Trilobite: Difference between revisions
→Fossil distribution: commercial collecting locations |
|||
| Line 97: | Line 97: | ||
A famous location for trilobite fossils in the [[United Kingdom]] is Wren's Nest, [[Dudley]] in the [[West Midlands (county)|West Midlands]], where ''Calymene blumenbachi'' is found in the [[Silurian]] Wenlock Limestone formation. This trilobite is featured on the town's [[coat of arms]] and was named the "Dudley locust" or "Dudley bug" by quarrymen who once worked many of the now abandoned [[limestone]] quarries. Other trilobites found there include ''Dalmanites'', ''Trimerus'' and ''Bumastus''. |
A famous location for trilobite fossils in the [[United Kingdom]] is Wren's Nest, [[Dudley]] in the [[West Midlands (county)|West Midlands]], where ''Calymene blumenbachi'' is found in the [[Silurian]] Wenlock Limestone formation. This trilobite is featured on the town's [[coat of arms]] and was named the "Dudley locust" or "Dudley bug" by quarrymen who once worked many of the now abandoned [[limestone]] quarries. Other trilobites found there include ''Dalmanites'', ''Trimerus'' and ''Bumastus''. |
||
Spectacular trilobite fossils, showing soft body parts like legs, gills and antennae, have been found in British Columbia (Burgess Shale Cambrian fossils, and similar localities in the Canadian Rockies); New York State (Odovician Walcott-Rust Quarry, near Utica, N.Y., and the Beecher Trilobite Beds, near Rome, N.Y.), in China (Burgess Shale-like Cambrian trilobites at Chengjiang, Germany (the Devonian Hunsruck Shale at Bundenbach, Germany) and, much more rarely, in trilobite-bearing strata in Utah and Ontario. |
Spectacular trilobite fossils, showing soft body parts like legs, gills and antennae, have been found in British Columbia (Burgess Shale Cambrian fossils, and similar localities in the Canadian Rockies); New York State (Odovician Walcott-Rust Quarry, near Utica, N.Y., and the Beecher Trilobite Beds, near Rome, N.Y.), in China (Burgess Shale-like Cambrian trilobites at Chengjiang), Germany (the Devonian Hunsruck Shale at Bundenbach, Germany) and, much more rarely, in trilobite-bearing strata in Utah and Ontario. |
||
Trilobites are collected commercially in Russia (especially in the St. Petersburg area), Germany, Morocco's Atlas Mountains, (where a burgeoning trade in faked trilobites is also under way), Utah, Ohio, British Columbia, and in other parts of Canada. |
|||
== References == |
== References == |
||
Revision as of 22:26, 10 March 2006
| Trilobite | |
|---|---|

| |
| Asaphiscus wheeleri, a trilobite from Cambrian-age shale in Utah | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Phylum: | |
| Class: | Trilobita Walch, 1771
|
| Orders | |
Trilobites are extinct arthropods in the class Trilobita. They appeared in the Cambrian period and flourished throughout the lower Palaeozoic before slowly declining to extinction. The last of the trilobites disappeared in the mass extinction at the end of the Permian 250 million years ago. Trilobites are well-known, possibly the second most famous fossil group after the dinosaurs, and are the most diverse group of animal species preserved in the fossil record, consisting of eight, possibly nine, orders and over 15,000 species. Most were simple, small marine animals that filtered mud to obtain food.
Physical description
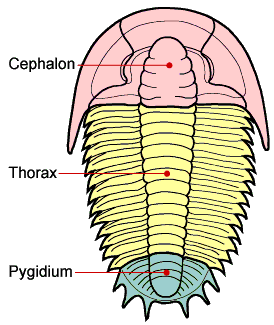

