1979 Atlantic hurricane season: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 120: | Line 120: | ||
|Formed=[[August 29]] |
|Formed=[[August 29]] |
||
|Dissipated=[[September 14]] |
|Dissipated=[[September 14]] |
||
|1-min winds= |
|1-min winds=117 |
||
|Pressure=943 |
|Pressure=943 |
||
}} |
}} |
||
Revision as of 00:00, 21 August 2008
| 1979 Atlantic hurricane season | |
|---|---|
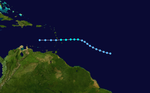
 Season summary map | |
| Seasonal boundaries | |
| First system formed | June 19, 1979 |
| Last system dissipated | October 25, 1998 |
| Strongest storm | |
| Name | David |
| • Maximum winds | 175 mph (280 km/h) (1-minute sustained) |
| • Lowest pressure | 924 mbar (hPa; 27.29 inHg) |
| Seasonal statistics | |
| Total storms | 9 |
| Hurricanes | 5 |
| Major hurricanes (Cat. 3+) | 2 |
| Total fatalities | 2118 |
| Total damage | $4.27 billion (1979 USD) |
The 1979 Atlantic hurricane season officially began on June 1, 1979, and lasted until November 30, 1979. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the Atlantic basin.
The most notable storm of 1979 was Hurricane David, a Category 5 storm on the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Scale that killed over 2,000 people, mostly in the Dominican Republic, and caused nearly 1.5 billion dollars in damage (1979 USD).
Hurricane Frederic, which caused $2.3 billion (1979 US dollars; $6.5 billion in 2005 USD), became the most expensive hurricane in United States history (at the time) when it made landfall near the border between Mississippi and Alabama.
Season summary
The 1979 season was an average but destructive season with 27 depressions, but only 9 became storms. The notable cyclones include Tropical Depression Two which caused one of Jamaica's worst natural disasters. Tropical Storm Claudette became one of the most destructive tropical storms of all time and creating a 24-hour rainfall record at the time. Hurricane David peaked at Category 5 status becoming the first hurricane of such strength to make landfall directly in the Dominican Republic, killing over 2000 people. Hurricane Frederic became a weak Category 4 hurricane with winds of 135 mph (217 km/h), doing over $4-8 billion dollars in damage (2005 USD) to the same area as Hurricane David. Hurricane Henri formed in Mid-September in the Gulf of Mexico and never made landfall, which is a rare occurrence. Damage for the whole season totaled out to $12.1 billion (2005 USD). [1]
Storms
Tropical Depression Two
A tropical depression formed west of Jamaica on June 11 produced heavy rainfalls with record floods in several parishes for two days with maximum sustained winds of 35 miles per hour (56 km/h). The depression continued north, parallelling the Florida coast on June 15 and made landfall in South Carolina on June 16. Tropical Depression Two dissipated over land.[1] The town of Friendship recorded 32 inches (810 mm) of rain with 15 in other parts of western Jamaica. Due to saturated mud from other rains, caused one of Jamaica's worst natural disaster in the 70s. Over 210,000 people were affected by floods on June 12 alone causing for major damage.[2] Economic damages totalled out to $27 million (1979 USD-$75 million in 2006 USD) with forty people killed.[1][3][4]
The flooding in western Jamaica from Tropical Depression Two devastated the area and caused the government to establish a permanent disaster management organization. [5]
Tropical Storm Ana
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | June 19 – June 24 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 60 mph (95 km/h) (1-min); 1005 mbar (hPa) |
Ana formed as the third tropical depression east of the Lesser Antilles on June 19. She was one of the first tropical storms to develop that far east during the month of June since the 1933 Atlantic hurricane season.[6] The depression curved gently northwest and strengthened into Tropical Storm Ana while 100 miles (160 km) northeast of Barbados on June 22. Ana crossed the Leeward Islands and weakened into a tropical depression. The storm degenerated the next morning in the central Caribbean Sea. [6]
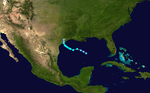
Hurricane Bob
| Category 1 hurricane (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | July 9 – July 13 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 75 mph (120 km/h) (1-min); 986 mbar (hPa) |
Bob was a weak hurricane that formed in the western Gulf of Mexico and curved northeast. The storm strengthened rapidly, reaching hurricane strength a couple hundred miles south of the Louisiana coast on July 11. It made landfall near Dulac, Louisiana later that day, killing two people and causing $20 million ($55.56 million in 2006 USD) in damages.[3] Bob dropped 3-5 inches of rain over southern Indiana before looping over the mid-Atlantic states and out into the Atlantic Ocean. [7] The storm finally dissipated on July 16.
