Insulin-like growth factor 2 receptor: Difference between revisions
→See also: added link to Mannose 6-phosphate receptor |
copyedit and ref reformatting |
||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
IGF2R functions to clear IGF2 from the cell surface to attenuate signalling, and to transport lysosomal [[acid hydrolase]] precursors from the Golgi apparatus to the [[lysosome]]. After binding IGF2 at the cell surface, IGF2Rs accumulate in forming [[clathrin]]-coated [[vesicle (biology)|vesicles]] and are [[endocytosis|internalized]]. In the [[Lumen (anatomy)|lumen]] of the ''trans''-Golgi network, the IGF2R binds M6P-tagged cargo.<ref name="pmid12612639">{{cite journal | author = Ghosh P, Dahms NM, Kornfeld S | title = Mannose 6-phosphate receptors: new twists in the tale | journal = Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. | volume = 4 | issue = 3 | pages = 202–12 | year = 2003 | month = March | pmid = 12612639 | doi = 10.1038/nrm1050 | url = | issn = }}</ref> The IGF2Rs (bound to their cargo) are recognized by the [[GGA]] family of [[clathrin]] adaptor proteins and accumulate in forming clathrin-coated vesicles.<ref name="pmid15511083">{{cite journal | author = Ghosh P, Kornfeld S | title = The GGA proteins: key players in protein sorting at the trans-Golgi network | journal = Eur. J. Cell Biol. | volume = 83 | issue = 6 | pages = 257–62 | year = 2004 | month = July | pmid = 15511083 | doi = 10.1078/0171-9335-00374 | url = | issn = }}</ref> IGF2Rs from both the cell surface and the Golgi are trafficked to the early [[endosome]] where, in the relatively low [[pH]] environment of the endosome, the IGF2Rs release their cargo. The IGF2Rs are recycled back to the Golgi by the [[retromer]] complex, again by way of interaction with GGAs and vesicles. The cargo proteins are then trafficked to the lysosome via the late endosome independently of the IGF2Rs. |
IGF2R functions to clear IGF2 from the cell surface to attenuate signalling, and to transport lysosomal [[acid hydrolase]] precursors from the Golgi apparatus to the [[lysosome]]. After binding IGF2 at the cell surface, IGF2Rs accumulate in forming [[clathrin]]-coated [[vesicle (biology)|vesicles]] and are [[endocytosis|internalized]]. In the [[Lumen (anatomy)|lumen]] of the ''trans''-Golgi network, the IGF2R binds M6P-tagged cargo.<ref name="pmid12612639">{{cite journal | author = Ghosh P, Dahms NM, Kornfeld S | title = Mannose 6-phosphate receptors: new twists in the tale | journal = Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. | volume = 4 | issue = 3 | pages = 202–12 | year = 2003 | month = March | pmid = 12612639 | doi = 10.1038/nrm1050 | url = | issn = }}</ref> The IGF2Rs (bound to their cargo) are recognized by the [[GGA]] family of [[clathrin]] adaptor proteins and accumulate in forming clathrin-coated vesicles.<ref name="pmid15511083">{{cite journal | author = Ghosh P, Kornfeld S | title = The GGA proteins: key players in protein sorting at the trans-Golgi network | journal = Eur. J. Cell Biol. | volume = 83 | issue = 6 | pages = 257–62 | year = 2004 | month = July | pmid = 15511083 | doi = 10.1078/0171-9335-00374 | url = | issn = }}</ref> IGF2Rs from both the cell surface and the Golgi are trafficked to the early [[endosome]] where, in the relatively low [[pH]] environment of the endosome, the IGF2Rs release their cargo. The IGF2Rs are recycled back to the Golgi by the [[retromer]] complex, again by way of interaction with GGAs and vesicles. The cargo proteins are then trafficked to the lysosome via the late endosome independently of the IGF2Rs. |
||
==Interactions== |
== Interactions == |
||
Insulin-like growth factor 2 receptor has been shown to [[Protein-protein_interaction|interact]] with [[M6PRBP1]].<ref name=pmid9590177>{{cite journal | |
Insulin-like growth factor 2 receptor has been shown to [[Protein-protein_interaction|interact]] with [[M6PRBP1]].<ref name="pmid9590177">{{cite journal | author = Díaz E, Pfeffer SR | title = TIP47: a cargo selection device for mannose 6-phosphate receptor trafficking | journal = Cell | volume = 93 | issue = 3 | pages = 433–43 | year = 1998 | month = May | pmid = 9590177 | doi = | url = | issn = }}</ref><ref name="pmid10908666">{{cite journal | author = Orsel JG, Sincock PM, Krise JP, Pfeffer SR | title = Recognition of the 300-kDa mannose 6-phosphate receptor cytoplasmic domain by 47-kDa tail-interacting protein | journal = Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. | volume = 97 | issue = 16 | pages = 9047–51 | year = 2000 | month = August | pmid = 10908666 | pmc = 16819 | doi = 10.1073/pnas.160251397 | url = | issn = }}</ref> |
