Glyceollin I: Difference between revisions
Appearance
Content deleted Content added
Updating {{chembox}} (changes to watched fields - added verified revid - updated 'UNII_Ref', 'ChemSpiderID_Ref', 'StdInChI_Ref', 'StdInChIKey_Ref', 'ChEMBL_Ref', 'KEGG_Ref') per [[Wikipedia:WikiProject Chemicals/Chembox validation|Chem/Drugbox valida |
|||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
| Autoignition = }} |
| Autoignition = }} |
||
}} |
}} |
||
'''Glyceollin I''' is a [[glyceollin]], a type of pterocarpan. It is a [[phytoalexin]] found in the [[soybean]].<ref>Glyceollin I, a Novel Antiestrogenic Phytoalexin Isolated from Activated Soy. M. Carla Zimmermann, Syreeta L. Tilghman, Stephen M. Boué, Virgilio A. Salvo, Steven Elliott, K. Y. Williams, Elena V. Skripnikova, Hasina Ashe, Florastina Payton-Stewart, Lyndsay Vanhoy-Rhodes, Juan Pablo Fonseca, Cynthia Corbitt, Bridgette M. Collins-Burow, Melanie H. Howell, Michelle Lacey, Betty Y. Shih, Carol Carter-Wientjes, Thomas E. Cleveland, John A. McLachlan, Thomas E. Wiese, Barbara S. Beckman and Matthew E. Burow, JPET January 2010 vol. 332 no. 1, {{doi|10.1124/jpet.109.160382}}</ref> |
'''Glyceollin I''' is a [[glyceollin]], a type of [[prenylated]] [[pterocarpan]]. It is a [[phytoalexin]] found in the [[soybean]].<ref>Glyceollin I, a Novel Antiestrogenic Phytoalexin Isolated from Activated Soy. M. Carla Zimmermann, Syreeta L. Tilghman, Stephen M. Boué, Virgilio A. Salvo, Steven Elliott, K. Y. Williams, Elena V. Skripnikova, Hasina Ashe, Florastina Payton-Stewart, Lyndsay Vanhoy-Rhodes, Juan Pablo Fonseca, Cynthia Corbitt, Bridgette M. Collins-Burow, Melanie H. Howell, Michelle Lacey, Betty Y. Shih, Carol Carter-Wientjes, Thomas E. Cleveland, John A. McLachlan, Thomas E. Wiese, Barbara S. Beckman and Matthew E. Burow, JPET January 2010 vol. 332 no. 1, {{doi|10.1124/jpet.109.160382}}</ref> |
||
[[Glyceollin synthase]] is an enzyme responsible for the production of glyceollin.<ref>{{cite journal | author = Welle R, Grisebach H | date = 1988 | title = Induction of phytoalexin synthesis in soybean: enzymatic cyclization of prenylated pterocarpans to glyceollin isomers | journal = Arch. Biochem. Biophys. | volume = 263 | pages = 191–8 | pmid = 3369863 | doi = 10.1016/0003-9861(88)90627-3 | issue = 1 }}</ref> The five substrates of this enzyme are [[2-dimethylallyl-(6aS,11aS)-3,6a,9-trihydroxypterocarpan]], [[4-dimethylallyl-(6aS,11aS)-3,6a,9-trihydroxypterocarpan]], [[nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate|NADPH]], [[hydrogen ion|H<sup>+</sup>]], and [[oxygen|O<sub>2</sub>]], whereas its three products are glyceollin, [[nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate|NADP<sup>+</sup>]], and [[water|H<sub>2</sub>O]]. |
[[Glyceollin synthase]] is an enzyme responsible for the production of glyceollin.<ref>{{cite journal | author = Welle R, Grisebach H | date = 1988 | title = Induction of phytoalexin synthesis in soybean: enzymatic cyclization of prenylated pterocarpans to glyceollin isomers | journal = Arch. Biochem. Biophys. | volume = 263 | pages = 191–8 | pmid = 3369863 | doi = 10.1016/0003-9861(88)90627-3 | issue = 1 }}</ref> The five substrates of this enzyme are [[2-dimethylallyl-(6aS,11aS)-3,6a,9-trihydroxypterocarpan]], [[4-dimethylallyl-(6aS,11aS)-3,6a,9-trihydroxypterocarpan]], [[nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate|NADPH]], [[hydrogen ion|H<sup>+</sup>]], and [[oxygen|O<sub>2</sub>]], whereas its three products are glyceollin, [[nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate|NADP<sup>+</sup>]], and [[water|H<sub>2</sub>O]]. |
||
Revision as of 03:22, 22 March 2011
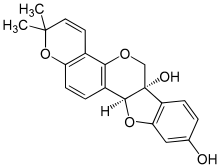
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC names
(6aS,11aS)-2,2-dimethyl-2H,6H-[1]benzofuro[3,2‑c]pyrano[2,3‑h]
chromene-6a,9(11aH)-diol | |
| Other names
(−)-Glyceollin I
| |
| Identifiers | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.222.666 |
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| Properties | |
| C20H18O5 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Glyceollin I is a glyceollin, a type of prenylated pterocarpan. It is a phytoalexin found in the soybean.[1]
Glyceollin synthase is an enzyme responsible for the production of glyceollin.[2] The five substrates of this enzyme are 2-dimethylallyl-(6aS,11aS)-3,6a,9-trihydroxypterocarpan, 4-dimethylallyl-(6aS,11aS)-3,6a,9-trihydroxypterocarpan, NADPH, H+, and O2, whereas its three products are glyceollin, NADP+, and H2O.
This molecule exhibits antiestrogenic properties.[3]
References
- ^ Glyceollin I, a Novel Antiestrogenic Phytoalexin Isolated from Activated Soy. M. Carla Zimmermann, Syreeta L. Tilghman, Stephen M. Boué, Virgilio A. Salvo, Steven Elliott, K. Y. Williams, Elena V. Skripnikova, Hasina Ashe, Florastina Payton-Stewart, Lyndsay Vanhoy-Rhodes, Juan Pablo Fonseca, Cynthia Corbitt, Bridgette M. Collins-Burow, Melanie H. Howell, Michelle Lacey, Betty Y. Shih, Carol Carter-Wientjes, Thomas E. Cleveland, John A. McLachlan, Thomas E. Wiese, Barbara S. Beckman and Matthew E. Burow, JPET January 2010 vol. 332 no. 1, doi:10.1124/jpet.109.160382
- ^ Welle R, Grisebach H (1988). "Induction of phytoalexin synthesis in soybean: enzymatic cyclization of prenylated pterocarpans to glyceollin isomers". Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 263 (1): 191–8. doi:10.1016/0003-9861(88)90627-3. PMID 3369863.
- ^ Glyceollin I enantiomers distinctly regulate ER-mediated gene expression. Florastina Payton-Stewart, Rahul S. Khupse, Stephen M. Boué, Steven Elliott, M. Carla Zimmermann, Elena V. Skripnikova, Hasina Ashe, Syreeta L. Tilghman, Barbara S. Beckman, Thomas E. Cleveland, John A. McLachlan, Deepak Bhatnagar, Thomas E. Wiese, Paul Erhardt and Matthew E. Burow, Steroids, Volume 75, Issue 12, December 2010, Pages 870-878, doi:10.1016/j.steroids.2010.05.007, PMID 20493896