Bob was the first July hurricane in the Gulf of Mexico since Hurricane Debra in the 1959 seasonCite error: A <ref> tag is missing the closing </ref> (see the help page)..
Tropical Storm Claudette
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | July 16 – July 26 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 50 mph (85 km/h) (1-min); 997 mbar (hPa) |
Claudette was a long-lived (July 15 - July 29) but fairly weak storm that spent almost its entire life as a tropical depression. Claudette formed in the central Atlantic east of the Windward Islands. It had two spells as a tropical storm; the first was a brief one east of Puerto Rico. The storm passed directly over the island just after weakening, where it killed one person from flooding. The depression moved casually through the Greater Antilles and moved into the Gulf of Mexico. Claudette restrengthened into a tropical storm south of Sabine, Texas and made landfall near Port Arthur, killing one person from floods. The storm stalled over Alvin, Texas on the evening of the 25th, and dropped 45 inches (1,100 mm) of rain there over the next 42 hours; this included 43 inches (1,100 mm) in 24 hours, the record 24-hour rainfall in US history at the time.[8] Damages from flooding in Texas were enormous, totaling $400 million (1979 USD ($1.1 billion 2005 USD)).[8] Claudette was one of the costliest storms on record that never reached hurricane intensity.
Tropical Depression Ten
The tenth tropical depression of the 1979 season formed on July 28 south of where TD Nine formed a week before. The depression moved to the northwest, making landfall as a tropical depression in Bermuda on August 4. The depression made landfall on the southeastern tip of Newfoundland on August 5 after passing southeast of Nova Scotia earlier that morning. Tropical Depression Ten dissipated on August 6 southeast of Labrador. No damage or fatality reports are available.[1]
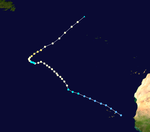
Hurricane David
| Category 5 hurricane (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | August 25 – September 6 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 175 mph (280 km/h) (1-min); 924 mbar (hPa) |
David ranks as one of the strongest and deadliest Atlantic hurricanes on record. It formed from a tropical wave in the central Atlantic east of the Windward Islands. The storm headed west, steadily strengthening. By the time David reached the Leeward Islands, it was at Category 4 intensity. David continued strengthening and reached Category 5 status south of Puerto Rico. It spent nearly two days at Category 5 intensity, storming through Santo Domingo, the capital of the Dominican Republic. Crossing Hispaniola weakened the storm greatly however, and David exited the island as a weak Category 1. It strengthened into a Category 2 off the south Florida coast. The western eyewall crossed the shoreline near Fort Lauderdale and continued up the entire length of the coast. The beach erosion was severe. David made landfall near Savannah, Georgia as a Category 1 and dissipated inland. David killed over 2,000 people in Hispaniola, 56 people on the island of Dominica, and 12 people in the U.S. as well as causing $1.54 billion (1979 USD ($4.36 billion 2005 USD)) in damage.[9]
David was only one of two storms to directly impact the Dominican Republic at such intensity, the only other being the Hurricane 2 of 1930. [9]
Tropical Storm Elena
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | August 30 – September 2 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 40 mph (65 km/h) (1-min); 1004 mbar (hPa) |
A weak tropical wave formed over Florida on August 27, however on August 29, ship and buoy reports mentioned a low-level circulation forming.[10] An Air Force reconnaissance flight confirmed the report and was upgraded into Tropical Depression Six on the same day. Slow development occurred causing the depression to gain strength slowly, however by the next day, it was able to strengthen into Tropical Storm Elena.[10] Elena did not intensify, peaking at 40 mph with a pressure of 1004 mbar. Elena turned toward the Texas coast near Matagorda Bay, spawning watches and warnings and made landfall on September 1 as a weak tropical storm. Elena could not even be identified as a tropical depression by the next day. [10]
