Sodium cyanoborohydride: Difference between revisions
m + ja |
|||
| Line 54: | Line 54: | ||
[[es:Cianoborohidruro de sodio]] |
[[es:Cianoborohidruro de sodio]] |
||
[[fr:Cyanoborohydrure de sodium]] |
[[fr:Cyanoborohydrure de sodium]] |
||
[[ja:シアノ水素化ホウ素ナトリウム]] |
|||
[[nl:Natriumcyanoboorhydride]] |
[[nl:Natriumcyanoboorhydride]] |
||
[[zh:氰基硼氢化钠]] |
[[zh:氰基硼氢化钠]] |
||
Revision as of 11:52, 12 March 2010
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Sodium cyanotrihydridoborate
| |
| Identifiers | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.043.001 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| Properties | |
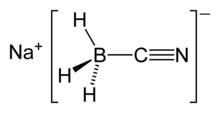
| NaBH3CN | |
| Molar mass | 62.84 g/mol |
| Appearance | white to off-white powder, hygroscopic |
| Density | 1.20 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 241 °C decomp. |
| soluble | |
| Hazards | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions
|
Sodium borohydride |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Sodium cyanoborohydride is the inorganic compound with the formula NaBH3(CN). This colourless salt is widely used in organic synthesis for the reduction of imines.
Preparation and use
The reagent may be prepared, either by treating sodium cyanide with borane, or by reacting sodium borohydride with mercuric cyanide. Owing to the presence of the electron-withdrawing cyanide substituent, [B(CN)H3]− is far less nucleophilic than is [BH4]−, as found in sodium borohydride.[1]
Sodium cyanoborohydride is a mild reducing agent that converts imines to amines. It can be used to exchange the oxygen for an amine group on the carbonyl carbon of aldehydes or ketones when reacted with ammonia or a primary amine. Selectivity is achieved at mildly basic solutions (pH 7-10). Owing to this selectively, the reagent is ideal for reductive aminations. This reduction is known sometimes as the Borch Reaction.[2] The salt is mildly water-sensitive, but tolerates aqueous conditions.[3] In addition, sodium cyanoborohydride is often used in hydrogenolysis reactions, such as the opening of acetals.
References
- ^ Ellen W. Baxter, Allen B. Reitz Reductive Aminations of Carbonyl Compounds with Borohydride and Borane Reducing Agents in Organic Reactions, 2002, John Wiley and Sons. doi:10.1002/0471264180.or059.01
- ^ Richard F. Borch and Mark D. Bernstein and H. Dupont Durst (1971). "Cyanohydridoborate Anion as a Selective Reducing Agent". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 93 (12): 2897–2904. doi:10.1021/ja00741a013.
- ^ Timothy M. Beard and Nicholas J. Turner (2002). "Deracemisation and Stereoinversion of alpha-Amino Acids Using D-Amino Acid Oxidase and Hydride Reducing Agents". Chemical Communications (3): 246–7.

