Peptide: Difference between revisions
→Notes on terminology: grouped |
|||
| Line 78: | Line 78: | ||
==Notes on terminology== |
==Notes on terminology== |
||
Length: |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
*A ''polypeptide'' is a single linear chain of amino acids. |
*A ''polypeptide'' is a single linear chain of amino acids. |
||
*A ''[[protein]]'' is one or more polypeptides more than about 50 amino acids long. |
*A ''[[protein]]'' is one or more polypeptides more than about 50 amino acids long. |
||
*An ''[[oligopeptide]]'' (or simply a ''peptide'') is a polypeptide less than 30-50 amino acids long. |
*An ''[[oligopeptide]]'' (or simply a ''peptide'') is a polypeptide less than 30-50 amino acids long. |
||
Number of amino acids: |
|||
*A ''monopeptide'' has one amino acid. |
*A ''monopeptide'' has one amino acid. |
||
*A ''[[dipeptide]]'' has two amino acids. |
*A ''[[dipeptide]]'' has two amino acids. |
||
| Line 94: | Line 96: | ||
*An ''undecapeptide'' (or ''monodecapeptide'') has eleven amino acids, a ''dodecapeptide'' (or ''didecapeptide'') has twelve amino acids, a ''tridecapeptide'' has thirteen amino acids, and so forth. |
*An ''undecapeptide'' (or ''monodecapeptide'') has eleven amino acids, a ''dodecapeptide'' (or ''didecapeptide'') has twelve amino acids, a ''tridecapeptide'' has thirteen amino acids, and so forth. |
||
*An ''icosapeptide'' has twenty amino acids, a ''tricontapeptide'' has thirty amino acids, a ''tetracontapeptide'' has forty amino acids, and so forth. |
*An ''icosapeptide'' has twenty amino acids, a ''tricontapeptide'' has thirty amino acids, a ''tetracontapeptide'' has forty amino acids, and so forth. |
||
| ⚫ | |||
Function: |
|||
*A ''[[neuropeptide]]'' is a peptide that is active in association with neural tissue. |
*A ''[[neuropeptide]]'' is a peptide that is active in association with neural tissue. |
||
*A ''[[lipopeptide]]'' is a peptide that has a [[lipid]] connected to it, and ''[[pepducin]]s'' are lipopeptides that interact with GPCRs. |
*A ''[[lipopeptide]]'' is a peptide that has a [[lipid]] connected to it, and ''[[pepducin]]s'' are lipopeptides that interact with GPCRs. |
||
Revision as of 04:02, 19 July 2012

green marked amino end (L-Valine) and
blue marked carboxyl end (L-Alanine).


Peptides (from the Greek πεπτός, "digested" from πέσσειν "to digest") are short polymers of amino acid monomers linked by peptide bonds. They are distinguished from proteins on the basis of size, typically containing fewer than 50 monomer units. The shortest peptides are dipeptides, consisting of two amino acids joined by a single peptide bond. There are also tripeptides, tetrapeptides, etc.
Amino acids which have been incorporated into a peptide are termed "residues"; every peptide has a N-terminus and C-terminus residue on the ends of the peptide (except for cyclic peptides). A polypeptide is a long, continuous, and unbranched peptide. Proteins consist of one or more polypeptides arranged in a biologically functional way and are often bound to cofactors, or other proteins.
The size boundaries which distinguish peptides, polypeptides, and proteins are arbitrary. Long peptides such as amyloid beta can be considered proteins, whereas small proteins such as insulin can be considered peptides.
Peptide classes
Peptides are divided into several classes, depending on how they are produced:
- Milk peptides
- Milk peptides are formed from milk proteins by enzymatic breakdown by digestive enzymes or by the proteinases formed by lactobacilli during the fermentation of milk. Several milk peptides have been shown to have antihypertensive effects in animal and in clinical studies (see also Lactotripeptides).
- Ribosomal peptides
- Ribosomal peptides are synthesized by translation of mRNA. They are often subjected to proteolysis to generate the mature form. These function, typically in higher organisms, as hormones and signaling molecules. Some organisms produce peptides as antibiotics, such as microcins.[1] Since they are translated, the amino acid residues involved are restricted to those utilized by the ribosome. However, these peptides frequently have posttranslational modifications, such as phosphorylation, hydroxylation, sulfonation, palmitylation, glycosylation and disulfide formation. In general, they are linear, although lariat structures have been observed.[2] More exotic manipulations do occur, such as racemization of L-amino acids to D-amino acids in platypus venom.[3]
- Nonribosomal peptides
- These peptides are assembled by enzymes that are specific to each peptide, rather than by the ribosome. The most common non-ribosomal peptide is glutathione, which is a component of the antioxidant defenses of most aerobic organisms.[4] Other nonribosomal peptides are most common in unicellular organisms, plants, and fungi and are synthesized by modular enzyme complexes called nonribosomal peptide synthetases.[5] These complexes are often laid out in a similar fashion, and they can contain many different modules to perform a diverse set of chemical manipulations on the developing product.[6] These peptides are often cyclic and can have highly-complex cyclic structures, although linear nonribosomal peptides are also common. Since the system is closely related to the machinery for building fatty acids and polyketides, hybrid compounds are often found. The presence of oxazoles or thiazoles often indicates that the compound was synthesized in this fashion.[7]
- Peptones
-
- See also Tryptone
- Peptones are derived from animal milk or meat digested by proteolytic digestion. In addition to containing small peptides, the resulting spray-dried material includes fats, metals, salts, vitamins and many other biological compounds. Peptone is used in nutrient media for growing bacteria and fungi.[8]
- Peptide fragments
- Peptide fragments refer to fragments of proteins that are used to identify or quantify the source protein.[9] Often these are the products of enzymatic degradation performed in the laboratory on a controlled sample, but can also be forensic or paleontological samples that have been degraded by natural effects.[10][11]
A combination of peptides and alpha hydroxy acid can help as a cream,which can be used for night cream.
