St. Louis: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
{{For|saints named Louis and other uses|Saint Louis (disambiguation){{!}}Saint Louis}} |
{{For|saints named Louis and other uses|Saint Louis (disambiguation){{!}}Saint Louis}} |
||
{{Infobox settlement |
{{Infobox settlement |
||
|name = St. Louis |
|name = St. Louis |
||
|official_name = City of St. Louis |
|official_name = City of St. Louis |
||
|settlement_type = [[Independent city (United States)|Independent City]] |
|settlement_type = [[Independent city (United States)|Independent City]] |
||
Revision as of 21:42, 31 August 2012
St. Louis | |
|---|---|
| City of St. Louis | |
 From top left: Forest Park Jewel Box, MetroLink (St. Louis) at Lambert-St. Louis International Airport, Apotheosis of St. Louis at the St. Louis Art Museum, Gateway Arch and the St. Louis skyline, Busch Stadium, and the St. Louis Zoo | |
| Nickname(s): | |
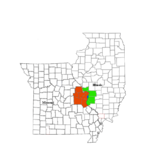
 Location in the state of Missouri | |
| Country | United States |
| State | Missouri |
| County | Independent city |
| Metro | Greater St. Louis |
| Founded | 1764 |
| Incorporated | 1822 |
| Government | |
| • Type | Mayor–council government |
| • Mayor | Francis G. Slay (D) |
| Area | |
| 66.2 sq mi (171.3 km2) | |
| • Land | 61.9 sq mi (160.4 km2) |
| • Water | 4.2 sq mi (11.0 km2) |
| Elevation | 466 ft (142 m) |
| Population (2011)[5] | |
| 318,069 | |
| • Rank | 58th |
| • Density | 4,804.7/sq mi (1,864/km2) |
| • Metro | 2,812,896 (18th) |
| Demonym | St. Louisan |
| Time zone | UTC−6 (CST) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−5 (CDT) |
| Area code(s) | 314, 636 |
| Website | http://stlouis-mo.gov/ |
St. Louis /seɪnt ˈluːɪs/ (French: Saint-Louis or St-Louis, Template:IPA-fr) is an independent city[6] on the eastern border of Missouri, United States, and is the second-largest city in the state. With a population of 318,069 in July 2011,[5] it was the 58th-largest U.S. city at the 2010 U.S. Census. The Metropolitan Statistical Area (MSA) population of 2,812,896 is the 18th-largest in the country. The Greater St. Louis combined statistical area's (CSA) population of 2,882,932 is the 15th-largest CSA in the country, the fourth-largest in the Midwest. The Greater St. Louis area is the largest metropolitan area in Missouri.
The city of St. Louis was founded in 1764 by Pierre Laclède and Auguste Chouteau, and after the Louisiana Purchase, it became a major port on the Mississippi River. Its population expanded after the American Civil War, and it became the fourth-largest city in the United States in the late 19th century. It seceded from St. Louis County in March 1877, allowing it to become an independent city and limiting its political boundaries. In 1904, it hosted the 1904 World's Fair and the 1904 Olympic Games. The city's population peaked in 1950, then began a long decline that continues in the 21st century.
The economy of St. Louis relies on service, manufacturing, trade, transportation of goods, and tourism. The region is home to several major corporations: Express Scripts, Enterprise Rent-A-Car, Graybar Electric, Scottrade, Sigma-Aldrich, Anheuser-Busch, Edward Jones Investments, Emerson Electric, Energizer, and Monsanto. St. Louis is home to three professional sports teams: the St. Louis Cardinals, one of the most successful Major League Baseball clubs; the hockey St. Louis Blues, and the football St. Louis Rams. The city is commonly identified with the Gateway Arch, part of the Jefferson National Expansion Memorial in downtown St. Louis.
History
The area that would become St. Louis was a center of Native American Mississippian culture, which built numerous temple and residential earthwork mounds in the region, giving the city its nickname, the "Mound City". European exploration of the area began in 1673, when French explorers Louis Jolliet and Jacques Marquette traveled through the Mississippi River valley. Five years later, La Salle claimed the region for France, and the earliest settlements in the area were built in Illinois during the 1690s and early 1700s at Cahokia, Kaskaskia, and Fort de Chartres. Migrants from the eastern French villages founded Ste. Genevieve, Missouri across the Mississippi River from Kaskaskia, and in early 1764, Pierre Laclède and his stepson Auguste Chouteau founded the city of St. Louis.[7]
From 1764 to 1803 European control of the area west of the Mississippi to the northernmost part of the Missouri River basin, called Louisiana, was assumed by the Spanish as part of the Viceroyalty of New Spain. In 1765, St. Louis was made the capital of French Upper Louisiana, and after 1767, control of the region was given to the Spanish. In 1780, St. Louis was attacked by British forces, mostly Native Americans, during the American Revolutionary War.[8] St. Louis was transferred back to France in 1800, then sold to the United States in 1803 as part of the Louisiana Purchase, and the city became the territorial capital. Shortly after the purchase, the Lewis and Clark Expedition left St. Louis in May 1804, reaching the Pacific Ocean in summer 1805, and returning on September 23, 1806. Both Lewis and Clark lived in St. Louis after the expedition. Many other explorers, settlers, and trappers (such as Ashley's Hundred) would later take a similar route to the West. The city elected its first municipal legislators (called trustees) in 1808.
Steamboats first arrived in St. Louis in 1818, improving connections with New Orleans and eastern markets. Missouri became a state in 1821, at which point the capital moved from St. Louis. However, St. Louis was incorporated as a city in 1822, and continued to see growth due to its port connections. Immigrants from Ireland and Germany arrived in St. Louis in significant numbers starting in the 1840s, and the population of St. Louis grew from less than 20,000 in 1840, to 77,860 in 1850, to more than 160,000 by 1860.

