Aruba: Difference between revisions
Vaquero100 (talk | contribs) clean up--Wikify--using AWB using AWB |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 36: | Line 36: | ||
<br /> - Total (2004 est.) |
<br /> - Total (2004 est.) |
||
<br /> - [[Population density|Density]] |
<br /> - [[Population density|Density]] |
||
| (Ranked |
| (Ranked 187th) |
||
<br /> 110 |
<br /> 110,000 (2005) |
||
<br /> 363/km² |
<br /> 363/km² |
||
|- |
|- |
||
Revision as of 18:55, 29 April 2006
| |||||
| National motto: One Happy Island | |||||
| |||||
| Official languages | Dutch, Papiamento | ||||
| Political status | State of the Kingdom of the Netherlands | ||||
| Capital | Oranjestad | ||||
| Queen | Beatrix | ||||
| Governor | Fredis Refunjol | ||||
| Prime Minister | Nelson O. Oduber | ||||
| Area - Total - % water |
(Not ranked) 180 km² Negligible | ||||
| Population
|
(Ranked 187th)
| ||||
| Currency | Aruban florin | ||||
| Time zone | UTC -4 | ||||
| National anthem | Aruba Dushi Tera | ||||
| Internet TLD | .aw | ||||
| Calling Code | +297 | ||||
Aruba is a 32 km long island in the Caribbean Sea, 27 km north of the Paraguaná Peninsula, Falcón State, Venezuela, and it forms a part of the Kingdom of the Netherlands. Unlike much of the Caribbean region, it has a dry climate and an arid, cactus-strewn landscape. This climate has helped tourism as visitors to the island can reliably expect warm, sunny weather.
History
- Main article: History of Aruba
Discovered and claimed for Spain in 1499, Aruba was conquered by the Dutch in 1636. The island's economy has been dominated by three main industries. A 19th-century gold rush was followed by prosperity brought on by the opening in 1924 of an oil refinery which supplied a large percentage of US oil during WWII. The last decades of the 20th century saw a boom in the tourism industry.
Aruba seceded from the Netherlands Antilles on January 1, 1986, and became a separate, self-governing member of the Kingdom of the Netherlands. Movement toward full independence by 1996 was halted at Aruba's request in 1990...
Politics
- Main article: Politics of Aruba
Aruba is a part of the Kingdom of the Netherlands, but maintains full control over its own affairs except for issues dealing with national defence, citizenship, foreign affairs, and extradition. Aruba has its own laws, constitution, government, and currency.
The Aruban head of state is the ruling monarch of the Netherlands, who is represented in Aruba by a governor, appointed for a six-year term. The head of government is the Prime Minister, who forms, together with the Council of Ministers, the executive branch of the government.
They are elected by the parliament, the unicameral Legislature or Staten, which holds 21 seats. Members are elected by direct, popular vote to serve four-year terms.
Law
Legal jurisdiction lies with a Gerecht in Eerste Aanleg on Aruba, a Common Court of Justice of the Netherlands Antilles and Aruba (Gemeenschappelijk Hof van Justitie voor de Nederlandse Antillen en Aruba) and the Supreme Court of Justice of the Netherlands.
Geography
- Main article: Geography of Aruba
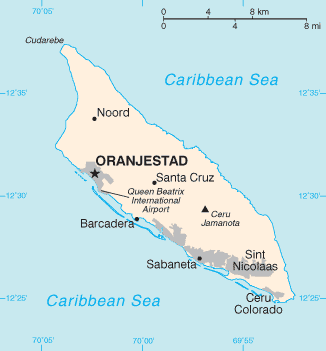
Aruba is a generally flat, riverless island renowned for its white sand beaches. Most of these are located on the western and southern coasts of the island, which are relatively sheltered from fierce ocean currents. The northern and eastern coasts, lacking this protection, are considerably more battered by the sea and have been left largely untouched by humans. The interior of the island features some rolling hills, the better two of which are called Hooiberg at 165 metres (541 ft) and Mount Jamanota, which is the highest on the island, at 188 metres (617 ft) above sea level. Oranjestad, the capital, is located at 12°19′N 70°1′W / 12.317°N 70.017°W.
As a separate member state of the Kingdom of the Netherlands, the island/state has no administrative subdivisions. On the east are Curaçao and Bonaire, two island territories which form the southwest part of the Netherlands Antilles; Aruba and these two Netherlands Antilles islands are also known as the ABC islands.
The local climate is a pleasant tropical marine climate. Little seasonal temperature variation exists, which helps Aruba to attract tourists all year round. Temperatures are almost constant at about 28 °C (82 °F), moderated by constant trade winds from the Atlantic Ocean. Yearly precipitation barely reaches 500 mm (20 in), most of it falling in late autumn.
Economy
- Main article: Economy of Aruba
Aruba enjoys one of the highest standards of living in the Caribbean region, with low poverty and unemployment rates. About half of the Aruban Gross National Product is earned with tourism or related activities. Most of the tourists are from Canada, the European Union and other places notably the United States, which is the country's largest trading partner. Before the Status Aparte (Secession from the Neth. Antilles) oil processing was the dominant industry in Aruba, despite expansion of the tourism sector. Today, the influence of the oil processing business is minimal. The size of the agriculture and manufacturing industries remains minimal.