The bodies of trilobites are divided into three parts (tagmata): a cephalon (head), composed of the two preoral and first four postoral segments completely fused together; a thorax composed of freely articulating segments; and a pygidium (tail) composed of the last few segments fused together with the telson. In the most primitive trilobites the pygidia are still fairly rudimentary. The thorax is fairly flexible—fossilised trilobites are often found curled up like modern woodlice for protection.
Trilobites had a single pair of preoral antennae and otherwise undifferentiated biramous limbs. Each exopodite (walking leg) had six segments, analogous to those of other early arthropods. The first segment also bore a feather-like epipodite, or gill branch, which was used for respiration and swimming. The limbs were covered by lateral projections called pleural lobes, extending outward from a central axial lobe. Contrary to popular belief, it is this longitudinal tripartite division into left and right pleural lobes and a central axial lobe that gives trilobites their name, not the division into cephalon, thorax and pygidium.
Although trilobites were only armored on top, they still had a fairly heavy exoskeleton. During moulting, the exoskeleton generally split between the head and thorax, which is why so many trilobite fossils are missing one or the other: many trilobite fossils are actually moulted exoskeletons rather than dead trilobites. In most groups there were two facial sutures on the cheeks to make shedding easier. The cheeks usually also supported a pair of crescent-shaped compound eyes, which were surprisingly advanced in some species. In fact, trilobites were the first animals to evolve true eyes, about 543 million years ago; the evolutionary appearance of eyes has been postulated as a trigger for the Cambrian Explosion.
Some trilobites such as those of the order Lichida evolved elaborate spiny forms, particularly during the Devonian period. Examples of these specimens have been found in the Hamar Laghdad formation of Alnif in Morocco. Spectacular spined trilobites have also been found in western Russia and Ontario, Canada. These spiny forms could possibly have been a defensive response to the evolutionary appearance of fish.
According to New Scientist magazine (May 2005), "some... trilobites... had horns on their heads similar to those of modern beetles." Based on the size, location, and shape of the horns, Rob Knell, a biologist at Queen Mary University of London and Richard Fortey of London's Natural History Museum, concluded that the most likely use of the horns was combat for mates, making trilobites the earliest exemplars of this behavior. While this study only covered the raphiophorid family, the conclusions can be applied to other groups as well, such as the Walliserops trifurcates
Trilobites range in length from one millimetre to 72 cm (1/25 inch to 28 inches), with a typical size range of two to seven centimetres (1 to 3 1/2 inches). The world's largest trilobite, Isotelus rex, was found in 1998 by Canadian scientists on the shores of Hudson's Bay.[1]
Sensory organs

Many trilobites had eyes and they had antennae that perhaps were used for taste and smell. Some trilobites were blind, probably living too deep in the sea for light to reach them. Others, such as Phacops rana, had eyes that were quite large.
The eyes of trilobites were made of calcite (calcium carbonate, CaCO3). Pure forms of calcite are transparent, and the trilobites used clear calcite crystals to form the lenses of their eyes. In this, they differ from most other arthropods, which have soft eyes. The rigid calcite lenses of a trilobites eyes was unable to accommodate to a change of focus like the soft lens in a human eye would; however, the calcite formed in a internal doublet structure, giving superb depth of field and minimal spherical aberration.
The trilobite eyes were typically compound, with each lens being an elongated prism. The number of lenses in such an eye varies, however: some trilobites had only one so they could only distinguish between light and dark, and some had thousands of lenses in one eye. In these compound eyes, the lenses are arranged hexagonally. A living species with similar eyes is the brittle star Ophiocoma wendtii.

