Bayonet mount: Difference between revisions
m Reverted edits by 58.107.169.105 to last version by 171.192.0.10 |
m →Uses: spaces |
||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
Some bulbs may have slightly offset lugs to ensure they can be only inserted in one direction; this is particularly true in Bulbs like the 1157 automobile taillight which has two different filaments to act as both a running light and a signal light. In the 1157 automotive bulb, each filament has a different brightness and is connected to a separate contact on the bottom of the base, the two contacts being symmetrically positioned about the axis of the base (unlike a "3-way" medium screw base in which the two filament contacts are a center circle and a ring,) so proper orientation of the bulb is necessary to connect each filament to the correct separate circuit. |
Some bulbs may have slightly offset lugs to ensure they can be only inserted in one direction; this is particularly true in Bulbs like the 1157 automobile taillight which has two different filaments to act as both a running light and a signal light. In the 1157 automotive bulb, each filament has a different brightness and is connected to a separate contact on the bottom of the base, the two contacts being symmetrically positioned about the axis of the base (unlike a "3-way" medium screw base in which the two filament contacts are a center circle and a ring,) so proper orientation of the bulb is necessary to connect each filament to the correct separate circuit. |
||
Bayonet bases or caps are often abbreviated to BC, often with a number after. The number refers to the diameter of the base, e.g. BC22 is a |
Bayonet bases or caps are often abbreviated to BC, often with a number after. The number refers to the diameter of the base, e.g. BC22 is a 22 mm diameter bayonet cap lamp. BC15, a 15 mm base, can also be referred to as SBC standing for Small Bayonet Cap. |
||
==Bulb bayonet mounts== |
==Bulb bayonet mounts== |
||
Revision as of 09:22, 10 March 2008
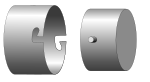

A bayonet mount or bayonet connector is a fastening mechanism that relies on mated surfaces; a male side with one or more pins or slots, and a female receptor with matching slots and a spring that maintains a clamping force.
To couple the two surfaces, users are expected to align the pin(s) on the male with the slot(s) on the female and push the two together. Once the pins reach the end of the slot, the two surfaces are turned in opposite directions to guide the pin into a perpendicular slot that prevents it from being removed. The spring then holds the pin in this position to prevent it from backing out. To disconnect the two surfaces the user pushes the two surfaces together to overcome the spring and uses a fraction of a turn to reverse the locking turn.
The strength of the joint relies solely on the shear strength of the pins, however a practiced user can connect them quickly and they are not subject to cross-threading.
Uses
This style of connector was named after its initial implementation for soldiers who need to mount bayonets to the ends of their rifles in a hurry. The same need also applies to photographers who may need to change lenses quickly.
Several classes of electrical cable connectors,including audio, video, and data cables uses bayonet connectors. Examples include BNC, C, and ST connectors.
Home light bulbs (230/240V mains voltage) in Australia, Ireland, New Zealand, the UK, Middle East and, in older installations, France, also have this type of "B" base, as well as the Edison screw "E" base used in the United States, Japan and other countries. They are also very common worldwide in applications where vibration may loosen conventional bulbs, such as automotive lighting and other small indicators, and in many flashlights.
Some bulbs may have slightly offset lugs to ensure they can be only inserted in one direction; this is particularly true in Bulbs like the 1157 automobile taillight which has two different filaments to act as both a running light and a signal light. In the 1157 automotive bulb, each filament has a different brightness and is connected to a separate contact on the bottom of the base, the two contacts being symmetrically positioned about the axis of the base (unlike a "3-way" medium screw base in which the two filament contacts are a center circle and a ring,) so proper orientation of the bulb is necessary to connect each filament to the correct separate circuit.
Bayonet bases or caps are often abbreviated to BC, often with a number after. The number refers to the diameter of the base, e.g. BC22 is a 22 mm diameter bayonet cap lamp. BC15, a 15 mm base, can also be referred to as SBC standing for Small Bayonet Cap.
Bulb bayonet mounts

| Type | IEC | DIN |
|---|---|---|
| B15d | IEC 60061-1 (7004-11) | DIN 49721 |
| BA15d | IEC 7004-11 A | DIN 49720 |
| BA15s | IEC 7004-11 A | DIN 49720 |
| BA20d | IEC 7004-12 | DIN 49730 |
| B21s-4 | ||
| B22d | IEC 60061-1 (7004-10) | |
| B24s-3 | ||
| GU10 | IEC 60061-1 (7004-121) | |
| GZ10 | IEC 60061-1 (7004-120) |
References
- IEC 61184: Bayonet lampholders, International Electrotechnical Commission, 1997. (also: BS EN 61184) – specifies requirements and tests for the B15 and B22 bayonet holders for light bulbs used in some Commonwealth countries
