2-Ethylanthraquinone: Difference between revisions
Appearance
Content deleted Content added
Script assisted update of identifiers from ChemSpider, CommonChemistry and FDA for the Chem/Drugbox validation project - Updated: ChEMBL. |
Updating {{chembox}} (no changed fields - added verified revid - updated 'UNII_Ref', 'ChEMBL_Ref', 'KEGG_Ref') per Chem/Drugbox validation (report errors |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{chembox |
{{chembox |
||
| verifiedrevid = |
| verifiedrevid = 413109678 |
||
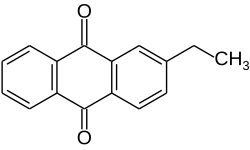
| Name = 2-Ethylanthraquinone |
| Name = 2-Ethylanthraquinone |
||
| ImageFile = 2-Ethylanthraquinone.svg |
| ImageFile = 2-Ethylanthraquinone.svg |
||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
| InChIKey = SJEBAWHUJDUKQK-UHFFFAOYAW |
| InChIKey = SJEBAWHUJDUKQK-UHFFFAOYAW |
||
| SMILES = O=C2c1c(cccc1)C(=O)c3c2ccc(c3)CC |
| SMILES = O=C2c1c(cccc1)C(=O)c3c2ccc(c3)CC |
||
| ChEMBL_Ref = {{ebicite|correct|EBI}} |
|||
| ChEMBL = 42355 |
| ChEMBL = 42355 |
||
| StdInChI_Ref = {{stdinchicite|correct|chemspider}} |
| StdInChI_Ref = {{stdinchicite|correct|chemspider}} |
||
Revision as of 14:31, 10 February 2011
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
2-Ethyl-9,10-anthracenedione
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.396 |
| EC Number |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
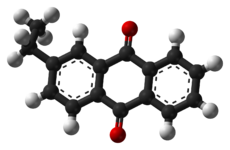
| C16H12O2 | |
| Molar mass | 236.27 g/mol |
| Density | 650 kg·m−3 |
| Melting point | 105 °C (221 °F; 378 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
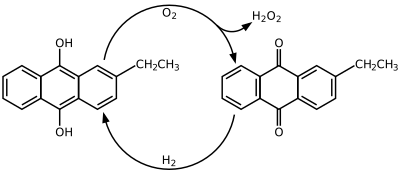
2-Ethylanthraquinone is an aromatic organic compound closely related to anthracene.
It is commonly used along with 2-ethyl-9,10-dihydroxyanthracene to create hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) by the Riedl-Pfleiderer, or autoxidation, process: