Bee colony optimization: Difference between revisions
m using discuss= parameter for merge template to reconcile syntax differences as part of merge template merger |
|||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
* [[Evolutionary computation]] |
* [[Evolutionary computation]] |
||
* [[Ant colony optimization]] |
* [[Ant colony optimization]] |
||
*[[Intelligent Water Drops]] |
|||
* [[Swarm intelligence]] |
* [[Swarm intelligence]] |
||
* [[Animal communication]] |
* [[Animal communication]] |
||
Revision as of 12:12, 11 April 2010
It has been suggested that this article be merged with Bees algorithm. (Discuss) Proposed since July 2008. |
The bee colony optimization algorithm is inspired by the behaviour of a honey bee colony in nectar collection. This biologically inspired approach is currently being employed to solve continuous optimization problems, training neural networks, mechanical and electronical componenets design optimization, combinatorial optimization problems such as job shop scheduling, the internet server optimization problem, the travelling salesman problem, etc.
Bee colony optimization in the job shop scheduling problem
The honey bees' effective foraging strategy can be applied to Job Shop Scheduling Problems.
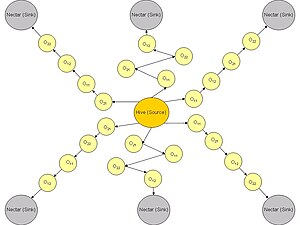
A feasible solution in a Job Shop Scheduling Problem is a complete schedule of operations specified in the problem. We can think of each solution as a path from the hive to the food source. The figure below illustrates such an analogy
The makespan of the solution is analogous to the profitability of the food source in terms of distance and sweetness of the nectar. Hence, the shorter the makespan, the higher the profitability of the solution path.
We can thus maintain a colony of bees, where each bee will traverse a potential solution path. Once a feasible solution is found, each bee will return to the hive to perform a Waggle Dance. The Waggle Dance will be represented by a list of Elite Solutions (Chong et al., 2006), from which other bees can choose to follow another bee's path. Bees with a better makespan will have a higher probability of adding its path to the list of Elite Solutions, promoting a convergence to an optimal solution.
Using the above scheme, the natural honey bee's self organizing foraging strategy can be applied to the Job Shop Scheduling Problem.
See also
- Bees algorithm
- Evolutionary computation
- Ant colony optimization
- Intelligent Water Drops
- Swarm intelligence
- Animal communication
- Bee learning and communication
- Waggle dance
Publications
- Pham D.T., Ashraf Afify, Ebubekir Koc "Manufacturing cell formation using the Bees Algorithm". IPROMS 2007 Innovative Production Machines and Systems Virtual Conference, Cardiff, UK.
- Nakrani S. and Tovey C., "On Honey Bees and Dynamic Server Allocation in Internet Hosting Centers". Adaptive Behaviour, 2004. 12(3-4):pp. 223-240.
- Tovey C., "The Honey Bee Algorithm: A Biological Inspired Approach to Internet Server Optimization". Engineering Enterprise, the Alumni Magazine for ISyE at Georgia Institute of Technology, Spring 2004, pp. 13-15.
- Yang X.S., "Engineering Optimizations Via Nature-Inspired Virtual Bee Algorithms". Artificial Intelligence and Knowledge Engineering Applications: A Bioinspired Approach, LECTURE NOTES IN COMPUTER SCIENCE 3562:2005, pp. 317-323 , Springer Berlin / Heidelberg.
- Chin Soon Chong, Malcolm Yoke Hean Low, Appa Iyer Sivakumar and Kheng Leng Gay, "A bee colony optimization algorithm to job shop scheduling", In Proceedings of the 2006 Winter Simulation Conference, December 3-6, 2006, Monterey, CA USA, pp. 1954-1961.
- Pham D.T., Ghanbarzadeh A., Koç E., Otri S., Rahim S., and M.Zaidi "The Bees Algorithm – A Novel Tool for Complex Optimisation Problems"", Proceedings of IPROMS 2006 Conference, pp.454-461
- Pham D.T., Ghanbarzadeh A. "Multi-Objective Optimisation using the Bees Algorithm"", Proceedings of IPROMS 2007 Conference
- Pham D.T., Koç E.,Ghanbarzadeh A., Otri S. "Optimisation of the Weights of Multi-Layered Perceptrons Using the Bees Algorithm". IMS’06 Intelligent Manufacturing Systems Conference. Sakarya, Turkey.
- Pham D.T., Ghanbarzadeh A., Koc E., and Otri S. "Application of the Bees Algorithm to the Training of Radial Basis Function Networks for Control Chart Pattern Recognition". Proc 5th CIRP International Seminar on Intelligent Computation in Manufacturing Engineering (CIRP ICME '06). 2006. Ischia, Italy, pp. 711-716.
- Pham D.T., Soroka A.J., Koç E.,Ghanbarzadeh A., Otri S., Packianather M. "Optimising Neural Networks for Identification of Wood Defects Using the Bees Algorithm". 4th International IEEE Conference on Industrial Informatics.INDIN’06 16-18 August 2006, Singapore.