During the American Civil War, St. Louis was the site of significant divisions, although no combat took place in the city after the 1861 Camp Jackson Affair. The war hurt St. Louis economically, due to the blockade of river traffic to the South, although the St. Louis Arsenal constructed ironclads for the Union. St. Louis profited via trade with the West after the war, and in 1874, the city completed the Eads Bridge, the first bridge over the Mississippi River in the area. On August 22, 1876, the city of St. Louis voted to secede from St. Louis County and become an independent city, and industrial production continued to increase during the late 19th century. The city also produced a number of notable people in the fields of literature, including Tennessee Williams and T.S. Eliot, and major corporations such as the Anheuser-Busch brewery and Ralston-Purina company were established. St. Louis also was home to Desloge Consolidated Lead Company and several brass era automobile companies, including the Success Automobile Manufacturing Company;[9] St. Louis also is the site of the Wainwright Building, an early skyscraper built in 1892.
In 1904, the city hosted the 1904 World's Fair and the 1904 Summer Olympics, becoming the first non-European city to host the Olympics.[10] Proceeds from the fair provided the city with Forest Park, the St. Louis Art Museum, the St. Louis Zoo and the Missouri History Museum.
Discrimination in housing and employment were common in St. Louis, and starting in the 1910s, many property deeds included racial or religious restrictive covenants. During World War II, the NAACP campaigned to integrate war factories, and restrictive covenants were prohibited in 1948 by the Shelley v. Kraemer U.S. Supreme Court decision, which originated as a lawsuit in St. Louis. However, de jure educational segregation continued into the 1950s, and de facto segregation continued into the 1970s, leading to a court challenge and interdistrict desegregation agreement.[11]
St. Louis, like many Midwestern cities, expanded in the early 20th century due to the formation of many industrial companies and due to wartime housing shortages. It reached its peak population of 856,796 at the 1950 census.[12] Suburbanization from the 1950s through the 1990s dramatically reduced the city's population, and although small increases in population were seen in the early 2000s, the city of St. Louis lost population from 2000 to 2010. Several urban renewal projects commenced in the 1950s, and the city achieved notoriety for its housing projects, particularly Pruitt-Igoe. Since the 1980s, revitalization efforts have focused on downtown St. Louis, and gentrification has taken place in the Washington Avenue Historic District.[13] Because of the upturn in urban revitalization, St. Louis received the World Leadership Award for urban renewal in 2006.[14]
Geography
Topography

According to the United States Census Bureau, St. Louis has a total area of 66.2 square miles (171.3 km²), of which 61.9 square miles (160.4 km²) is land and 4.2 square miles (11.0 km² or 6.39%) is water. The city is built primarily on bluffs and terraces that rise 100–200 feet above the western banks of the Mississippi River, in the Midwestern United States just south of the Missouri-Mississippi confluence. Much of the area is a fertile and gently rolling prairie that features low hills and broad, shallow valleys. Both the Mississippi River and the Missouri River have cut large valleys with wide flood plains.
Limestone and dolomite of the Mississippian epoch underlie the area, and parts of the city are karst in nature. This is particularly true of the area south of downtown, which has numerous sinkholes and caves. Most of the caves in the city have been sealed, but many springs are visible along the riverfront. Coal, brick clay, and millerite ore were once mined in the city, and the predominant surface rock, the St. Louis Limestone, is used as dimension stone and rubble for construction.
Near the southern boundary of the City of St. Louis (separating it from St. Louis County) is the River des Peres, virtually the only river or stream within the city limits that is not entirely underground.[15] Most of River des Peres was confined to a channel or put underground in the 1920s and early 1930s. The lower section of the river was the site of some of the worst flooding of the Great Flood of 1993.
The city's eastern border is the Mississippi River, which also separates Missouri from Illinois. The Missouri River forms the northern border of St. Louis County, except for a few areas where the river has changed its course. The Meramec River forms most of its southern border.
Climate

St. Louis lies in the transitional zone between the humid continental climate type and the humid subtropical climate type (Köppen Dfa and Cfa, respectively), with neither large mountains nor large bodies of water to moderate its temperature. It is subject to both cold Arctic air and hot, humid tropical air from the Gulf of Mexico. The city has four distinct seasons. Spring is the wettest season and produces severe weather ranging from tornadoes to winter storms. Summers are hot and humid; temperatures of 90 °F (32 °C) or higher occur 35 to 40 days a year, while days of 100 °F (38 °C) or higher average less than five yearly.[16] Fall is mild with lower humidity and can produce intermittent bouts of heavy rainfall with the first snowflakes usually falling before late mid November. Winters can be cold and snowy with temperatures frequently below freezing. Winter storm systems, such as Alberta Clippers and Panhandle hooks, can bring days of heavy freezing rain, ice pellets, and snowfall.
The average annual temperature recorded at nearby Lambert-St. Louis International Airport, is 57.0 °F (14 °C), and average precipitation is 41.0 inches (1,040 mm). The normal high temperature in July is 90.1 °F (32 °C), and the normal low temperature in January is 23.7 °F (−5 °C), although this varies from year to year. Both 100 °F (37.8 °C) and 0 °F (−17.8 °C) temperatures can be seen on an average 2 or 3 days per year. The official record low is −22 °F (−30 °C) on January 5, 1884, although there were unofficial readings of −23 °F (−31 °C) on January 29, 1873 and −25 °F (−32 °C) on January 1, 1864; and the record high is 115 °F (46 °C) on July 14, 1954.[17] July 2012 was the hottest month in the 138-year recorded weather temperatures in St. Louis history starting in 1874, with an average daily temperature of 88.1 °F (31 °C). [17]
Winter (December through February) is the driest season, with an average 7.5 inches (191 mm) of precipitation. The average seasonal snowfall is 17.7 inches (45 cm). Spring (March through May), is typically the wettest season, with 11.7 inches (297 mm) of precipitation. Dry spells lasting one to two weeks are common during the growing seasons.