Deficit spending has been a staple in Aruba's history, and modestly high inflation has been present as well, although recent efforts at tightening monetary policy may correct this. Aruba receives some development aid from the Dutch government each year. The Aruban guilder has a fixed exchange rate with the United States dollar of 1.79:1.
Demographics

Having poor soil and aridity, Aruba was saved from plantation economics and the slave trade. In 1515, the Spanish transported the entire population to Hispaniola to work in the copper mines; most were allowed to return when the mines were tapped out. The Dutch, who took control a century later, left the Arawaks to graze livestock, using the island as a source of meat for other Dutch possessions in the Caribbean. The Arawak heritage is stronger on Aruba than on most Caribbean islands. No full-blooded Aboriginals remain, but the features of the islanders clearly indicate their genetic heritage. The majority of the population is descended from Arawak, Dutch and Spanish ancestors. Recently there has been substantial immigration to the island from neighboring Latin American and Caribbean nations, attracted by the lure of well-paying jobs.
The two official languages are the Dutch language and the predominant, national language Papiamento, which is classified as a Creole language. This creole language is formed primarily from 16th century Portuguese, and several other languages. Spanish and English are also spoken. Islanders can often speak four or more languages and are mostly Roman Catholic.
Population: 103,000 (April 2004 est.)
Age structure:
- 0-14 years: 20.7% (male 7,540; female 7,121)
- 15-64 years: 68.3% (male 23,427; female 24,955)
- 65 years and over: 11% (male 3,215; female 4,586) (2003 est.)
Median age:
- total: 37.1 years
- male: 35.3 years
- female: 38.5 years (2002)
Population growth rate: 0.55% (2003 est.)
Birth rate: 11.86 births/1,000 population (2003 est.)
Death rate: 6.38 deaths/1,000 population (2003 est.)
Net migration rate: 0 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2003 est.)
Sex ratio:
at birth: 1.05 male(s)/female
under 15 years: 1.06 male(s)/female
15-64 years: 0.94 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.7 male(s)/female
total population: 0.93 male(s)/female (2003 est.)
Infant mortality rate:
- total: 6.14 deaths/1,000 live births
- female: 5.25 deaths/1,000 live births (2003 est.)
- male: 6.99 deaths/1,000 live births
Life expectancy at birth:
- total population: 78.83 years
- male: 75.48 years
- female: 82.34 years (2003 est.)
Total fertility rate: 1.79 children born/woman (2003 est.)
Nationality:
noun: Aruban(s)
adjective: Aruban; Dutch
Religions: Roman Catholic 82%, Protestant 8%, Hindu, Muslim, Confucian, Jewish
Languages: Dutch (official), Papiamento (national language), Spanish, English.
Culture
- Main article: Culture of Aruba
The origins of the population and location of the island give Aruba a mixed culture. Dutch influence can still be seen, even though not much of the population is of Dutch origin. Tourism from the United States has recently also increased the visibility of American culture on the island. Queen Beatrix International Airport, located near Oranjestad, currently serves the whole island of Aruba. This airport has access to various cities across the eastern U.S., from Miami, Orlando, Houston, Atlanta to New York. It also connects Aruba with Europe through Schiphol Airport in the Netherlands.
The holiday of Carnival is an important one in Aruba, as it is in many Caribbean and Latin American countries. Carnival is usually held from the beginning of January until the end of February, with a large parade on the final Sunday of the festivities.
See also: Music of Aruba and the Netherlands Antilles
Language
Language can be seen as an important part of island culture in Aruba. The cultural mixture has given way to a linguistic mixture known as "Papiamento". However, islanders are known to speak many languages. Islanders often speak Papiamento, English, Dutch and Spanish. In recent years the government of Aruba has shown an increased interest in acknowledging the cultural and historical importance of its native language.
Places of interest
- Alto Vista Chapel
- Arikok National Park
- Ayo and Casibari Rock Formations
- California Lighthouse
- Frenchman's Pass
- Hooiberg
- Lourdes Grotto
- Natural Bridge (Collapsed on September 2, 2005 [1])
- Natural Pool
- Palm and Eagle Beaches
See also
- Communications in Aruba
- Foreign relations of Aruba
- Transportation in Aruba
- Military of Aruba
- Scouting Aruba
External links
- Aruba.com - Official governmental portal
- Aruba Hotels and Travel Info
- ArubaTourism.com - The original website for Aruba Visitors, established in 1996.
- Library of Congress Portals on the World - Aruba
- CIA - The World Factbook -- Aruba - CIA World Factbook on Aruba
- An island map of Aruba and a detailed map of Oranjestad are available at Caribbean-On-Line.com
- Aruba Travel Forums - Aruba Message Board
- Visit Aruba Travel Forums - Aruba Message Board
- Photos & Pictures of Aruba
- Aruba Airport Authority
- Free Aruba Ecards
- CBAruba.org - The official Central Bank of Aruba.
- Aruba Aloe
- Aruba Bound!
- N.V. Elmar - Aruba's electric utility
- Aruba Guide - The Definitive Aruba Vacation Guide
- http://www.arubayp.com/ - telephone directory
- Beaches of Aruba - Vacation guide for first-time Aruba visitors