Arsenic triiodide: Difference between revisions
+3 state |
|||
| Line 44: | Line 44: | ||
[[Hydrolysis]] occurs slowly in water forming [[arsenic trioxide]] and [[hydroiodic acid]]. The reaction proceeds via formation of [[arsenous acid]] which exists in [[Chemical equilibrium|equilibrium]] with hydroiodic acid. |
[[Hydrolysis]] occurs slowly in water forming [[arsenic trioxide]] and [[hydroiodic acid]]. The reaction proceeds via formation of [[arsenous acid]] which exists in [[Chemical equilibrium|equilibrium]] with hydroiodic acid. |
||
The aqueous solution is highly acidic, pH of 0.1N solution is 1.1. It readily decomposes to arsenic trioxide, elemental arsenic and iodine when heated in air at 200 °C. The decomposition, however, commences at 100 °C. |
The aqueous solution is highly acidic, pH of 0.1N solution is 1.1. It readily decomposes to arsenic trioxide, elemental arsenic and iodine when heated in air at 200 °C. The decomposition, however, commences at 100 °C. A example of a decomposition reaction would be: |
||
:6 AsI<sub>3</sub> + 3 O<sub>2</sub> → 2 As<sub>2</sub>O<sub>3</sub> + 2 As + 9 I<sub>2<sub> |
|||
== Former uses == |
== Former uses == |
||
Revision as of 17:40, 29 May 2010
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.029.153 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| AsI3 | |
| Molar mass | 455.635 g/mol |
| Appearance | orange-red crystalline solid |
| Density | 4.69 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 146 °C |
| Boiling point | 403 °C |
| 6 g/100 mL | |
| Solubility | soluble in alcohol, ether, CS2 |
Refractive index (nD)
|
2.23 |
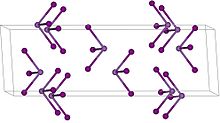
| Structure | |
| Rhombohedral, hR24, SpaceGroup = R-3, No. 148 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Arsenic triiodide is the chemical compound with the formula AsI3. It is a pyramidial molecule with covalent bonding. [2] It contains arsenic in its +3 oxidation state.
Preparation
It is prepared by a reaction between arsenic(III) chloride and an iodine salt:
- AsCl3(aq) + 3KI(aq) → AsI3(aq) + 3KCl(aq)
Reactions
Hydrolysis occurs slowly in water forming arsenic trioxide and hydroiodic acid. The reaction proceeds via formation of arsenous acid which exists in equilibrium with hydroiodic acid.
The aqueous solution is highly acidic, pH of 0.1N solution is 1.1. It readily decomposes to arsenic trioxide, elemental arsenic and iodine when heated in air at 200 °C. The decomposition, however, commences at 100 °C. A example of a decomposition reaction would be:
- 6 AsI3 + 3 O2 → 2 As2O3 + 2 As + 9 I2
Former uses
Under the name of Donovan's solution, it was once recommended to treat rheumatism, arthritis, malaria, trypanosome infections, tuberculosis, and diabetes.[1]
References
- ^ a b Shakhashiri BZ, "Chemical of the Week: Arsenic", University of Wisconsin–Madison Chemistry Dept.
- ^ Pradyot Patnaik. Handbook of Inorganic Chemicals. McGraw-Hill, 2002, ISBN 0070494398