St. Louis experiences thunderstorms 48 days a year on average.[18] Especially in the spring, these storms can often be severe, with high winds, large hail and tornadoes. Lying within the hotbed of Tornado Alley, St. Louis reigns as one of the most frequently tornadic metropolitan areas, and has an extensive history of particularly damaging tornadoes.
Some late autumns feature the warm weather known as Indian summer; some years see roses in bloom as late as early December.
| Climate data for St. Louis, Missouri (Lambert–St. Louis Int'l), 1991−2020 normals,[a] extremes 1874−present[b] | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °F (°C) | 77 (25) |
85 (29) |
92 (33) |
93 (34) |
98 (37) |
108 (42) |
115 (46) |
110 (43) |
104 (40) |
94 (34) |
86 (30) |
76 (24) |
115 (46) |
| Mean maximum °F (°C) | 64.7 (18.2) |
71.0 (21.7) |
79.4 (26.3) |
86.4 (30.2) |
90.4 (32.4) |
95.5 (35.3) |
99.2 (37.3) |
99.1 (37.3) |
93.4 (34.1) |
87.0 (30.6) |
75.5 (24.2) |
66.9 (19.4) |
100.7 (38.2) |
| Mean daily maximum °F (°C) | 40.4 (4.7) |
45.8 (7.7) |
56.6 (13.7) |
68.0 (20.0) |
77.1 (25.1) |
85.9 (29.9) |
89.6 (32.0) |
88.3 (31.3) |
81.1 (27.3) |
69.2 (20.7) |
55.5 (13.1) |
44.5 (6.9) |
66.8 (19.3) |
| Daily mean °F (°C) | 32.1 (0.1) |
36.7 (2.6) |
46.6 (8.1) |
57.5 (14.2) |
67.5 (19.7) |
76.5 (24.7) |
80.4 (26.9) |
78.8 (26.0) |
71.0 (21.7) |
59.1 (15.1) |
46.5 (8.1) |
36.5 (2.5) |
57.4 (14.1) |
| Mean daily minimum °F (°C) | 23.8 (−4.6) |
27.6 (−2.4) |
36.7 (2.6) |
47.0 (8.3) |
57.9 (14.4) |
67.2 (19.6) |
71.1 (21.7) |
69.3 (20.7) |
60.9 (16.1) |
49.1 (9.5) |
37.4 (3.0) |
28.5 (−1.9) |
48.0 (8.9) |
| Mean minimum °F (°C) | 4.4 (−15.3) |
9.6 (−12.4) |
17.8 (−7.9) |
32.2 (0.1) |
43.5 (6.4) |
55.5 (13.1) |
61.4 (16.3) |
60.1 (15.6) |
47.1 (8.4) |
33.6 (0.9) |
22.0 (−5.6) |
11.0 (−11.7) |
1.2 (−17.1) |
| Record low °F (°C) | −22 (−30) |
−18 (−28) |
−5 (−21) |
20 (−7) |
31 (−1) |
43 (6) |
51 (11) |
47 (8) |
32 (0) |
21 (−6) |
1 (−17) |
−16 (−27) |
−22 (−30) |
| Average precipitation inches (mm) | 2.59 (66) |
2.23 (57) |
3.50 (89) |
4.73 (120) |
4.82 (122) |
4.49 (114) |
3.93 (100) |
3.38 (86) |
2.96 (75) |
3.15 (80) |
3.42 (87) |
2.50 (64) |
41.70 (1,059) |
| Average snowfall inches (cm) | 5.7 (14) |
4.3 (11) |
2.3 (5.8) |
0.2 (0.51) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.9 (2.3) |
3.2 (8.1) |
16.6 (42) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.01 in) | 9.3 | 8.7 | 10.8 | 11.5 | 12.6 | 9.8 | 8.9 | 8.4 | 7.3 | 8.5 | 9.0 | 9.0 | 113.8 |
| Average snowy days (≥ 0.1 in) | 4.7 | 3.9 | 1.7 | 0.2 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.8 | 3.2 | 14.5 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 73.0 | 72.0 | 68.3 | 63.5 | 66.5 | 67.1 | 68.0 | 70.0 | 71.6 | 68.7 | 72.2 | 75.8 | 69.7 |
| Average dew point °F (°C) | 20.1 (−6.6) |
24.1 (−4.4) |
33.1 (0.6) |
42.3 (5.7) |
52.9 (11.6) |
62.1 (16.7) |
66.6 (19.2) |
65.1 (18.4) |
58.6 (14.8) |
46.0 (7.8) |
36.0 (2.2) |
25.5 (−3.6) |
44.4 (6.9) |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 161.2 | 158.3 | 198.3 | 223.5 | 266.5 | 291.9 | 308.9 | 269.8 | 236.1 | 208.4 | 140.9 | 129.9 | 2,593.7 |
| Percent possible sunshine | 53 | 53 | 53 | 56 | 60 | 66 | 68 | 64 | 63 | 60 | 47 | 44 | 58 |
| Average ultraviolet index | 1.7 | 2.7 | 4.5 | 6.4 | 7.9 | 9.0 | 9.1 | 8.2 | 6.3 | 4.0 | 2.3 | — | — |
| Source 1: NOAA (relative humidity, dew point, and sun 1961−1990)[20][21][22] | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: UV Index Today (1995 to 2022)[23] | |||||||||||||
Flora and fauna

Before the founding of the city, the area was prairie and open forest maintained by burning by Native Americans. Trees are mainly oak, maple, and hickory, similar to the forests of the nearby Ozarks; common understory trees include Eastern Redbud, Serviceberry, and Flowering Dogwood. Riparian areas are forested with mainly American sycamore. Most of the residential area of the city is planted with large native shade trees. The largest native forest area is found in Forest Park. In Autumn, the changing color of the trees is notable. Most species here are typical of the Eastern Woodland, although numerous decorative non-native species are found; the most notable invasive species is Japanese honeysuckle, which is actively removed from some parks.