Elena caused less than $10 million dollars (1979 USD) ($28 million 2005 USD) in damage but managed to kill two people in floods.[3]
Hurricane Frederic
| Category 4 hurricane (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | August 29 – September 14 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 135 mph (215 km/h) (1-min); 943 mbar (hPa) |
Frederic was a long-lived Cape Verde-type hurricane. It first became a hurricane in the central Atlantic east of the Windward Islands but soon weakened back into a tropical storm. Frederic crossed Hispaniola and weakened into a tropical depression. Frederic then crossed Cuba and regained tropical storm strength before entering the Gulf of Mexico. It was then that Frederic started to strengthen rapidly. By the time it reached a point just east of the Mississippi River Delta, Frederic was a Category 4. It made landfall near the Alabama/Mississippi border. Due to prior warning, the death toll was a minimal five people; however, damages soared to $2.3 billion (1979 dollars ($6.5 billion 2005 dollars)) in damage.
Hurricane Gloria
| Category 2 hurricane (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | September 4 – September 15 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 100 mph (155 km/h) (1-min); 975 mbar (hPa) |
Hurricane Gloria began as a large African disturbance and became Tropical Depression Seventeen on September 4 off the northwestern African coast.[11] As common with early September, TD Seventeen took a northwesterly direction, passing to the northeast of the Cape Verde Islands. The northwesterly course was influenced by the depression's large size. On September 6, the depression became Tropical Storm Gloria and reached hurricane strength the next day. After becoming a hurricane, Gloria slowed down to just about 15 mph (24 km/h) to the northwest until September 10.[11] However, rising pressures caused Gloria to go in a westerly drift for a few days. Rapid acceleration to the northeast occurred with satellites indicating that Gloria had reached her peak intensity of 105 mph (169 km/h) on September 13 with a minimum pressure of 975 mbar. Gloria merged with a low-pressure system on September 15 and lost tropical characteristics.[11]
Gloria did not affect landmasses and was only a threat to marine interests. [11]
Hurricane Henri
| Category 1 hurricane (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | September 15 – September 22 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 85 mph (140 km/h) (1-min); 983 mbar (hPa) |
Henri was a weak hurricane that took an unusual track through the Gulf of Mexico. It formed as a tropical depression off Cancún and curved around the peninsula, entering the Bay of Campeche. Henri quickly strengthened into a tropical storm and reached hurricane strength on September 17. It soon weakened back to a tropical storm and stalled off Tampico, Mexico. Henri then doubled back the way it came, weakened into a tropical depression, and curved sharply east into the open Gulf of Mexico, dissipating in the eastern Gulf. No damage was reported. This was a rare example of a storm entering the Gulf of Mexico and dissipating without making landfall. [12]
Tropical Depression Twenty
The 20th tropical depression of the 1979 season formed as a non-tropical low on September 19 off the coast of Brownsville, Texas. The low appeared in the same area as Hurricane Henri was drifting around in the Gulf of Mexico. The low became TD 20 on the 20th of September off the Texas coast. The depression made landfall in Texas on September 21, dissipating over land. The depression left 10-15 inches of rainfall throughout the area from Corpus Christi, Texas to southwestern Louisiana. [1]
Tropical Depression Twenty-Two
A tropical depression formed on October 12 near Honduras and moved to the northeast towards Cuba. The depression passed by Cuba and turned back towards the Yucatan Peninsula. The depression made landfall in the Yucatan on October 20 and dissipated afterwards. [1]
