Rumenic acid: Difference between revisions
Appearance
Content deleted Content added
m →References: fix up accessdate using AWB |
m →Biological properties: deprecated parameters cleanup(2) format cite template dates (2), combine day, month & year, using Project:AWB |
||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
:{{see main|Conjugated linoleic acid}} |
:{{see main|Conjugated linoleic acid}} |
||
Laboratory studies indicate that rumenic acid shows [[anticarcinogen]]ic properties.<ref name=lock>{{cite journal |
Laboratory studies indicate that rumenic acid shows [[anticarcinogen]]ic properties.<ref name=lock>{{cite journal |
||
|url =http://jn.nutrition.org/cgi/content/abstract/134/10/2698| journal=J Nutr| |
|url =http://jn.nutrition.org/cgi/content/abstract/134/10/2698| journal=J Nutr|volume=134(10)|pages=2698–704 |
||
|month=October|volume=134(10)|pages=2698–704 |
|||
|title= The anticarcinogenic effect of trans-11 18:1 is dependent on its conversion to cis-9, trans-11 CLA by delta9-desaturase in rats |
|title= The anticarcinogenic effect of trans-11 18:1 is dependent on its conversion to cis-9, trans-11 CLA by delta9-desaturase in rats |
||
|author= Lock AL, Corl BA, Barbano DM, Bauman DE, Ip C.|accessdate=2007-01-15 |
|author= Lock AL, Corl BA, Barbano DM, Bauman DE, Ip C.|accessdate=2007-01-15 |
||
|pmid= 15465769 |
|pmid= 15465769 |
||
|issue =10 |
|issue =10 |
||
| |
|date = October 1, 2004 }}</ref> |
||
==References== |
==References== |
||
{{Reflist}} |
{{Reflist}} |
||
Revision as of 12:25, 1 December 2009
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
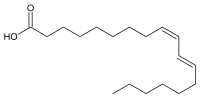
| IUPAC name
(9Z,11E)-octadeca-9,11-dienoic acid
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| Properties | |
| C18H32O2 | |
| Molar mass | 280.445 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Rumenic acid, also known as bovinic acid, is a conjugated linoleic acid (CLA) found in the fat of ruminants and in dairy products. It is an omega-7 trans fat. Its lipid shorthand name is cis-9, trans-11 18:2 acid. The name was proposed by Kramer et al. in 1998.[1] It is formed along with vaccenic acid by biohydrogenation of dietary polyunsaturated fatty acids in the rumen.[2] It can be considered as the principal dietary form, accounting for as much as 85-90% of the total CLA content in dairy products.[3]
Biological properties
Laboratory studies indicate that rumenic acid shows anticarcinogenic properties.[4]
References
- ^ Kramer J, Parodi P, Jensen R, Mossoba M, Yurawecz M, Adlof R (1998). "Rumenic acid: a proposed common name for the major conjugated linoleic acid isomer found in natural products". Lipids. 33 (8): 835. doi:10.1007/s11745-998-0279-6. PMID 9727617.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ F. Destaillats, E. Buyukpamukcu, P.-A. Golay, F. Dionisi and F. Giuffrida (2005). "Letter to the Editor: Vaccenic and Rumenic Acids, A Distinct Feature of Ruminant Fats". J. Dairy Sci. 88 (449).
{{cite journal}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Cyberlipid. "Polyenoic Fatty Acids". Retrieved 2007-01-17.
- ^ Lock AL, Corl BA, Barbano DM, Bauman DE, Ip C. (October 1, 2004). "The anticarcinogenic effect of trans-11 18:1 is dependent on its conversion to cis-9, trans-11 CLA by delta9-desaturase in rats". J Nutr. 134(10) (10): 2698–704. PMID 15465769. Retrieved 2007-01-15.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