Holochroal eyes
Holochroal eyes had a great number of (tiny) lenses (sometimes over 15,000), and are found in all orders of trilobite. These lenses were packed closely together (hexagonally) and touched each other. A single corneal membrane covered all lenses. These eyes had no sclera, the white layer covering most current eyes.
Schizochroal eyes
Schizochroal eyes typically had less (and larger) lenses (to around 700), and are found only in Phacopida. The lenses were separate, with each lens having an individual cornea which extended into a rather large sclera.
Abathochroal eyes
Abathochroal eyes had few (and small) lenses (to around 70), and are found only in Cambrian Eodiscina. Each lens was separate and had an individual cornea. The sclera was separate from the cornea, and did not run as deep as the sclera in schizochroal eyes.
Development
An egg hatched to give a tiny larva called a protaspid, in which only the fused segments of the cephalon are present. Subsequent thoracic segments were added behind the cephalon in successive molts during an intermediate stage called meraspid, until finally the adult number of segments was reached, at which point the animal is called a holaspid. Trilobite larvae are reasonably well known and provide an important aid in their classification.
Terminology
When describing differences between different taxa of trilobites, the presence, size, and shape of the cephalic features above are often mentioned.
Figure 1 shows gross morphology of the cephalon. The cheeks (genae) are the pleural lobes on each side of the axial feature, the glabella. When trilobites molt or die, the librigenae (the so-called "free cheeks") often separate, leaving the cranidium (glabella + fixigenae). Figure 2 shows a more detailed view of the cephalon.
 |
 |
Extinction

The exact reason for the extinction of the trilobites is not clear, although it would seem to be no coincidence that their numbers began to decrease with the arrival of the first sharks and other early fishes in the Silurian and Devonian periods. Trilobites may have provided a rich source of food for these new arrivals. Additionally, their relatively low numbers and diversity at the end of the Permian no doubt contributed to their extinction during that great mass extinction event. Foreshadowing this, the Ordovician mass extinction, though far less substantial than the Permian one, also seems to have significantly narrowed the extant trilobite diversity.
Fossil distribution

Trilobites appear to have been exclusively marine organisms since the fossilized remains of trilobites are always found in rock containing fossils of other salt-water animals such as brachiopods, crinoids, and coral, and they are found in a range of environments from extremely shallow water to very deep water. The tracks left behind by trilobites crawling on the sea floor are occasionally preserved as trace fossils.

Trilobite fossils are found worldwide, with many thousands of known species. Because they evolved rapidly, trilobites serve as excellent index fossils, enabling geologists to date the age of the rocks in which they are found. They were among the first fossils to attract widespread attention, and new species are being discovered every year. Some Native Americans, recognizing that trilobites were water creatures, had a name for them which means "little water bug in the rocks".
A famous location for trilobite fossils in the United Kingdom is Wren's Nest, Dudley in the West Midlands, where Calymene blumenbachi is found in the Silurian Wenlock Limestone formation. This trilobite is featured on the town's coat of arms and was named the "Dudley locust" or "Dudley bug" by quarrymen who once worked many of the now abandoned limestone quarries. Other trilobites found there include Dalmanites, Trimerus and Bumastus.
Spectacular trilobite fossils, showing soft body parts like legs, gills and antennae, have been found in British Columbia (Burgess Shale Cambrian fossils, and similar localities in the Canadian Rockies); New York State (Odovician Walcott-Rust Quarry, near Utica, N.Y., and the Beecher Trilobite Beds, near Rome, N.Y.), in China (Burgess Shale-like Cambrian trilobites at Chengjiang), Germany (the Devonian Hunsruck Shale at Bundenbach, Germany) and, much more rarely, in trilobite-bearing strata in Utah and Ontario.
Trilobites are collected commercially in Russia (especially in the St. Petersburg area), Germany, Morocco's Atlas Mountains, (where a burgeoning trade in faked trilobites is also under way), Utah, Ohio, British Columbia, and in other parts of Canada.
References
- Trilobite! - Richard Fortey (ISBN 0002570122)
- Riccardo Levi-Setti. Trilobites. University of Chicago Press, 1993.
- A Guide to the Orders of Trilobite by Sam Gon III - an excellent, well-researched site with information covering trilobites from all angles. Includes many line drawings and photographs.
- Earliest combatants in sexual contests revealed from "New Scientist" magazine.
- The Trilobite papers
- Trilo-Eye
