Glyceollin I: Difference between revisions
Appearance
Content deleted Content added
m r2.7.1) (Robot: Adding fa:گلیسئولین I |
use consistent citation format, add pmid, pmc, etc. |
||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
| Autoignition = }} |
| Autoignition = }} |
||
}} |
}} |
||
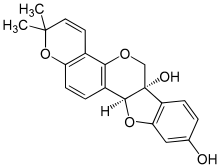
'''Glyceollin I''' is a [[glyceollin]], a type of [[prenylated]] [[pterocarpan]]. It is a [[phytoalexin]] found in the [[soybean]].<ref> |
'''Glyceollin I''' is a [[glyceollin]], a type of [[prenylated]] [[pterocarpan]]. It is a [[phytoalexin]] found in the [[soybean]].<ref>{{Cite doi|10.1124/jpet.109.160382|noedit}}</ref> |
||
[[Glyceollin synthase]] is an enzyme responsible for the production of glyceollin.<ref>{{cite |
[[Glyceollin synthase]] is an enzyme responsible for the production of glyceollin.<ref>{{cite doi|10.1016/0003-9861(88)90627-3 |noedit}}</ref> The five substrates of this enzyme are [[2-dimethylallyl-(6aS,11aS)-3,6a,9-trihydroxypterocarpan]], [[4-dimethylallyl-(6aS,11aS)-3,6a,9-trihydroxypterocarpan]], [[nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate|NADPH]], [[hydrogen ion|H<sup>+</sup>]], and [[oxygen|O<sub>2</sub>]], whereas its three products are glyceollin, [[nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate|NADP<sup>+</sup>]], and [[water|H<sub>2</sub>O]]. |
||
This molecule exhibits [[antiestrogenic]] properties.<ref>{{Cite doi|10.1016/j.steroids.2010.05.007|noedit }}</ref> |
|||
This molecule exhibits [[antiestrogenic]] properties.<ref>Glyceollin I enantiomers distinctly regulate ER-mediated gene expression. Florastina Payton-Stewart, Rahul S. Khupse, Stephen M. Boué, Steven Elliott, M. Carla Zimmermann, Elena V. Skripnikova, Hasina Ashe, Syreeta L. Tilghman, Barbara S. Beckman, Thomas E. Cleveland, John A. McLachlan, Deepak Bhatnagar, Thomas E. Wiese, Paul Erhardt and Matthew E. Burow, Steroids, Volume 75, Issue 12, December 2010, Pages 870-878, {{doi|10.1016/j.steroids.2010.05.007}}, {{PMID|20493896}}</ref> |
|||
== References == |
== References == |
||
{{ |
{{Reflist}} |
||
<!-- ==External links== --> |
<!-- ==External links== --> |
||
Revision as of 16:07, 2 June 2012
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC names
(6aS,11aS)-2,2-dimethyl-2H,6H-[1]benzofuro[3,2‑c]pyrano[2,3‑h]
chromene-6a,9(11aH)-diol | |
| Other names
(−)-Glyceollin I
| |
| Identifiers | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.222.666 |
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| Properties | |
| C20H18O5 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Glyceollin I is a glyceollin, a type of prenylated pterocarpan. It is a phytoalexin found in the soybean.[1]
Glyceollin synthase is an enzyme responsible for the production of glyceollin.[2] The five substrates of this enzyme are 2-dimethylallyl-(6aS,11aS)-3,6a,9-trihydroxypterocarpan, 4-dimethylallyl-(6aS,11aS)-3,6a,9-trihydroxypterocarpan, NADPH, H+, and O2, whereas its three products are glyceollin, NADP+, and H2O.
This molecule exhibits antiestrogenic properties.[3]
References
- ^ Attention: This template ({{cite doi}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by doi:10.1124/jpet.109.160382, please use {{cite journal}} (if it was published in a bona fide academic journal, otherwise {{cite report}} with
|doi=10.1124/jpet.109.160382instead. - ^ Attention: This template ({{cite doi}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by doi:10.1016/0003-9861(88)90627-3 , please use {{cite journal}} (if it was published in a bona fide academic journal, otherwise {{cite report}} with
|doi=10.1016/0003-9861(88)90627-3instead. - ^ Attention: This template ({{cite doi}}) is deprecated. To cite the publication identified by doi:10.1016/j.steroids.2010.05.007, please use {{cite journal}} (if it was published in a bona fide academic journal, otherwise {{cite report}} with
|doi=10.1016/j.steroids.2010.05.007instead.