Large mammals found in the city include urbanized coyotes and usually a White-tailed deer. Eastern Gray Squirrel, Cottontail rabbit, and other rodents are abundant, as well as the nocturnal Virginia Opossum. Large bird species are abundant in parks and include Canada goose, Mallard duck, as well as shorebirds, including the Great Egret and Great Blue Heron. Gulls are common along the Mississippi River; these species typically follow barge traffic. Winter populations of Bald Eagles are found by the Mississippi River around the Chain of Rocks Bridge. The city is on the Mississippi Flyway, used by migrating birds, and has a large variety of small bird species, common to the eastern US. The Eurasian Tree Sparrow, an introduced species, is limited in North America to the counties surrounding St. Louis. Tower Grove Park is a well-known birdwatching area in the city.
Frogs are commonly found in the springtime, especially after extensive wet periods. Common species include the American toad and species of chorus frogs commonly called spring peepers that are found in nearly every pond. Some years have outbreaks of cicadas or ladybugs. Mosquitos and houseflies are common insect nuisances; because of this, windows are nearly universally fitted with screens, and screened-in porches are common in homes of the area. Invasive populations of honeybees have sharply declined in recent years, and numerous native species of pollinator insects have recovered to fill their ecological niche.
Demographics
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
|---|---|---|
| 1810 | 1,600 | — |
| 1820 | — | |
| 1830 | 4,977 | — |
| 1840 | 16,469 | +230.9% |
| 1850 | 77,860 | +372.8% |
| 1860 | 160,773 | +106.5% |
| 1870 | 310,864 | +93.4% |
| 1880 | 350,518 | +12.8% |
| 1890 | 451,770 | +28.9% |
| 1900 | 575,238 | +27.3% |
| 1910 | 687,029 | +19.4% |
| 1920 | 772,897 | +12.5% |
| 1930 | 821,960 | +6.3% |
| 1940 | 816,048 | −0.7% |
| 1950 | 856,796 | +5.0% |
| 1960 | 750,026 | −12.5% |
| 1970 | 622,236 | −17.0% |
| 1980 | 452,801 | −27.2% |
| 1990 | 396,685 | −12.4% |
| 2000 | 348,189 | −12.2% |
| 2010 | 319,294 | −8.3% |
| 2011 estimate | 318,069 | −0.4% |
| [24] [25]
[26][27] | ||

According to the 2010 United States Census, in the city of St. Louis, there were 319,294 people living in 142,057 households, of which 67,488 households were families. The population density was 5,158.2 people per square mile (1,990.6/km²). The age distribution of the city showed approximately 24% of the population was 19 or younger, 9% were 20 to 24, 31% were 25 to 44, 25% were 45 to 64, and 11% were 65 or older. The median age was approximately 34 years. The racial makeup of the city of St. Louis was approximately 49.2% African American, 43.9% White (42.2% Non-Hispanic White), 2.9% Asian, 0.3% Native American/Alaska Native, and 2.4% reporting two or more races. Hispanic or Latino of any race were 3.5% of the population.[28]
19% of the city's housing units were vacant, and slightly less than half of these were vacant structures not for sale or rent. In 2000, the median income for a household in the city was $29,156, and the median income for a family was $32,585. Males had a median income of $31,106 versus $26,987 for females. The per capita income for the city was $18,108.
St. Louis experienced slow growth from its founding in the 1760s through the American Civil War, and after the war it grew quickly with industrialization, reaching its peak population in 1950. In 1950, the Census Bureau reported St. Louis' population as 82% White and 17.9% African American.[29] The area experienced a population shift to the suburbs in the 20th century; first because of increased demand for new housing following World War II, and later white flight from older neighborhoods to newer ones.[30]
In 2010, the city of St. Louis was awarded for being one of the most generous large cities in the United States for online monetary donations and has also been recognized for having an extremely high volunteer rate in comparison to other major U.S cities.[31]
| United States Census Population | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year | 1860 | 1870 | 1880 | 1890 | 1900 | 1910 | 1920 | 1930 | 1940 | 1950 | 1960 | 1970 | 1980 | 1990 | 2000 | 2010 |
| Population | 160,773 | 310,864 | 350,518 | 451,770 | 575,238 | 687,029 | 772,897 | 821,960 | 816,048 | 856,796 | 750,026 | 622,236 | 452,801 | 396,685 | 348,189 | 319,294 |
| U.S. Rank[32][33] | 8 | 4 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 4 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 8 | 10 | 18 | 26 | 34 | 51 | 58 |
Economy
The 2011 Gross Metropolitan Product (GMP) of St. Louis was $133.1 billion, 21st-highest in the country.[34] According to the 2007 Economic Census, manufacturing in the city conducted nearly $11 billion in business, followed by the health care and social service industry with $3.5 billion, professional or technical services with $3.1 billion, and the retail trade with $2.5 billion. The health care sector was the biggest employer in the area with 34,000 workers, followed by administrative and support jobs, 24,000; manufacturing, 21,000, and food service, 20,000.[35]
The rivers of St. Louis play a large role in moving goods, especially bulk commodities such as grain, coal, salt, and certain chemicals and petroleum products. The Port of St. Louis in 2004 was the third-largest inland port by tonnage in the country, and the 21st-largest of any sort.[36]
Major companies and institutions
As of 2011, the St. Louis area is home to nine Fortune 500 companies, including Express Scripts, Emerson Electric, Monsanto, Reinsurance Group of America, Ameren, Charter Communications, Peabody Energy, Graybar Electric, and Centene.[37]
Other notable corporations from the area include Cassidy Turley, Edward Jones Investments, AT&T Communications, Scottrade, Wells Fargo Advisors (formerly A.G. Edwards), Energizer Holdings, Furniture Brands International, Kerry Group, Post Holdings, Inc., United Van Lines and Mayflower Transit, Ralcorp, Hardee's, and Enterprise Holdings (parent company of several car rental companies). Health care and biotechnology institutions with operations in St. Louis include Pfizer, the Donald Danforth Plant Science Center, the Solae Company, Sigma-Aldrich, and Multidata Systems International. General Motors makes railroad cars in the area, although Chrysler closed its production facility in nearby Fenton, Missouri.