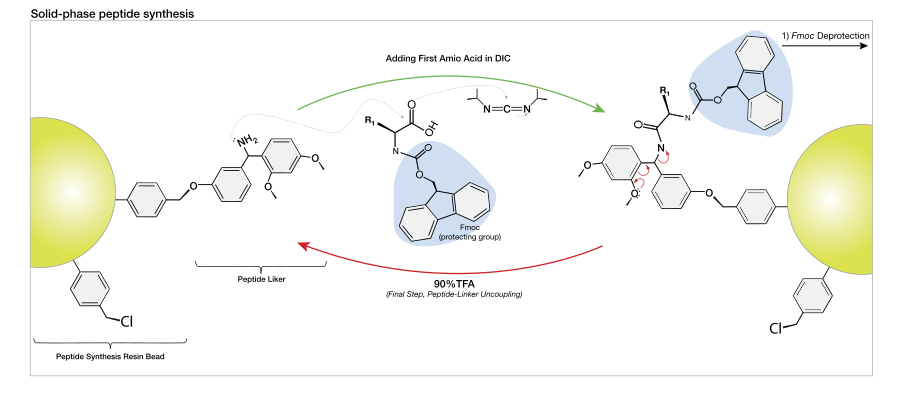
Peptide synthesis
Peptides in molecular biology
Peptides have recently received prominence in molecular biology for several reasons. The first is that peptides allow the creation of peptide antibodies in animals without the need to purify the protein of interest.[12] This involves synthesizing antigenic peptides of sections of the protein of interest. These will then be used to make antibodies in a rabbit or mouse against the protein.
Another reason is that peptides have become instrumental in mass spectrometry, allowing the identification of proteins of interest based on peptide masses and sequence. In this case the peptides are most often generated by in-gel digestion after electrophoretic separation of the proteins.
Peptides have recently been used in the study of protein structure and function. For example, synthetic peptides can be used as probes to see where protein-peptide interactions occur- see the page on Protein tags.
Inhibitory peptides are also used in clinical research to examine the effects of peptides on the inhibition of cancer proteins and other diseases.
Well-known peptide families in humans
The peptide families in this section are ribosomal peptides, usually with hormonal activity. All of these peptides are synthesized by cells as longer "propeptides" or "proproteins" and truncated prior to exiting the cell. They are released into the bloodstream where they perform their signalling functions.
Tachykinin peptides
Vasoactive intestinal peptides
- VIP (Vasoactive Intestinal Peptide; PHM27)
- PACAP Pituitary Adenylate Cyclase Activating Peptide
- Peptide PHI 27 (Peptide Histidine Isoleucine 27)
- GHRH 1-24 (Growth Hormone Releasing Hormone 1-24)
- Glucagon
- Secretin
Pancreatic polypeptide-related peptides
Opioid peptides
- Proopiomelanocortin (POMC) peptides
- Enkephalin pentapeptides
- Prodynorphin peptides
Calcitonin peptides
Other peptides
- B-type Natriuretic Peptide (BNP) - produced in myocardium & useful in medical diagnosis
- Lactotripeptides - Lactotripeptides might reduce blood pressure,[13][14][15] although the evidence is mixed.[16]
Notes on terminology
Length:
- A polypeptide is a single linear chain of amino acids.
- A protein is one or more polypeptides more than about 50 amino acids long.
- An oligopeptide (or simply a peptide) is a polypeptide less than 30-50 amino acids long.
Number of amino acids:
- A monopeptide has one amino acid.
- A dipeptide has two amino acids.
- A tripeptide has three amino acids.
- A tetrapeptide has four amino acids.
- A pentapeptide has five amino acids.
- A hexapeptide has six amino acids.
- A heptapentide has seven amino acids.
- An octapeptide has eight amino acids (e.g., angiotensin II).
- A nonapeptide has nine amino acids (e.g., oxytocin).
- A decapeptide has ten amino acids (e.g., gonadotropin-releasing hormone & angiotensin I).
