Phyz: Difference between revisions
Upd info box new version, expanded platform reqs, referencies |
Pasted info to screenshot section from Commons |
||
| Line 42: | Line 42: | ||
==Screenshots== |
==Screenshots== |
||
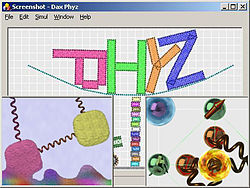
[[Image:Dax Phyz scenes.jpg|640px|Dax Phyz scene screenshots]] |
[[Image:Dax Phyz scenes.jpg|640px|Dax Phyz scene screenshots]] |
||
# [http://phyz.ath.cx/scenes/scenes.htm#Hammer Hammer scene] (upper left; deformable objects): The hammer's centre of mass is displaced from it's rotational axis, creating a torque which keeps the ruler from rotating. |
|||
# [http://phyz.ath.cx/scenes/scenes.htm#Wedge Wedge scene] (upper right; breakable objects): How to make an impression. |
|||
# [http://phyz.ath.cx/scenes/scenes.htm#Yoda Yoda scene] (lower left; bitmap import, metaballics): 3.446 vertices and 13.336 rods; the vertices form metaballs with colour information from a photograph of a clay model. |
|||
# [http://phyz.ath.cx/scenes/scenes.htm#Balloon Balloon scene] (lower right; heat constraints): "Why am I lighter in the water?" Dax asked after a recent swimming lesson. Dax, like balloons, floats since there are more particles pushing on the bottom than on the top, as in [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Buoyancy buoyancy]. |
|||
==See also== |
==See also== |
||
Revision as of 18:19, 4 April 2009
 | |
 | |
| Stable release | 1.42
/ 2009-03-29 |
|---|---|
| Operating system | Windows |
| Type | Game Engine |
| License | Public domain |
| Website | http://phyz.ath.cx |
Phyz (Dax Phyz), is a public domain,[1] 2.5D physics engine with built-in editor and DirectX graphics and sound. In contrast to most other real-time physics engines, it is vertex based and stochastic. It's integrator is based on a SIMD-enabled assembly version of the Mersenne Twister random number generator, instead of traditional LCP or iterative methods, allowing simulation of large numbers of micro objects[2] with Brownian motion and macro effects such as object resonance[3] and deformation.
Description
Purpose
Dax Phyz is used to model and simulate rigid and soft body dynamics, as well as electrostatic and magnetic phenomina, for educational and recreational purposes. There is no specified correlation between Phyz and reality.[4]
Features
- Deformable and breakable objetcs.
- Rod, stick, pin, slot, rocket, charge, magnet, heat, actuator and custom constraints.
- Explosives.
- Collision and break sound effects.
- Message based interface.
- Real-time, constraint-aware editing.
- Metaballics effects.
Platform availability
Phyz requires Windows with DirectX 9.0c or later, a display adapter with hardware support for DirectX 9, a CPU with full SSE2 support, and 1 GB of free RAM.[5] The metaballics effects require a GPGPU-capable display adapter.[6]
PhyzLizp
PhyzLizp, included with Phyz, is an external application based on the Lisp programming language (Lizp 4). It can be used to measure and control events in Phyz, and to create Phyz extensions such as graphical interfaces, network gateways, non-linear constraints or games.[7]
Screenshots
- Hammer scene (upper left; deformable objects): The hammer's centre of mass is displaced from it's rotational axis, creating a torque which keeps the ruler from rotating.
- Wedge scene (upper right; breakable objects): How to make an impression.
- Yoda scene (lower left; bitmap import, metaballics): 3.446 vertices and 13.336 rods; the vertices form metaballs with colour information from a photograph of a clay model.
- Balloon scene (lower right; heat constraints): "Why am I lighter in the water?" Dax asked after a recent swimming lesson. Dax, like balloons, floats since there are more particles pushing on the bottom than on the top, as in buoyancy.
See also
References
- ^ Phyz public domain release statement
- ^ Vladislav Popkov et al, 2002, J. Phys. A, Math. Gen. 35 7187-7204: A sufficient criterion for integrability of stochastic many-body dynamics. ISBN 9785901548127
- ^ Jan A. Freund (Humboldt-University, Germany) et al, ORAL session C32, 2006-03-12, Washington: Stochastic Resonance and Noise-Induced Phase Synchronization
- ^ Phyz scale FAQ
- ^ Phyz platform requirements
- ^ Metaballics FAQ
- ^ PhyzLizp description