||
==See also== |
==See also== |
||
| Line 46: | Line 47: | ||
}} |
}} |
||
{{refend}} |
{{refend}} |
||
| ⚫ | |||
==External links== |
==External links== |
||
* {{MeshName|Insulin-Like-Growth-Factor+II+Receptor}} |
* {{MeshName|Insulin-Like-Growth-Factor+II+Receptor}} |
||
| ⚫ | |||
{{Clusters of differentiation}} |
{{Clusters of differentiation}} |
||
{{Growth factor receptors}} |
{{Growth factor receptors}} |
||
| Line 60: | Line 61: | ||
| require_manual_inspection = no |
| require_manual_inspection = no |
||
| update_protein_box = yes |
| update_protein_box = yes |
||
| update_summary = |
| update_summary = no |
||
| update_citations = yes |
| update_citations = yes |
||
}} |
}} |
||
Revision as of 07:37, 21 March 2010
Template:PBB In biochemistry and cell biology, the insulin-like growth factor 2 receptor (IGF2R), also called the cation-independent mannose-6-phosphate receptor (CI-MPR), is a multifunctional protein receptor that binds insulin-like growth factor 2 (IGF2) at the cell surface and mannose-6-phosphate (M6P)-tagged proteins in the trans-Golgi network.
Structure
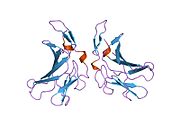
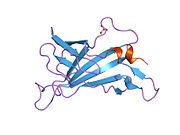
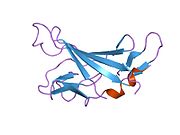
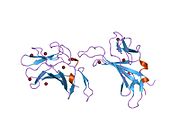
The structure of the IGF2R is a type I transmembrane protein (that is, it has a single transmembrane domain with its C-terminus on the cytoplasmic side of lipid membranes) with a large extracellular/lumenal domain and a relatively short cytoplasmic tail.[1] The extracellular domain consists a small region homologous to the collagen-binding domain of fibronectin and of fifteen repeats of approximately 147 amino acid residues. Each of these repeats is homologous to the 157-residue extracytoplasmic domain of the mannose 6-phosphate receptor. Binding to IGF2 is mediated through one of the repeats, while two different repeats are responsible for binding to mannose-6-phosphate. The IGF2R is approximately 300 kDa in size it appears to exist and function as a dimer.
Function
IGF2R functions to clear IGF2 from the cell surface to attenuate signalling, and to transport lysosomal acid hydrolase precursors from the Golgi apparatus to the lysosome. After binding IGF2 at the cell surface, IGF2Rs accumulate in forming clathrin-coated vesicles and are internalized. In the lumen of the trans-Golgi network, the IGF2R binds M6P-tagged cargo.[1] The IGF2Rs (bound to their cargo) are recognized by the GGA family of clathrin adaptor proteins and accumulate in forming clathrin-coated vesicles.[2] IGF2Rs from both the cell surface and the Golgi are trafficked to the early endosome where, in the relatively low pH environment of the endosome, the IGF2Rs release their cargo. The IGF2Rs are recycled back to the Golgi by the retromer complex, again by way of interaction with GGAs and vesicles. The cargo proteins are then trafficked to the lysosome via the late endosome independently of the IGF2Rs.
Interactions
Insulin-like growth factor 2 receptor has been shown to interact with M6PRBP1.[3][4]
See also
References
- ^ a b Ghosh P, Dahms NM, Kornfeld S (2003). "Mannose 6-phosphate receptors: new twists in the tale". Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 4 (3): 202–12. doi:10.1038/nrm1050. PMID 12612639.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Ghosh P, Kornfeld S (2004). "The GGA proteins: key players in protein sorting at the trans-Golgi network". Eur. J. Cell Biol. 83 (6): 257–62. doi:10.1078/0171-9335-00374. PMID 15511083.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ Díaz E, Pfeffer SR (1998). "TIP47: a cargo selection device for mannose 6-phosphate receptor trafficking". Cell. 93 (3): 433–43. PMID 9590177.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ Orsel JG, Sincock PM, Krise JP, Pfeffer SR (2000). "Recognition of the 300-kDa mannose 6-phosphate receptor cytoplasmic domain by 47-kDa tail-interacting protein". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 97 (16): 9047–51. doi:10.1073/pnas.160251397. PMC 16819. PMID 10908666.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
Further reading
External links
- Insulin-Like-Growth-Factor+II+Receptor at the U.S. National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)