Subtropical Storm One
| Subtropical storm (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | October 23 – October 25 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 85 mph (140 km/h) (1-min); 980 mbar (hPa) |
Subtropical Storm One formed south of Bermuda on October 23 and headed north. The subtropical depression grazed Bermuda and became a subtropical storm. This unnamed storm continued north and continued to strengthen. The storm briefly reached hurricane strength (though it was not a hurricane because it was not tropical) before weakening. The storm made landfall on Newfoundland on the 25th and dissipated later that day. No damage was reported. [13]
Tropical Depression Twenty-Five
The 25th tropical depression of the 1979 season formed near Panama on October 24. The depression moved to the north towards Cuba but changed directions and headed towards Nicaragua, where it made landfall on October 29, dissipating over land. [1]
Tropical Depression Twenty-Six
The 26th tropical depression of the 1979 season formed from an old baroclinic zone on November 8 near Puerto Rico. The depression moved northeastward but appeared to have made contact with the westerlies. However, strong pressure rises caused the depression to weaken and turn back to the southwest. Ships that passed through the system recorded winds of 35-40 mph.[1]
Accumulated Cyclone Energy (ACE) Rating
| ACE (104kt²) – Storm: Source | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 44.0 | David | 6 | 1.62 | Claudette |
| 2 | 20.7 | Frederic | 7 | 0.980 | Elena |
| 3 | 17.4 | Gloria | 8 | 0.815 | Ana |
| 4 | 3.70 | Henri | |||
| 5 | 2.10 | Bob | |||
| Total= 91.2725 (91) | |||||
The table on the right shows the ACE for each storm in the season. The ACE is, broadly speaking, a measure of the power of the hurricane multiplied by the length of time it existed for, so hurricanes that lasted a long time have higher ACEs.
Storm names
The following names were used for named storms that formed in the north Atlantic in 1979. This season marked the debut of the current set of six lists containing both male and female names, replacing the ten-year set of female name lists introduced in 1971; this was due to protests from women's rights groups. Unisex names were considered, though prior to the start of the season the World Meteorological Organization approved of the current list alternating between male and female names of English, Spanish, and French origin.[14] Initially, male names were scheduled to be introduced in the 1981 season.[15] The name Elena was previously used in the 1965 season, and the name Gloria was used in 1976. The names not retired from this list were used again in the 1985 season. Names that were not assigned are marked in gray.
|
|
Retirement
The World Meteorological Organization retired two names in the spring of 1980: David and Frederic. They were replaced in the 1985 season by Danny and Fabian.
See also
- List of Atlantic hurricanes
- List of Atlantic hurricane seasons
- 1979 Pacific hurricane season
- 1979 Pacific typhoon season
- Pre-1980 North Indian Ocean cyclone seasons
- Southern Hemisphere tropical cyclone seasons: 1978-79, 1979-80
References
- ^ a b c d e f g h Tropical depressions of the 1979 season
- ^ EM-DAT's Jamaica Page
- ^ a b c 1979 Monthly Weather Review
- ^ MANAGING NATURAL HAZARDS IN JAMAICA
- ^ Office of Disaster Preparedness and Emergency Management
- ^ a b Tropical Storm Ana Preliminary Report
- ^ Hurricane Bob Preliminary Report
- ^ a b Tropical Storm Claudette Preliminary Report
- ^ a b Hurricane David Preliminary Report
- ^ a b c Tropical Storm Elena Preliminary Report
- ^ a b c d Hurricane Gloria Preliminary Report
- ^ Hurricane Henri Preliminary Report
- ^ Subtropical Storm One Preliminary Report
- ^ National Geographic News Service (1979-07-24). "His and hur-ricane season comes East for first time". Retrieved 2007-12-01.
- ^ Associated Press (1978-05-31). "Hedge Bets on Hurricanes". Retrieved 2007-12-01.