Anti-mitochondrial antibody: Difference between revisions
ce |
Simoncaulton (talk | contribs) m Correction |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
'''Anti-mitochondrial antibodies''' (AMA) are [[autoantibodies]], consisting of [[immunoglobulins]] formed against [[mitochondria]],<ref>{{MedlinePlus|003529}}</ref> primarily mitochondria in [[cell (biology)|cells]] of the [[liver]]. The presence of AMAs in the [[blood]] or [[blood plasma|serum]] of a person is indicative of several [[autoimmune disease]]s such as [[primary biliary cirrhosis]] (PBC) (a scarring of liver tissue, confined primarily to the bile duct drainage system of the liver). It is present in about 95% of cases.<ref>{{cite journal |author=Oertelt S, Rieger R, Selmi C, Invernizzi P, Ansari A, Coppel R, Podda M, Leung P, Gershwin |
'''Anti-mitochondrial antibodies''' (AMA) are [[autoantibodies]], consisting of [[immunoglobulins]] formed against [[mitochondria]],<ref>{{MedlinePlus|003529}}</ref> primarily mitochondria in [[cell (biology)|cells]] of the [[liver]]. The presence of AMAs in the [[blood]] or [[blood plasma|serum]] of a person is indicative of several [[autoimmune disease]]s such as [[primary biliary cirrhosis]] (PBC) (a scarring of liver tissue, confined primarily to the bile duct drainage system of the liver). It is present in about 95% of cases.<ref>{{cite journal |author=Oertelt S, Rieger R, Selmi C, Invernizzi P, Ansari A, Coppel R, Podda M, Leung P, Gershwin M |title=A sensitive bead assay for antimitochondrial antibodies: Chipping away at AMA-negative primary biliary cirrhosis |journal=Hepatology |volume=45 |issue=3 |pages=659–65 |year=2007 |pmid=17326160 |doi=10.1002/hep.21583}}</ref> |
||
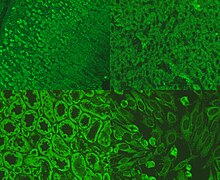
[[File:AMA ANTIBODIES.jpg|thumb|alt=Picture of immunofluorescence staining pattern of AMA antibodies.|Immunofluorescence staining pattern of AMA |
[[File:AMA ANTIBODIES.jpg|thumb|alt=Picture of immunofluorescence staining pattern of AMA antibodies.|Immunofluorescence staining pattern of AMA shown on stomach (top left), liver (top right), kidney (bottom left) and hep-20-10 cells (bottom right).]] |
||
Primary biliary cirrhosis is seen primarily in middle-aged women, and in those afflicted with other autoimmune diseases. PBC is an [[autoimmune disorder]], a condition in which the human body's immune defense system mistakenly attacks the body's own cells, or in this case parts of the cells. |
Primary biliary cirrhosis is seen primarily in middle-aged women, and in those afflicted with other autoimmune diseases. PBC is an [[autoimmune disorder]], a condition in which the human body's immune defense system mistakenly attacks the body's own cells, or in this case parts of the cells. |
||
| Line 16: | Line 15: | ||
Fifty seven percent of acute liver failure patients had elevated [[anti-transglutaminase antibodies]] (anti-tTG), which correlate with gluten-sensitive |
Fifty seven percent of acute liver failure patients had elevated [[anti-transglutaminase antibodies]] (anti-tTG), which correlate with gluten-sensitive |
||
enteropathy (see [[coeliac disease]], [[Gluten-sensitive enteropathy associated conditions#Diseases of the pancreas.2C gall bladder.2C bile duct|gluten-sensitive enteropathy associated conditions]]).<ref name="pmid17657817"/> |
enteropathy (see [[coeliac disease]], [[Gluten-sensitive enteropathy associated conditions#Diseases of the pancreas.2C gall bladder.2C bile duct|gluten-sensitive enteropathy associated conditions]]).<ref name="pmid17657817"/> |
||
The inflammation produced by gluten-sensitive cellular immunity may cause the oxidative stress resulting in the modification of mitochondrial |
