Mobile High-Definition Link: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
[[Image:Figura3_en.jpg|center|frame|''Connector uses'']] |
[[Image:Figura3_en.jpg|center|frame|''Connector uses'']] |
||
By transporting the digital content in digital form, the full impact of the picture (whether still images or video) can be seen on [[High-definition television|HDTV]]s. |
By transporting the digital content in digital form, the full impact of the picture (whether still images or video) can be seen on [[High-definition television|HDTV]]s. |
||
The content stream is compliant to the HDMI specification, through the use of a bridge chip in a smart cable or docking station. The mobile device plugs into the bridge, where it can be recharged while playing content up to [[720p]] or [[1080i]] to the display device. |
|||
The requirements of this connector are: |
The requirements of this connector are: |
||
| Line 25: | Line 22: | ||
* Two pins on the device’s connector are reserved for a single Transition Minimized Differential Signaling ([[TMDS]]) lane carrying audio/video packets |
* Two pins on the device’s connector are reserved for a single Transition Minimized Differential Signaling ([[TMDS]]) lane carrying audio/video packets |
||
* A single pin is reserved for a bi-directional control bus, which supports authentication, A/V format discovery, and various control functions. |
* A single pin is reserved for a bi-directional control bus, which supports authentication, A/V format discovery, and various control functions. |
||
[[Image:Figura1_en.jpg|center|frame|''Connections]] |
[[Image:Figura1_en.jpg|center|frame|''Connections]] |
||
== '''Other information''' == |
== '''Other information''' == |
||
MHL technology was invented by [[Silicon Image]]<ref>{{cite news |title=Mobile High-Definition Link Technology Gives Consumers the Ability to Link Mobile Devices to HDTVs with Support for Audio and Video |publisher=Silicon Image |url=http://www.siliconimage.com/news/releasedetails.aspx?id=480 |date=January 15, 2009 |accessdate=2009-01-15}}</ref>, one of the founders of the HDMI standard. The MHL technology link has been optimized for low power operation of the mobile device, and includes provision for charging the mobile device through the MHL cable. |
|||
MHL technology chips have been announced for the HDTV side of the interconnect.<ref>{{cite news |title=Silicon Image introduces First Products |publisher=Silicon Image |url=http://www.siliconimage.com/news/releasedetails.aspx?id=582 |date=June 22, 2009 |accessdate=2009-06-24}}</ref> |
|||
A working group was announced in September 2009 to develop a specification based on MHL Technology.<ref>{{cite news |title=Leading Companies Form Mobile High-Definition Interface Working Group to Drive Industry Standard for Mobile Wired Connectivity |publisher=Silicon Image |url=http://www.siliconimage.com/news/releasedetails.aspx?id=591 |date=September 28, 2009 |accessdate=2009-09-30}}</ref> The group includes [[Nokia]], [[Samsung]], Silicon Image, [[Sony]], and [[Toshiba]]. |
A working group was announced in September 2009 to develop a specification based on MHL Technology.<ref>{{cite news |title=Leading Companies Form Mobile High-Definition Interface Working Group to Drive Industry Standard for Mobile Wired Connectivity |publisher=Silicon Image |url=http://www.siliconimage.com/news/releasedetails.aspx?id=591 |date=September 28, 2009 |accessdate=2009-09-30}}</ref> The group includes [[Nokia]], [[Samsung]], Silicon Image, [[Sony]], and [[Toshiba]]. |
||
== '''Silicon Image products''' == |
|||
* '''MHL Transmitters''' |
|||
MHL transmitters contain two pins for transmitting digital data through a single TMDS transmission which reduces the pin count for small devices. These transmitters distributed video and audio high definition on five pins. MHL Transmitters are available with input support for [[MIPI]] (Mobile Industry Processor Interface) or parallel RGB/YCbCr/ITU.601/ITU.656 for digital video input. The low active and standby power consumption of MHL transmitters extend battery life in mobile devices. |
|||
Silicon Image’s MHL transmitters include ''SiI9224'', which supports the MIPI input interface, and SiI9226, which supports parallel RGB/YCbCr/ ITU.601/ITU.656 input interfaces. |
|||
*'''MHL Bridges''' |
|||
MHL-to-HDMI bridges convert an MHL technology enabled device’s audio and video signals into a standard HDMI signal. The MHL bridge provides a cost-effective solution for a docking station or dongle that is HDMI compatible. The ''SiI9290'' MHL bridge is Silicon Image’s HDMI-to-MHL bridge solution. |
|||
*'''HDMI Receivers with MHL Support''' |
|||
Silicon Image’s include ''SiI9223'' is a four-port HDMI receiver that delivers advanced HDMI 1.3 HDTV features including 1080p, [[Deep Color]] and [[xvYCC | x.v.Color]] expanded color gamut, and includes support for MHL technology. |
|||
==References and notes== |
==References and notes== |
||
Revision as of 20:45, 9 April 2010
The Mobile High-definition Link (MHL) is a compact audio/video connector interface for transmitting uncompressed digital video and audio streams. It represents a digital alternative to consumer analog standards such as composite video and S-Video. MHL is compatible with DVI and HDMI, but uses many fewer pins and therefore can attach with smaller connectors and thinner cable. Smaller connectors are favored by makers of smaller and smaller portable devices.[1]
Features
- MHL technology provides HD audio/video with a low pin count, enabling high definition audio and video using the mobile device’s existing multipurpose connector.
- MHL technology conserves battery life with ultra-low active and standby power draw.
- MHL technology supports high-quality digital HD video up to 1080p.
- MHL technology can be compatible with the HDMI input ports found on most HDTVs today with an MHL-to-HDMI bridge
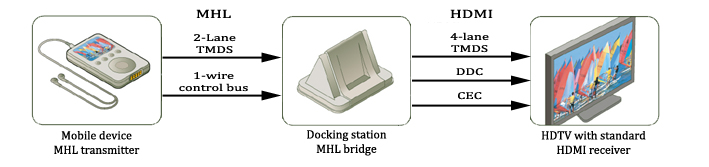
Connections
MHL connects mobile digital audio/video sources such as cameras, portable media players, and camera phones to any HDMI device's input. Also this connector uses for power charging, data transfer, and audio/video transfer.

By transporting the digital content in digital form, the full impact of the picture (whether still images or video) can be seen on HDTVs.
The requirements of this connector are:
- Two pins on the device’s connector are reserved for a single Transition Minimized Differential Signaling (TMDS) lane carrying audio/video packets
- A single pin is reserved for a bi-directional control bus, which supports authentication, A/V format discovery, and various control functions.
Other information
A working group was announced in September 2009 to develop a specification based on MHL Technology.[2] The group includes Nokia, Samsung, Silicon Image, Sony, and Toshiba.
References and notes
- ^ "New Dual-Mode HDMI/MHL Technology Solution Reduces BOM Cost, Extends battery life and prepares handsets for an HD connection to HDTVs". Silicon Image. July 14, 2008. Retrieved 2009-01-15.
- ^ "Leading Companies Form Mobile High-Definition Interface Working Group to Drive Industry Standard for Mobile Wired Connectivity". Silicon Image. September 28, 2009. Retrieved 2009-09-30.