Several once-independent pillars of the local economy have been purchased by other corporations. Among them are Anheuser-Busch, purchased by Belgium-based InBev; McDonnell-Douglas, whose operations are now part of Boeing Defense, Space & Security;[38] Mallinckrodt Incorporated, purchased by Tyco International; and Ralston Purina, now a wholly owned subsidiary of Nestle.[39] The May Department Stores Company (which owned Famous-Barr and Marshall Field's stores) was purchased by Federated Department Stores, which has its regional headquarters in the area.
The Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis in downtown is one of two federal reserve banks in Missouri.[40]
Culture
With its French past and numerous Catholic immigrants in the 19th and 20th centuries, St. Louis is a major center of Roman Catholicism in the United States. St. Louis also boasts the largest Ethical Culture Society in the United States. Several places of worship in the city also are noteworthy, such as the Cathedral Basilica of St. Louis, home of the world's largest mosaic installation.[41] Other locally notable churches include the Basilica of St. Louis, King of France, the oldest Roman Catholic cathedral west of the Mississippi River and the oldest church in St. Louis, the St. Louis Abbey, whose distinctive architectural style garnered multiple awards at the time of its completion in 1962, and St. Francis de Sales Oratory, a neo-Gothic church completed in 1908 and the second largest church in the city.
Many cultural attractions are located in the Greater St. Louis area, such as the Gateway Arch and the Delmar Loop. The city is also defined by music and the performing arts, especially its association with blues, jazz, and ragtime. St. Louis is home to the St. Louis Symphony, the second-oldest symphony orchestra in the United States, and until 2010, it was also home to KFUO-FM, one of the oldest classical music FM radio stations west of the Mississippi River.[42]
Unique city and regional cuisine includes toasted ravioli, gooey butter cake, Provel cheese, the slinger, the Gerber sandwich, the St. Paul sandwich, and St. Louis style pizza.
Sports
St. Louis is home to professional Major League Baseball, National Football League, and National Hockey League teams, notable collegiate-level soccer teams, and has hosted several collegiate sports tournaments.
| Club | Sport | League | Venue |
|---|---|---|---|
| St. Louis Cardinals | Baseball | Major League Baseball | Busch Stadium |
| St. Louis Rams | American football | National Football League | Edward Jones Dome |
| St. Louis Blues | Ice hockey | National Hockey League | Scottrade Center |
Professional sports
The St. Louis Cardinals, one of the oldest franchises in Major League Baseball, have accumulated 11 World Series titles, with the most recent being in 2011, and two minor league baseball teams play in the area, the Gateway Grizzlies and the River City Rascals. The St. Louis Rams, an American football NFL team, play at the Edward Jones Dome and have won one Super Bowl championship. The St. Louis Blues, a franchise of the National Hockey League, play at the Scottrade Center, and the region hosts NHRA drag racing and NASCAR events at the Gateway International Raceway in Madison, Illinois.
Amateur sports
At the collegiate level, St. Louis has hosted the Final Four of both the women's and men's college basketball NCAA Division I championship tournaments, and the Frozen Four collegiate ice hockey tournament. Although the area does not support a National Basketball Association team, it hosts an American Basketball Association team called the St. Louis Phoenix. St. Louis University has won 10 NCAA Men's Soccer Championships, and the city has hosted the College Cup several times. In addition to collegiate soccer, St. Louisans have played for the United States men's national soccer team, and 20 St. Louisans have been elected into the National Soccer Hall of Fame. St. Louis also is the origin of the sport of corkball, a type of baseball in which there is no base running.
Parks

The city operates more than 100 parks, with amenities that include sports facilities, playgrounds, concert areas, picnic areas, and lakes. Forest Park, located on the western edge of city, is the largest park in the city, although it is not the largest park in the region. Another significant park in the city is the Jefferson National Expansion Memorial, a National Memorial located on the riverfront in downtown St. Louis. The centerpiece of the park is the 630 feet (192 m) tall Gateway Arch, designed by noted architect Eero Saarinen and completed on October 28, 1965. Also part of the park is the Old Courthouse, where the first two trials of Dred Scott v. Sandford were held in 1847 and 1850.
