artificial laser guide stars. Based on these measurements, a pair of deformable mirrors will be adjusted many times per second to correct optical wavefront distortions caused by the intervening turbulence.
This system will produce diffraction-limited images over a 30 arcsecond diameter field-of-view. For example, the core of the [[point spread function]] will have a size of 0.015 arcsecond at a wavelength of 2.2 micron, almost 10 times better than the [[Hubble Space Telescope]].
Scientific instrumentation
Early-light capabilities
When TMT science operations begin, three instruments will be available for scientific observations.
The Wide Field Optical Spectrometer (WFOS) will provide near-ultraviolet and optical (0.3 – 1.0 μm wavelength) imaging and spectroscopy over a more than 40 square arcminute field-of-view. Using precision cut focal plane masks, WFOS will enable long-slit observations of single objects as well as short-slit observations of hundreds of objects simultaneously. WFOS will use natural (uncorrected) seeing images.
The Infrared Imaging Spectrometer (IRIS) will be mounted on the observatory MCAO system and be capable of diffraction-limited imaging and integral-field spectroscopy at near-infrared wavelengths (0.8 – 2.5 μm).
The Infrared Multi-object Spectrometer (IRMS) will allow close to diffraction-limited imaging and slit spectroscopy over a 2 arcminute diameter field-of-view at near-infrared wavelengths (0.8 – 2.5 μm).
Additional first-decade capabilities
For planning purposes, TMT has developed concepts for an additional six instruments to be deployed during the first decade of science operations. These plans will be reviewed and updated on a roughly bi-annual basis starting in 2010.
In no order of preference, planned additional scientific capabilities include:
- Extremely high contrast (1 part in 108 @ 1.65 μm) exoplanet imaging and spectroscopy at near-infrared wavelengths
- Diffraction-limited echelle spectroscopy (resolving power ~ 25 000) at near-infrared wavelengths (1.0 – 2.5 μm)
- Diffraction-limited imaging and echelle spectroscopy (resolving power ~ 50 000) at mid-infrared wavelengths (8 – 28 μm)
- High precision (0.0005 arcsecond) astrometric imaging at near-infrared wavelengths (1.0 – 2.5 μm)
- Multiple integral-field unit spectrometers deployable over a 5 arcminute diameter field-of-view, each with individual adaptive optics correction, at near-infrared wavelengths (1.0 – 2.5 μm)
Location
In cooperation with AURA, the TMT project has recently completed a multi-year site evaluation program.
The sites included in this program were:
- Cerro Armazones, Antofagasta Region, Republic of Chile
- Cerro Tolanchar, Antofagasta Region, Republic of Chile
- Cerro Tolar, Antofagasta Region, Republic of Chile
The final TMT site selection decision will be based on a combination of scientific, financial, and political criteria. Local cultural sensitivities will also be an important part of any TMT site decision.
Partnership
The TMT Observatory Corporation is a partnership between:
- Association of Canadian Universities for Research in Astronomy (ACURA) [3]
- California Institute of Technology (Caltech)
- University of California (UC)
The current US$ 80 million, five year design and development program is planned for completion in 2009. Construction is expected to commence immediately thereafter, leading to initial science operations in the second half of the next decade. The Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation has committed US$ 200 million for construction. Caltech and University of California have committed an additional US$ 50 million each. TMT is actively seeking additional major partners for the construction and operations phase.
TMT has received design and development funding from the following public and private organizations:
- Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation
- Canada Foundation for Innovation
- Ontario Ministry of Research and Innovation
- National Research Council of Canada
- Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada
- British Columbia Knowledge Development Fund
- Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy (AURA)
- National Science Foundation (NSF)
See also
References
- http://www.tmt.org/foundation-docs/TMT-DSC-2007-R1.pdf
- http://www.tmt.org/news/TMT-Construction%20Proposal-Public.pdf
- http://www.astro.utoronto.ca/acura/en/index.html
External links
- Project web site: http://www.tmt.org
- TMT foundation documents: http://www.tmt.org/foundation-docs/index.html
- Construction Proposal (2007)
- Detailed Science Case (2007)
- Observatory Requirements Document
- Observatory Architecture Document
- Operations Concept Document
