Member states of NATO: Difference between revisions
Hello32020 (talk | contribs) →Member states: add reflist |
SpellingBot (talk | contribs) m aganist → against |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Image:Location NATO.svg|350px|thumb|right|NATO members highlighted in green]] |
[[Image:Location NATO.svg|350px|thumb|right|NATO members highlighted in green]] |
||
[[Image:Map of NATO chronological.gif|350px|right|thumb|Timeline of countries becoming NATO members. Dark blue marks countries that were already NATO members at the given time. Light blue marks new members.]] |
[[Image:Map of NATO chronological.gif|350px|right|thumb|Timeline of countries becoming NATO members. Dark blue marks countries that were already NATO members at the given time. Light blue marks new members.]] |
||
The [[North Atlantic Treaty Organization]] (NATO) is a [[military alliance]] that consists of 26 member states from [[North America]] and [[Europe]]. It was established at the signing of the [[North Atlantic Treaty]] on [[4 April]] [[1949]].<ref>{{cite web|title=Frequently Asked Questions|url=http://www.nato.int/issues/faq/index.html|publisher=North Atlantic Treaty Organization|date=2008-06-11 |accessdate=2008-06-16}}</ref> Article Five of the treaty states that if an armed attack occurs |
The [[North Atlantic Treaty Organization]] (NATO) is a [[military alliance]] that consists of 26 member states from [[North America]] and [[Europe]]. It was established at the signing of the [[North Atlantic Treaty]] on [[4 April]] [[1949]].<ref>{{cite web|title=Frequently Asked Questions|url=http://www.nato.int/issues/faq/index.html|publisher=North Atlantic Treaty Organization|date=2008-06-11 |accessdate=2008-06-16}}</ref> Article Five of the treaty states that if an armed attack occurs against one of the member states, it should be [[Collective defense|considered an attack against all members]], and other members shall assist the attacked member, with [[armed forces]] if necessary.<ref>{{cite web|title=The North Atlantic Treaty |url=http://www.nato.int/issues/faq/index.html|publisher=North Atlantic Treaty Organization|date=1949-04-04|accessdate=2008-06-16}}</ref> |
||
Of the 26 members of NATO, two are [[North America|North American]] countries, 23 are [[Europe|European]] countries, and one is a [[Eurasia|Eurasian]] country. All members have militaries, except [[Iceland]], which joined on the condition they would not have to create a military. Three of NATO's members [[List of states with nuclear weapons|have nuclear weapons]], the [[United Kingdom]], [[France]], and the [[United States]]. |
Of the 26 members of NATO, two are [[North America|North American]] countries, 23 are [[Europe|European]] countries, and one is a [[Eurasia|Eurasian]] country. All members have militaries, except [[Iceland]], which joined on the condition they would not have to create a military. Three of NATO's members [[List of states with nuclear weapons|have nuclear weapons]], the [[United Kingdom]], [[France]], and the [[United States]]. |
||
Revision as of 21:46, 29 June 2008

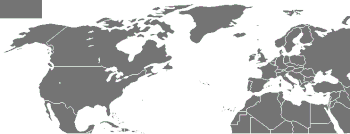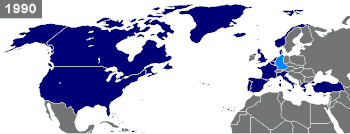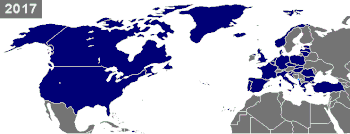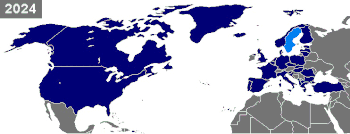
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) is a military alliance that consists of 26 member states from North America and Europe. It was established at the signing of the North Atlantic Treaty on 4 April 1949.[1] Article Five of the treaty states that if an armed attack occurs against one of the member states, it should be considered an attack against all members, and other members shall assist the attacked member, with armed forces if necessary.[2]
Of the 26 members of NATO, two are North American countries, 23 are European countries, and one is a Eurasian country. All members have militaries, except Iceland, which joined on the condition they would not have to create a military. Three of NATO's members have nuclear weapons, the United Kingdom, France, and the United States.
Member states
| Date | Country | Enlargement | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| April 4 1949 | Founders | ||
| France withdrew from the integrated military command in 1966 to pursue an independent defence system. However, there are now plans for it to rejoin sometime in 2008.[3] | |||
| Iceland, the sole member that does not have its own standing army, joined on the condition that it would not be expected to establish one. However, its strategic geographic position in the Atlantic made it an invaluable member. It has a Coast Guard and has recently provided troops trained in Norway for NATO peacekeeping. | |||
| 18 February 1952 | First | Greece withdrew its forces from NATO’s military command structure from 1974 to 1980 as a result of Greco-Turkish tensions following the 1974 Turkish invasion of Cyprus. | |
| 9 May 1955 | Second | Joined as West Germany; Saarland reunited with it in 1957 and the territories of Berlin and the former German Democratic Republic reunited with it on 3 October 1990. | |
| 30 May 1982 | Third | ||
| 12 March 1999 | Fourth | ||
| 29 March 2004 | Fifth | ||
References
- ^ "Frequently Asked Questions". North Atlantic Treaty Organization. 2008-06-11. Retrieved 2008-06-16.
- ^ "The North Atlantic Treaty". North Atlantic Treaty Organization. 1949-04-04. Retrieved 2008-06-16.
- ^ Marquand, Robert (2008-04-04). "U.S., Europe gulf opens at NATO summit". The Christian Science Monitor. Retrieved 2008-04-04.
{{cite news}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|publisher=(help)