Other notable parks in the city include the Missouri Botanical Garden, Tower Grove Park, and Citygarden. The Missouri Botanical Garden, a private garden and botanical research facility, includes the Climatron, a greenhouse built as a geodesic dome. Immediately south of the Missouri Botanical Garden is Tower Grove Park, a gift to the City by Henry Shaw. Citygarden is an urban sculpture park located in downtown St. Louis, with art from Fernand Léger, Aristide Maillol, Julian Opie, Tom Otterness, Niki de Saint Phalle, and Mark di Suvero.[43][44] The park is also divided into three sections, each of which represent a different theme: river bluffs; flood plains; and urban gardens. The park also has a restaurant – The Terrace View.[45] Another downtown sculpture park is the Serra Sculpture Park, with the 1982 Richard Serra sculpture Twain.[46]
Government
The city of St. Louis has a mayor-council government with legislative authority vested in the Board of Aldermen of the City of St. Louis and with executive authority in the Mayor of St. Louis and six other separately elected officials.[47] The Board of Aldermen is made up of 28 members (one elected from each of the city's wards) plus a board president who is elected city-wide.[48] As of 2008, 257,442 registered voters lived in the city.[49]
Local and regional government
Municipal elections in St. Louis city are held in odd numbered years, with the primary elections in March and the general election in April. The mayor is elected in odd numbered years following the United States Presidential Election, as are the aldermen representing odd-numbered wards. The President of the Board of Aldermen and the aldermen from even-numbered wards are elected in the off-years. The Democratic Party has dominated St. Louis city politics for decades. The city has not had a Republican mayor since 1949 and the last time a Republican was elected to another city-wide office was in the 1970s. As of 2006, 27 of the city's 28 Aldermen are Democrats.
Although St. Louis City and County separated in 1876, some mechanisms have been put in place for joint funding management and funding of regional assets. The St. Louis Zoo-Museum district collects property taxes from residents of both St. Louis City and County and the funds are used to support cultural institutions including the St. Louis Zoo, St. Louis Art Museum and the Missouri Botanical Gardens. Similarly, the Metropolitan Sewer District provides sanitary and storm sewer service to the city and much of St. Louis County. The Bi-State Development Agency (now known as Metro) runs the region's MetroLink light rail system and bus system.
State and federal government
The city of St. Louis is represented by eleven districts in the Missouri House of Representatives: the 57th, 58th, 59th, 60th, 61st, 63rd, 65th, 67th and 108th are entirely within the city limits, while the 64th and 66th include part of the city and part of St. Louis County.[50] Two Missouri State Senate districts, the 4th and 5th, are entirely within the city, while the 1st Senate district includes part of the city and part of St. Louis County.[50]
The City of St. Louis is split roughly in half north to south by Missouri's 1st and 3rd U.S. Congressional districts. The 1st is represented by Lacy Clay and the 3rd by Russ Carnahan. Both are members of the Democratic Party; a Republican has not represented a significant portion of St. Louis in the U.S. House since 1949. Each district also includes a significant portion of St. Louis County. Both the city and county lost population in the 2010 Census which contributed to Missouri losing a Congressional seat effective 2013. Initial redistricting maps indicate that the 3rd district would be absorbed into the 1st district placing Carnahan and Clay in the same district and giving St. Louis only one representative in Congress.[51]
The United States Court of Appeals for the Eighth Circuit and the United States District Court for the Eastern District of Missouri are based in the Thomas F. Eagleton United States Courthouse in downtown St. Louis. St. Louis is also home to a Federal Reserve System branch, the Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis. The National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency (NGA) also maintains major facilities in the St. Louis area.[52]
Crime
Since the mid 1990s, St. Louis index crime rates have declined, although homicide rates in the city of St. Louis have remained higher than the United States national average. St. Louis also frequently is ranked among the "most dangerous" in the country by CQ Press, although these rankings are controversial and do not reflect the crime rate of Greater St. Louis.[53][54]
Education
The St. Louis Public Schools serves the city of St. Louis with 77 schools, and it is run by a state appointed board.[55] With more than 25,000 students, the district is the largest in Greater St. Louis. The city of St. Louis has several private high schools, both secular and religiously affiliated, including numerous Catholic and Lutheran schools.
According to the Carnegie Classification of Institutions of Higher Education, the city of St. Louis is home to two national research universities: Washington University in St. Louis and St. Louis University.
Media
Greater St. Louis commands the 21st largest media market in the United States, a position it has held with little variation for more than ten years.[56] All of the major U.S. television networks have affiliates in St. Louis, including KTVI 2 (Fox), KMOV 4 (CBS), KSDK 5 (NBC), KETC 9 (PBS), KPLR-TV 11 (CW), KDNL 30 (ABC), WRBU 46 (MNTV), and WPXS 51 Daystar Television Network. Among the most popular radio stations in the St. Louis area are KMOX (AM sports and talk), KLOU (FM oldies), WIL-FM (FM country), WARH (FM adult hits), and KSLZ (FM top 40 mainstream).[57] St. Louis also supports public radio with KWMU, an NPR affiliate, and community radio with KDHX. All-sports stations, such as KFNS 590 AM "The Fan", WXOS "101.1 ESPN", and KSLG are also popular in St. Louis.
The St. Louis Post-Dispatch is the region's major daily newspaper. Other newspapers in the region include the Suburban Journals, serving parts of St. Louis County, while the primary alternative newspaper is the Riverfront Times. Three weeklies serve the African-American community: the St. Louis Argus, the St. Louis American, and the St. Louis Sentinel. St. Louis Magazine, a local monthly magazine, covers topics such as local history, cuisine, and lifestyles, while the weekly St. Louis Business Journal provides coverage of regional business news. St. Louis is also home to the nation's last remaining metropolitan journalism review, the Gateway Journalism Review, based at Webster University in the suburb of Webster Groves.[58] Furthermore, St. Louis is served by an online newspaper, the St. Louis Beacon, which operates in partnership and shares facilities with KETC 9 TV.[59]
Infrastructure
Transportation

The city of St. Louis is served by four interstates and several U.S. highways and state roadways. Although there are no airports within the city limits, the city owns and operates Lambert-St. Louis International Airport, located in northwest St. Louis County. Freight rail and passenger rail service operate in the city on tracks owned by BNSF Railway, with passenger service provided by Amtrak and served at the Gateway Multimodal Transportation Center in downtown St. Louis. Rapid transit and commuter rail service in the city is provided by the Bi-State Development Agency, also known as Metro. St. Louis also maintains a port authority for river shipping, and taxicabs are regulated within the city.
