5-Fluoro-DMT: Difference between revisions
Appearance
Content deleted Content added
m Journal cites (journal names):, using AWB (8068) |
m corrected journal title to medicinal |
||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
}} |
}} |
||
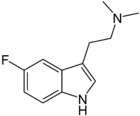
'''5-Fluoro-''N'',''N''-dimethyltryptamine''' ('''5-fluoro-DMT''') is a [[tryptamine]] derivative related to compounds such as [[5-bromo-DMT]] and [[5-MeO-DMT]]. Fluorination of hallucinogenic tryptamines either reduces or has little effect on 5-HT<sub>2A/C</sub> receptor affinity or intrinsic activity, although 6-fluoro-DET is inactive as a hallucinogen despite acting as a 5-HT<sub>2A</sub> agonist (cf. [[lisuride]]), while [[4-fluoro-5-methoxy-DMT]] is a much stronger agonist at 5-HT<sub>1A</sub> than 5-HT<sub>2A</sub>.<ref>{{cite journal | last1 = Blair | first1 = JB | last2 = Kurrasch-Orbaugh | first2 = D | last3 = Marona-Lewicka | first3 = D | last4 = Cumbay | first4 = MG | last5 = Watts | first5 = VJ | last6 = Barker | first6 = EL | last7 = Nichols | first7 = DE | title = Effect of ring fluorination on the pharmacology of hallucinogenic tryptamines | journal = Journal of |
'''5-Fluoro-''N'',''N''-dimethyltryptamine''' ('''5-fluoro-DMT''') is a [[tryptamine]] derivative related to compounds such as [[5-bromo-DMT]] and [[5-MeO-DMT]]. Fluorination of hallucinogenic tryptamines either reduces or has little effect on 5-HT<sub>2A/C</sub> receptor affinity or intrinsic activity, although 6-fluoro-DET is inactive as a hallucinogen despite acting as a 5-HT<sub>2A</sub> agonist (cf. [[lisuride]]), while [[4-fluoro-5-methoxy-DMT]] is a much stronger agonist at 5-HT<sub>1A</sub> than 5-HT<sub>2A</sub>.<ref>{{cite journal | last1 = Blair | first1 = JB | last2 = Kurrasch-Orbaugh | first2 = D | last3 = Marona-Lewicka | first3 = D | last4 = Cumbay | first4 = MG | last5 = Watts | first5 = VJ | last6 = Barker | first6 = EL | last7 = Nichols | first7 = DE | title = Effect of ring fluorination on the pharmacology of hallucinogenic tryptamines | journal = Journal of Medicinal Chemistry | volume = 43 | issue = 24 | pages = 4701–10 | year = 2000 | pmid = 11101361 | doi=10.1021/jm000339w}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | last1 = Rabin | first1 = RA | last2 = Regina | first2 = M | last3 = Doat | first3 = M | last4 = Winter | first4 = JC | title = 5-HT2A receptor-stimulated phosphoinositide hydrolysis in the stimulus effects of hallucinogens | journal = Pharmacology, Biochemistry, and Behavior | volume = 72 | issue = 1–2 | pages = 29–37 | year = 2002 | pmid = 11900766 | doi=10.1016/S0091-3057(01)00720-1}}</ref> |
||
==See also== |
==See also== |
||
Revision as of 01:21, 1 August 2012
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C12H15FN2 |
| Molar mass | 206.259 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
5-Fluoro-N,N-dimethyltryptamine (5-fluoro-DMT) is a tryptamine derivative related to compounds such as 5-bromo-DMT and 5-MeO-DMT. Fluorination of hallucinogenic tryptamines either reduces or has little effect on 5-HT2A/C receptor affinity or intrinsic activity, although 6-fluoro-DET is inactive as a hallucinogen despite acting as a 5-HT2A agonist (cf. lisuride), while 4-fluoro-5-methoxy-DMT is a much stronger agonist at 5-HT1A than 5-HT2A.[1][2]
See also
References
- ^ Blair, JB; Kurrasch-Orbaugh, D; Marona-Lewicka, D; Cumbay, MG; Watts, VJ; Barker, EL; Nichols, DE (2000). "Effect of ring fluorination on the pharmacology of hallucinogenic tryptamines". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 43 (24): 4701–10. doi:10.1021/jm000339w. PMID 11101361.
- ^ Rabin, RA; Regina, M; Doat, M; Winter, JC (2002). "5-HT2A receptor-stimulated phosphoinositide hydrolysis in the stimulus effects of hallucinogens". Pharmacology, Biochemistry, and Behavior. 72 (1–2): 29–37. doi:10.1016/S0091-3057(01)00720-1. PMID 11900766.
