GV (nerve agent): Difference between revisions
Appearance
Content deleted Content added
Luckas-bot (talk | contribs) m robot Adding: ru:GV (химическое оружие) |
m Interwikifix |
||
| Line 42: | Line 42: | ||
{{organic-compound-stub}} |
{{organic-compound-stub}} |
||
[[de: |
[[de:GV (Nervenkampfstoff)]] |
||
[[ja:GVガス]] |
[[ja:GVガス]] |
||
[[ru:GV (химическое оружие)]] |
[[ru:GV (химическое оружие)]] |
||
Revision as of 07:48, 24 February 2010
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
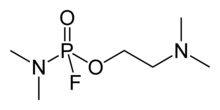
2-(dimethylamino-fluorophosphoryl)oxy-N,N-dimethylethanamine
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H16FN2O2P | |
| Molar mass | 198.176 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
GV (O-[2-(dimethylamino)ethyl]-N,N-dimethylphosphoramidic fluoride) is an organophosphate nerve agent. GV is a part of a new series of nerve agents with properties similar to both the "G-series" and "V-series". It is a potent acetylcholinesterase inhibitor with properties similar to other nerve agents, being a highly poisonous vapour. Treatment for poisoning with GV involves drugs such as atropine, benactyzine, obidoxime and HI-6.[1][2]
References
- ^ Fusek J, Bajgar J. Treatment of intoxication with GV compound in laboratory rats. Sbornik Vedeckych Praci Lekarske Fakulty Karlovy Univerzity v Hradci Kralove. 1994;37(2):57-62. PMID 7784799
- ^ Kassa J, Bajgar J. Therapeutic efficacy of obidoxime or HI-6 with atropine against intoxication with some nerve agents in mice. Acta Medica (Hradec Kralove). 1996;39(1):27-30. PMID 9106387
External links
- Identification, Purification, and Partial Characterization of the GV-Degrading Enzyme from ATCC # 29660 Alteromonas Undina
- Some Toxic Chemicals as Potential Chemical Warfare Agents - The Threat for the Future?