Health care
St. Louis is a center of medicine and biotechnology.[citation needed] The Washington University School of Medicine is affiliated with Barnes-Jewish Hospital, the fifth largest hospital in the world, and the two institutions operate the Alvin J. Siteman Cancer Center.[citation needed] The School of Medicine also is affiliated with St. Louis Children's Hospital, one of the country's top pediatric hospitals.[citation needed] Both hospitals are owned by BJC HealthCare. The school's Genome Sequencing Center played a major role in the Human Genome Project.[citation needed] St. Louis University Medical School is affiliated with Tenet Healthcare's St. Louis University Hospitasl and SSM Health Care's Cardinal Glennon Children's Hospital. It also has a cancer center, vaccine research center and a bioethics institute. Several different organizations operate hospitals in the area, including BJC HealthCare, SSM Health Care, Tenet and St. John's Mercy Healthcare.
Architecture and neighborhoods
St. Louis possesses several significant examples of 19th century architecture, such as the early stone construction Emmanuel DeHodiamont House, the Greek Revival style Chatillon-DeMenil House in the Soulard neighborhood, the Victorian era Campbell House, and the Wainwright Building, an early Louis Sullivan skyscraper. The city is divided into 79 government-designated neighborhoods.[60] The neighborhood divisions have no legal standing, although some neighborhood associations administer grants or hold veto power over historic-district development.
Sister cities
St. Louis has 15 sister cities.[61] Template:Multicol
 – Bologna, Italy
– Bologna, Italy – Bogor, Indonesia
– Bogor, Indonesia – Brčko, Bosnia and Herzegovina
– Brčko, Bosnia and Herzegovina – Donegal, Co. Donegal, Ireland
– Donegal, Co. Donegal, Ireland – Galway, Co. Galway, Ireland
– Galway, Co. Galway, Ireland – Georgetown, Guyana
– Georgetown, Guyana – Lyon, France
– Lyon, France – Nanjing, China
– Nanjing, China
| class="col-break " |
 – Saint-Louis, Senegal
– Saint-Louis, Senegal – São Luís, Maranhão, Brazil
– São Luís, Maranhão, Brazil – Samara, Russia
– Samara, Russia – San Luis Potosí, Mexico
– San Luis Potosí, Mexico – Stuttgart, Germany
– Stuttgart, Germany – Suwa, Japan
– Suwa, Japan – Szczecin, Poland
– Szczecin, Poland – Wuhan, China
– Wuhan, China
|}
See also
- Roman Catholic Archdiocese of St. Louis
- Caves of St. Louis
- Great Flood of 1993
- Heat wave of 2006 derecho series
- LaClede Town
- List of Mayors of St. Louis
- History of the Jews in St. Louis
- National Register of Historic Places listings in St. Louis (city, A–L), Missouri
- National Register of Historic Places listings in St. Louis (city, M-Z), Missouri
- St. Louis in the Civil War
- St. Louis smog episode (1939)
- Neighborhoods of St. Louis, Missouri
References
- ^ "St. Louis United States – Visiting the Gateway to the West". Globosapiens.net. Retrieved March 14, 2011.
- ^ St. Louis Public Library on "Mound City".
- ^ STLtoday.com on "The Lou".
- ^ "St. Louis City, Missouri – Population Finder – American FactFinder". United States Geological Survey. October 24, 1980. Retrieved December 23, 2008.
- ^ a b U.S. Census Bureau (July 2011). "Population Estimates by County". Retrieved May 29, 2012.
- ^ Missouri QuickFacts from the US Census Bureau.
- ^ Hoffhaus. (1984). Chez Les Canses: Three Centuries at Kawsmouth, Kansas City: Lowell Press. ISBN 0-913504-91-2.
- ^ Usgennet.org Attack On St. Louis: May 26, 1780.
- ^ Clymer, Floyd. Treasury of Early American Automobiles, 1877–1925 (New York: Bonanza Books, 1950), p. 32.
- ^ "1904 Summer Olympics". International Olympics Committee.
- ^ "St. Louis: Desegregation and School Choice in the Land of Dred Scott" (PDF). Retrieved October 1, 2010.
- ^ "Physical Growth of the City of St. Louis". Retrieved July 27, 2010.
- ^ "St. Louis: From Carthage to Rising Phoenix" (PDF). Rental Car Tours (Demographia). Retrieved December 17, 2007.
- ^ Spence Jackson (December 8, 2006). "Steinhoff Congratulates St. Louis on Receiving Urban Renewal Award". Missouri Department of Economic Development. Archived from the original on April 19, 2008. Retrieved February 18, 2008.
- ^ St. Louis – News – A Sewer Runs Through It.
- ^ The Climatology of St. Louis and the Bi-State Area. http://www.crh.noaa.gov/lsx/?n=cli_of_stl
- ^ a b "Just like it felt, July was hottest month on record in St. Louis". St. Louis Post-Dispatch. August 2, 2012.
{{cite web}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|publisher=(help) - ^ "Historical Weather for St. Louis, Missouri". Retrieved October 15, 2009.