- An undecapeptide (or monodecapeptide) has eleven amino acids, a dodecapeptide (or didecapeptide) has twelve amino acids, a tridecapeptide has thirteen amino acids, and so forth.
- An icosapeptide has twenty amino acids, a tricontapeptide has thirty amino acids, a tetracontapeptide has forty amino acids, and so forth.
Function:
- A neuropeptide is a peptide that is active in association with neural tissue.
- A lipopeptide is a peptide that has a lipid connected to it, and pepducins are lipopeptides that interact with GPCRs.
- A peptide hormone is a peptide that acts as a hormone.
- A proteose is a mixture of peptides produced by the hydrolysis of proteins. The term is somewhat archaic.
See also
- Antineoplaston
- Argireline
- Beefy meaty peptide
- Bis-peptide
- Epidermal Growth Factor
- Journal of Peptide Science
- Lactotripeptides
- Pancreatic hormone
- Peptide Spectral Library
- Peptide synthesis
- Peptidomimetics (such as peptoids and β-peptides) to peptides, but with different properties.
- Ribosome
- Translation
References
- ^ Duquesne S, Destoumieux-Garzón D, Peduzzi J, Rebuffat S (2007). "Microcins, gene-encoded antibacterial peptides from enterobacteria". Natural Product Reports. 24 (4): 708–34. doi:10.1039/b516237h. PMID 17653356.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Pons M, Feliz M, Antònia Molins M, Giralt E (1991). "Conformational analysis of bacitracin A, a naturally occurring lariat". Biopolymers. 31 (6): 605–12. doi:10.1002/bip.360310604. PMID 1932561.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Torres AM, Menz I, Alewood PF; et al. (2002). "D-Amino acid residue in the C-type natriuretic peptide from the venom of the mammal, Ornithorhynchus anatinus, the Australian platypus". FEBS Letters. 524 (1–3): 172–6. doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(02)03050-8. PMID 12135762.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Meister A, Anderson ME (1983). "Glutathione". Annual Review of Biochemistry. 52 (1): 711–60. doi:10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.003431. PMID 6137189.
- ^ Hahn M, Stachelhaus T (2004). "Selective interaction between nonribosomal peptide synthetases is facilitated by short communication-mediating domains". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 101 (44): 15585–90. doi:10.1073/pnas.0404932101. PMC 524835. PMID 15498872.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ Finking R, Marahiel MA (2004). "Biosynthesis of nonribosomal peptides1". Annual Review of Microbiology. 58 (1): 453–88. doi:10.1146/annurev.micro.58.030603.123615. PMID 15487945.
- ^ Du L, Shen B (2001). "Biosynthesis of hybrid peptide-polyketide natural products". Current Opinion in Drug Discovery & Development. 4 (2): 215–28. PMID 11378961.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ Payne JW (1976). "Peptides and micro-organisms". Advances in Microbial Physiology. 13: 55–113. doi:10.1016/S0065-2911(08)60038-7. PMID 775944.
- ^ Hummel J, Niemann M, Wienkoop S; et al. (2007). "ProMEX: a mass spectral reference database for proteins and protein phosphorylation sites". BMC Bioinformatics. 8: 216. doi:10.1186/1471-2105-8-216. PMC 1920535. PMID 17587460.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Webster J, Oxley D (2005). "Peptide mass fingerprinting: protein identification using MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry". Methods in Molecular Biology. 310: 227–40. doi:10.1007/978-1-59259-948-6_16. PMID 16350956.
- ^ Marquet P, Lachâtre G (1999). "Liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry: potential in forensic and clinical toxicology". Journal of Chromatography B. 733 (1–2): 93–118. doi:10.1016/S0378-4347(99)00147-4. PMID 10572976.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ Bulinski JC (1986). "Peptide antibodies: new tools for cell biology". International Review of Cytology. 103: 281–302. doi:10.1016/S0074-7696(08)60838-4. PMID 2427468.
- ^ Boelsma E, Kloek J (2009). "Lactotripeptides and antihypertensive effects: a critical review". The British Journal of Nutrition. 101 (6): 776–86. doi:10.1017/S0007114508137722. PMID 19061526.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ Xu JY, Qin LQ, Wang PY, Li W, Chang C (2008). "Effect of milk tripeptides on blood pressure: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials". Nutrition. 24 (10): 933–40. doi:10.1016/j.nut.2008.04.004. PMID 18562172.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Pripp AH (2008). "Effect of peptides derived from food proteins on blood pressure: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials". Food & Nutrition Research. 52 (0). doi:10.3402/fnr.v52i0.1641. PMC 2596738. PMID 19109662.
- ^ Engberink MF, Schouten EG, Kok FJ, van Mierlo LA, Brouwer IA, Geleijnse JM (2008). "Lactotripeptides show no effect on human blood pressure: results from a double-blind randomized controlled trial". Hypertension. 51 (2): 399–405. doi:10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.107.098988. PMID 18086944.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
