Vestibular membrane: Difference between revisions
Appearance
Content deleted Content added
m robot Adding: gl:Membrana de Reissner |
m →External links: en dash for campus name using AWB |
||
| Line 33: | Line 33: | ||
* {{UIUCHistologySubject|76}} |
* {{UIUCHistologySubject|76}} |
||
* [http://lobe.ibme.utoronto.ca/presentations/Passive_DPOAE/PassiveDPoae30.htm Powerpoint] at [[University of Toronto]] |
* [http://lobe.ibme.utoronto.ca/presentations/Passive_DPOAE/PassiveDPoae30.htm Powerpoint] at [[University of Toronto]] |
||
* [http://www.neurophys.wisc.edu/h&b/textbook/chap-6.html#Obj1 Overview] at [[University of |
* [http://www.neurophys.wisc.edu/h&b/textbook/chap-6.html#Obj1 Overview] at [[University of Wisconsin–Madison]] |
||
* [http://medic.med.uth.tmc.edu/Lecture/Main/ear.htm#duct description] at [[University of Texas]] |
* [http://medic.med.uth.tmc.edu/Lecture/Main/ear.htm#duct description] at [[University of Texas]] |
||
* [http://faculty.une.edu/com/abell/histo/cochleaw.jpg Image] at [[University of New England, Maine]] |
* [http://faculty.une.edu/com/abell/histo/cochleaw.jpg Image] at [[University of New England, Maine]] |
||
Revision as of 20:21, 9 October 2009
| Vestibular membrane | |
|---|---|
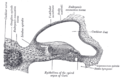
 Diagrammatic longitudinal section of the cochlea. (label is 'vestibular membrane') | |
 Cross section of the cochlea. | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | paries vestibularis ductus cochlearis |
| Anatomical terminology | |
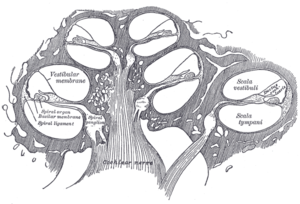
Reissner's membrane (vestibular membrane, vestibular wall) is a membrane inside the cochlea of the inner ear. It separates scala media from scala vestibuli. Together with the basilar membrane it creates a compartment in the cochlea filled with endolymph, which is important for the function of the organ of Corti. It primarily functions as a diffusion barrier, allowing nutrients to travel from the perilymph to the endolymph of the membranous labyrinth.
Histologically, the membrane is composed of two layers of flattened epithelium, separated by a basal lamina. Its structure suggests that its function is transport of fluid and electrolytes.
Reissner's membrane is named after German anatomist Ernst Reissner (1824-1878).
Additional images
-
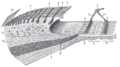
Transverse section of the cochlear duct of a fetal cat.
-
Floor of ductus cochlearis.
-
Limbus laminæ spiralis and membrana basilaris.