- ^ ThreadEx
- ^ "Station Name: MO ST LOUIS LAMBERT INTL AP". U.S. Climate Normals 2020: U.S. Monthly Climate Normals (1991–2020). National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved July 22, 2021.
- ^ "NowData – NOAA Online Weather Data". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved July 22, 2021.
- ^ "WMO Climate Normals for ST. LOUIS/LAMBERT, MO 1961–1990". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved July 22, 2021.
- ^ "Historical UV Index Data - St. Louis, MO". UV Index Today. Retrieved April 22, 2023.
- ^ Census shows city is 'hollowing out', St. Louis Post-Dispatch (February 25, 2011)
- ^ St. Louis city QuickFacts, U.S. Census Bureau (July 1, 2009)
- ^ "Census of 1850" (PDF). United States Census. page 36
- ^ Campbell Gibson. "Population of the 100 largest cities and other urban places in the United States: 1790 to 1990". United States Bureau of the Census.
- ^ "Race and Hispanic or Latino Origin: 2010". United States Census.
- ^ "Race and Hispanic Origin for Selected Cities and Other Places: Earliest Census to 1990". U.S. Census Bureau. Retrieved April 21, 2012.
- ^ Gibson, Campbell (1998). "Population of the 100 largest cities and other urban places in the United States: 1790 to 1990". U.S. Census Bureau. Retrieved December 12, 2007.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ Druart, T. (2010). "Convio ranks most generous online cities". convio. Retrieved August 21, 2011.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ Gibson, Campbell (1998). "Table 1. Rank by Population of the 100 Largest Urban Places, Listed Alphabetically by State: 1790–1990". U.S. Census Bureau. Archived from the original on May 13, 2007. Retrieved May 1, 2007.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ Atwater, Isaac (1893). History of the city of Minneapolis, Minnesota. Munsell via Google Books.
- ^ "U.S. Cities With Bigger Economies Than Entire Countries". Retrieved July 31, 2012.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ 2007 Economic Census.
- ^ "River Transportation through and to St. Louis". St. Louis Commerce Magazine. 2005. Retrieved October 4, 2009.
- ^ Fortune 500 List (2011).
- ^ Stoller, Gary (March 24, 2003). "JDAM smart bombs prove to be accurate and a good buy". USA Today. Retrieved March 14, 2011.
- ^ "Ratings and Rankings – Area Companies". Stlrcga.org. Retrieved March 14, 2011.
- ^ "About Us | The Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis". St. Louis Fed. Retrieved March 14, 2011.
- ^ "25 Things to Do in St. Louis". Retrieved 02/17/2012.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help) - ^ The station was sold by the Lutheran Church-Missouri Synod for $18 million, funded in part through a donation by then-St. Louis Cardinals star Albert Pujols, and converted to contemporary Christian music.Deidre Pujols sounds off on Christian radio, STLtoday.com, Dec. 12, 2011
- ^ Tim Bryant, "Citygarden an immediate hit with visitors." St. Louis Post-Dispatch. Jul. 1, 2009.
- ^ David Bonetti, "Spectacular Citygarden is opening on schedule in St. Louis." St. Louis Post-Dispatch. Jun. 28, 2009.
- ^ Joe Bonwich, "Eatery will round out sculpture garden." St. Louis Post-Dispatch. Jun. 12, 2009.
- ^ http://stlouis.missouri.org/citygov//parks/parks_div/serra.html
- ^ "City of St. Louis Elected Officials". Stlouis-mo.gov. July 8, 2010. Retrieved March 24, 2012.
- ^ Guide to the Board of Aldermen, StLouis-mo.gov
- ^ "SoS, Missouri – Elections: Registered Voters in Missouri 2008". Sos.mo.gov. Retrieved April 1, 2012.
- ^ a b "Missouri House of Representatives". House.mo.gov. Retrieved March 24, 2012.
- ^ "UPDATE: House Redistricting Committee Unveils Map". OzarksFirst.com. Retrieved March 31, 2011.
- ^ "Who We Are". National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency. August 4, 2008. Retrieved January 22, 2010.
- ^ "St. Louis Named Most Dangerous U.S. City". CBS News. November 22, 2010.
- ^ "Methodology". Morganquitno.com. Retrieved March 14, 2011.
- ^ "Slps.org". Slps.org. Retrieved March 14, 2011.
- ^ "Nielsen Media 2010–2011 Local Market Estimates". Nielsen Media Research. Broadcast Employment Services. October 1, 2010. Retrieved July 20, 2011.
- ^ Arbitron (June 2011).
- ^ Malone, Roy. "Gateway Journalism Review". Sjreview.org. Retrieved March 24, 2012.
- ^ stlbeacon.org
- ^ Neighborhoods of the City of St. Louis, StLouis-mo.gov
- ^ "St. Louis Sister Cities". St. Louis Center for International Relations. Retrieved March 20, 2011.
External links
- Built St. Louis
- St. Louis Convention & Visitors Bureau
- St. Louis Regional Chamber and Growth Association
- Template:Wikitravel
- City-data.com – St. Louis
- Washington University - About St. Louis
Template:Missouri cities and mayors of 100,000 population Template:USLargestCities
Cite error: There are <ref group=lower-alpha> tags or {{efn}} templates on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=lower-alpha}} template or {{notelist}} template (see the help page).
- St. Louis, Missouri
- Communities on U.S. Route 66
- Host cities of the Summer Olympic Games
- Independent cities in the United States
- Populated places established in 1764
- Populated places in the United States with African American plurality populations
- Missouri populated places on the Mississippi River
- United States colonial and territorial capitals
- Regions of Greater St. Louis