Tamponade: Difference between revisions
iwiki |
Added webster dictionary definition to beginning paragraph and rearranged sentences. |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
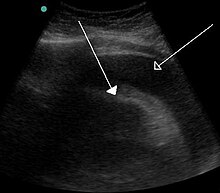
[[Image:Hemorragic effusion.jpg|thumb|A very large hemorrhagic pericardial effusion due to malignancy as seen on ultrasound which was causing tamponade. closed arrow: the heart, open arrow: the effusion]] |
[[Image:Hemorragic effusion.jpg|thumb|A very large hemorrhagic pericardial effusion due to malignancy as seen on ultrasound which was causing tamponade. closed arrow: the heart, open arrow: the effusion]] |
||
'''Tamponade''' is the closure or blockage (as of a wound or body cavity) as if by a tampon especially to stop bleeding.<ref name=Merriam-webster.com>{{cite web|title=Tamponade - Definition|url=http://www.merriam-webster.com/medical/tamponade|accessdate=6.1.2011}}</ref> |
|||
'''Tamponade''' is a condition of [[blood]] flow stoppage into a [[blood vessel]] by a constriction of the vessel by an outside force. |
|||
Tamponade is a useful method of stopping a [[hemorrhage]]. This can be achieved by applying an absorbent dressing directly onto a wound, thereby absorbing excess blood and creating a blockage, or by applying direct pressure with a hand or a [[tourniquet]]. |
Tamponade is a useful method of stopping a [[hemorrhage]]. This can be achieved by applying an absorbent dressing directly onto a wound, thereby absorbing excess blood and creating a blockage, or by applying direct pressure with a hand or a [[tourniquet]]. |
||
There can, however, be disastrous consequences when tamponade occurs as a result of health problems, as in the case of [[cardiac tamponade]]. In this situation, fluid collects between the heart muscle and the [[pericardium]]. The pressure within the pericardium prevents the heart from expanding fully and filling the [[ventricle (heart)|ventricles]], with the result that a significantly reduced amount of blood circulates within the body. If left unchecked, this condition will result in [[death]]. |
There can, however, be disastrous consequences when tamponade occurs as a result of health problems, as in the case of [[cardiac tamponade]]. In this situation, fluid collects between the heart muscle and the [[pericardium]]. The pressure within the pericardium prevents the heart from expanding fully and filling the [[ventricle (heart)|ventricles]], with the result that a significantly reduced amount of blood circulates within the body. If left unchecked, this condition will result in [[death]]. |
||
==References== |
|||
{{reflist}} |
|||
[[Category:Medical terms|Tamponade]] |
[[Category:Medical terms|Tamponade]] |
||
Revision as of 19:50, 1 June 2011
Tamponade is the closure or blockage (as of a wound or body cavity) as if by a tampon especially to stop bleeding.[1] Tamponade is a useful method of stopping a hemorrhage. This can be achieved by applying an absorbent dressing directly onto a wound, thereby absorbing excess blood and creating a blockage, or by applying direct pressure with a hand or a tourniquet.
There can, however, be disastrous consequences when tamponade occurs as a result of health problems, as in the case of cardiac tamponade. In this situation, fluid collects between the heart muscle and the pericardium. The pressure within the pericardium prevents the heart from expanding fully and filling the ventricles, with the result that a significantly reduced amount of blood circulates within the body. If left unchecked, this condition will result in death.
References
- ^ "Tamponade - Definition". Retrieved 6.1.2011.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help)
