Ekiga: Difference between revisions
m Robot - Speedily moving category On-line chat to Category:Online chat per CFDS. |
|||
| Line 55: | Line 55: | ||
* April 2007 – Version 2.0.9 was the first version to include support for [[Microsoft Windows]] |
* April 2007 – Version 2.0.9 was the first version to include support for [[Microsoft Windows]] |
||
* September 2008 – Version 3.0.0 |
* September 2008 – Version 3.0.0 |
||
* March 2009 - First release of the 3.2.x series. Added support for G.722 audio as well as unified the support for H.263 and H.263. |
|||
* May 2011 - First release of the 3.3.x series, currently categorized as "unstable". |
|||
== See also == |
== See also == |
||
Revision as of 18:22, 24 March 2012
 | |
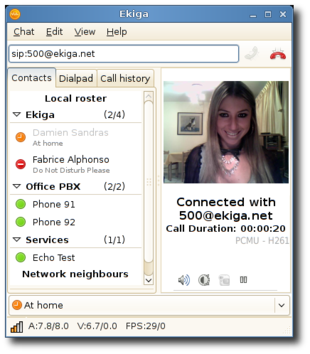 Ekiga 3.0.0 | |
| Developer(s) | Damien Sandras |
|---|---|
| Preview release | n/a (n/a) [±] |
| Repository | |
| Written in | C/C++, but the GUI is written in C[1] |
| Platform | Unix-like, Windows |
| Type | VoIP Video conferencing |
| License | GNU General Public License |
| Website | www.ekiga.org |
Ekiga /i k ai g a/ (formerly called GnomeMeeting) is a VoIP and video conferencing application for GNOME and Windows. It is distributed as free software under the terms of the GNU General Public License. It was the default VoIP client in Ubuntu until October 2009, when it was replaced by Empathy.[2] Ekiga supports both the SIP and H.323 (based on OPAL) protocols and is fully interoperable with any other SIP compliant application and with Microsoft NetMeeting. It supports many high-quality audio and video codecs.[3]
Ekiga was initially written by Damien Sandras in order to graduate from the Université catholique de Louvain. It is currently developed by a community-based team led by Sandras. The logo was designed based on his concept by Andreas Kwiatkowski.[4]
Ekiga.net also serves as a free and private SIP registrar, which enables its members to originate and terminate (receive) calls from and to each other directly over the Internet.
Features
Features of Ekiga include:[5]
Integration
Ekiga is integrated with a number of different software packages and protocols such as LDAP directories registration and browsing along with support for Novell Evolution so that contacts are shared between both programs and ZeroConf (Apple Bonjour) support. It auto-detects devices including USB, ALSA and legacy OSS soundcards, Video4linux and FireWire camera.
User interface
Ekiga sports a Contact list based interface along with Presence support with custom messages. It allows for the monitoring of contacts and viewing call history along with an addressbook, dialpad, and chat window. SIP URLs and H.323/callto support is built-in along with full-screen videoconferencing (accelerated using a graphics card).
Technical features
- Call forwarding on busy, no answer, always (SIP and H.323)
- Call transfer (SIP and H.323)
- Call hold (SIP and H.323)
- DTMF support (SIP and H.323)
- Basic instant messaging (SIP)
- Text chat (SIP and H.323)
- Register with several registrars (SIP) and gatekeepers (H.323) simultaneously
- Ability to use an outbound proxy (SIP) or a gateway (H.323)
- Message waiting indications (SIP)
- Audio and video (SIP and H.323)
- STUN support (SIP and H.323)
- LDAP support
- Audio codec algorithms: iLBC, GSM 06.10, MS-GSM, G.711 A-law, G.711 µ-law, G.726, G.721, Speex, G.722, CELT (also G.723.1, G.728, G.729, GSM 06.10, GSM-AMR, G.722.2 [GSM‑AMR-WB] using Intel IPP)[6]
- Video codec algorithms: H.261, H.263+, H.264, Theora, MPEG-4[7]
History
Ekiga was originally started over Christmas in the year 2000.[8] Originally written by Damien Sandras it grew to being maintained by a team of nine regular contributors by 2011.[9] Sandras wanted to create a Netmeeting clone for Linux as his graduating project at the Université Catholique de Louvain.[4]
It was referred to as GnomeMeeting until 2004 when a name change was thought necessary by the developers.[10] Concerns were cited that the original name was associated with a dead project called NetMeeting, as well as the fact that the program was not always recoginized as VoIP software. Also it was proposed that some people assume they needed to run GNOME to run GnomeMeeting, which was no longer the case. In order to distance itself from all of these problems, thought was given to a name change. Eventually on January 18, 2006 the name Ekiga was chosen based on an old way of communicating between villages in Cameroon.[11] Since then the name has remained the same. The name change also was significant because around that the time the direction of the software project was changed and it turned into a SIP client.[4]
The following shows major version releases:
- March 2004 – Version 1.0 under the name GnomeMeeting
- March 2006 – Version 2.0 was released under name Ekiga, it was bundled with GNOME 2.14
- April 2007 – Version 2.0.9 was the first version to include support for Microsoft Windows
- September 2008 – Version 3.0.0
- March 2009 - First release of the 3.2.x series. Added support for G.722 audio as well as unified the support for H.263 and H.263.
- May 2011 - First release of the 3.3.x series, currently categorized as "unstable".
See also
References
- ^ "Inside GnomeMeeting". O'Reily Linux devcentre.com. 2005-03-17.
- ^ "Ekiga". Ubuntu Documentation. 2008-10-23. Retrieved 2009-04-13.
- ^ "About Ekiga". Ekiga Wiki. 23 February 2007. Retrieved 2009-04-13.
- ^ a b c "Ekiga". Josetteorama. 25 October 2011. Retrieved 2011-12-25.
- ^ "Features". Ekiga Wiki. 27 September 2008. Retrieved 2009-04-13.
- ^ "OPAL Plug-In for Intel Integrated Performance Primitives". Vox Lucida. Retrieved 2009-04-13.
- ^ Ekiga Current Features, Retrieved on 2009-07-09
- ^ "Video-Conferencing". NotesBIT. 24 March 2009. Retrieved 2011-12-25.
- ^ "Community". Ekiga. Retrieved 2011-12-25.
- ^ "1.2 Roadmap - Name Change". GnomeMeeting-list. 23 May 2004. Retrieved 2011-12-25.
- ^ "5 years of Open Source Voice over IP". Damien Sandras. 03 July 2006. Retrieved 2011-12-25.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help)