The inflammation produced by gluten-sensitive cellular immunity may cause the oxidative stress resulting in the modification of mitochondrial antigens and acute liver failure. [[anti-glycoprotein-210 antibodies|Anti-gp210 antibodies]] are also found in 47% of PBC patients.<ref name="pmid7504063">{{cite journal | author = Nickowitz RE, Worman HJ | title = Autoantibodies from patients with primary biliary cirrhosis recognize a restricted region within the cytoplasmic tail of nuclear pore membrane glycoprotein Gp210 | journal = J. Exp. Med. | volume = 178 | issue = 6 | pages = 2237–42 | year = 1993 | pmid = 7504063 | doi = 10.1084/jem.178.6.2237| pmc = 2191303 }}</ref><ref name="pmid17621358">{{cite journal | author = Bauer A, Habior A | title = Measurement of gp210 autoantibodies in sera of patients with primary biliary cirrhosis | journal = J. Clin. Lab. Anal. | volume = 21 | issue = 4 | pages = 227–31 | year = 2007 | pmid = 17621358 | doi = 10.1002/jcla.20170}}</ref> |
||
== See also == |
== See also == |
||
Revision as of 20:30, 10 August 2012
Anti-mitochondrial antibodies (AMA) are autoantibodies, consisting of immunoglobulins formed against mitochondria,[1] primarily mitochondria in cells of the liver. The presence of AMAs in the blood or serum of a person is indicative of several autoimmune diseases such as primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC) (a scarring of liver tissue, confined primarily to the bile duct drainage system of the liver). It is present in about 95% of cases.[2]
Primary biliary cirrhosis is seen primarily in middle-aged women, and in those afflicted with other autoimmune diseases. PBC is an autoimmune disorder, a condition in which the human body's immune defense system mistakenly attacks the body's own cells, or in this case parts of the cells.
Cause of AMAs is postulated that xenobiotic-induced and/or oxidative modification of mitochondrial autoantigens is a critical step leading to loss of tolerance. In acute liver failure AMA are found against all major liver antigens.[3]
- Pyruvate dehydrogenase, E2 subunits
- 2-oxo-glutarate dehydrogenase
- Branched chain 2-oxo-acid dehydrogenase
Anti-cardiolipin antibodies are another type of AMA, cardiolipin is found on the inner mitochondrial membrane.
Correlation with non-mitochondrial antigens
Fifty seven percent of acute liver failure patients had elevated anti-transglutaminase antibodies (anti-tTG), which correlate with gluten-sensitive enteropathy (see coeliac disease, gluten-sensitive enteropathy associated conditions).[3] The inflammation produced by gluten-sensitive cellular immunity may cause the oxidative stress resulting in the modification of mitochondrial antigens and acute liver failure. Anti-gp210 antibodies are also found in 47% of PBC patients.[4][5]
See also
References
- ^ MedlinePlus Encyclopedia: 003529
- ^ Oertelt S, Rieger R, Selmi C, Invernizzi P, Ansari A, Coppel R, Podda M, Leung P, Gershwin M (2007). "A sensitive bead assay for antimitochondrial antibodies: Chipping away at AMA-negative primary biliary cirrhosis". Hepatology. 45 (3): 659–65. doi:10.1002/hep.21583. PMID 17326160.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b Leung PS, Rossaro L, Davis PA; et al. (2007). "Antimitochondrial antibodies in acute liver failure: Implications for primary biliary cirrhosis". Hepatology (Baltimore, Md.). 46 (5): 1436–42. doi:10.1002/hep.21828. PMID 17657817.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Nickowitz RE, Worman HJ (1993). "Autoantibodies from patients with primary biliary cirrhosis recognize a restricted region within the cytoplasmic tail of nuclear pore membrane glycoprotein Gp210". J. Exp. Med. 178 (6): 2237–42. doi:10.1084/jem.178.6.2237. PMC 2191303. PMID 7504063.
- ^ Bauer A, Habior A (2007). "Measurement of gp210 autoantibodies in sera of patients with primary biliary cirrhosis". J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 21 (4): 227–31. doi:10.1002/jcla.20170. PMID 17621358.
