OAuth: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 167: | Line 167: | ||
| 1.0a |
| 1.0a |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| [[ |
| [[XING]] |
||
| 1.0<ref>https://dev.xing.com/docs/authentication</ref> |
| 1.0<ref>https://dev.xing.com/docs/authentication</ref> |
||
|- |
|- |
||
Revision as of 04:30, 6 January 2013

OAuth is an open standard for authorization. OAuth provides a method for clients to access server resources on behalf of a resource owner (such as a different client or an end-user). It also provides a process for end-users to authorize third-party access to their server resources without sharing their credentials (typically, a username and password pair), using user-agent redirections.
OAuth is a service that is complementary to, and therefore distinct from, OpenID.
History
OAuth began in November 2006 when Blaine Cook was developing the Twitter OpenID implementation. Meanwhile, Ma.gnolia needed a solution to allow its members with OpenIDs to authorize Dashboard Widgets to access their service. Cook, Chris Messina and Larry Halff from Ma.gnolia met with David Recordon to discuss using OpenID with the Twitter and Ma.gnolia APIs to delegate authentication. They concluded that there were no open standards for API access delegation. [citation needed]
The OAuth discussion group was created in April 2007, for the small group of implementers to write the draft proposal for an open protocol. DeWitt Clinton from Google learned of the OAuth project, and expressed his interest in supporting the effort. In July 2007 the team drafted an initial specification. Eran Hammer joined and coordinated the many OAuth contributions, creating a more formal specification. On October 3, 2007, the OAuth Core 1.0 final draft was released.
At the 73rd Internet Engineering Task Force meeting in Minneapolis in November 2008, an OAuth BoF was held to discuss bringing the protocol into the IETF for further standardization work. The event was well attended and there was wide support for formally chartering an OAuth working group within the IETF.
The OAuth 1.0 Protocol was published as RFC 5849, an informational Request for Comments, in April 2010.
Since August 31, 2010, all third party Twitter applications have been required to use OAuth.[1]
The OAuth 2.0 Framework was published as RFC 6749, and the Bearer Token Usage as RFC 6750, both standards track Requests for Comments, in October 2012. Additional RFCs are still being worked on.
OAuth 2.0
OAuth 2.0 is the next evolution of the OAuth protocol and is not backward compatible with OAuth 1.0. OAuth 2.0 focuses on client developer simplicity while providing specific authorization flows for web applications, desktop applications, mobile phones, and living room devices. The specification and associated RFCs are being developed[2] within the IETF OAuth WG; the main framework was published in October 2012. (It was expected to be finalized by the end of 2010 according to Eran Hammer.[3] However, due to discording views about the evolution of OAuth, Hammer left the working group[4])
Facebook's new Graph API only supports OAuth 2.0 and is the largest implementation of the emerging standard.[5] As of 2011, both Google[6] and Microsoft[7] had added OAuth 2.0 experimental support to their APIs.
The OAuth 2.0 Framework[8] and Bearer Token Usage[9] were published in October 2012. Other documents are still being worked on within the OAuth working group.
Security
On April 23, 2009, a session fixation security flaw in the 1.0 protocol was announced. It affects the OAuth authorization flow (also known as "3-legged OAuth") in OAuth Core 1.0 Section 6.[10] Version 1.0a of the OAuth Core protocol was issued to address this issue.[11]
There is a debate over security concerns of OAuth 2.0; specifically, OAuth 2.0 doesn't support signature, encryption, channel binding, or client verification other than bearer. It relies completely on SSL for some degree of confidentiality and server authentication.[12][13]
Non-interoperability
Because OAuth 2.0 is more like a framework rather than a defined protocol, any OAuth 2.0 implementation is unlikely to naturally be interoperable with any other OAuth 2.0 implementation. Further deployment profiling and specification would be required for any interoperability.[14]
Uses
OAuth can be potentially used as an authorizing mechanism to consume secured (i.e., authenticated) RSS/ATOM feeds. Consumption of RSS/ATOM feeds that requires authentication has always been an issue. For example; an RSS feed from a secured Google Site can not be consumed using Google Reader. 3-Legged OAuth can be used to authorize Google Reader to access the RSS feed from that Google Site.
List of OAuth service providers
| Service provider | OAuth protocol |
|---|---|
| AllPlayers.com | 1.0[15] |
| Bitbucket | 1.0a |
| bitly | 2.0 |
| Dropbox | 1.0 |
| 2.0 draft 12[4] | |
| Flickr | 1.0a |
| Formstack | 2.0 |
| Foursquare | 2.0 |
| GitHub | 2.0 |
| 2.0 | |
| HnyB.me | 2.0 |
| Huddle | 2.0 |
| 2.0 | |
| 1.0a | |
| Microsoft (Hotmail, Windows Live, Messenger, Xbox) | 2.0 |
| Mixi | 1.0[16] |
| MySpace | 1.0a |
| Netflix | 1.0a |
| OpenLink Data Spaces | 1.0[17] |
| OpenTable | 1.0a |
| PayPal | 2.0 |
| Plurk | 1.0a[18] |
| Salesforce.com | 1.0a, 2.0 |
| Sina Weibo | 2.0 |
| StatusNet | 1.0a |
| Stripe.com | 2.0 |
| Tent.io | 2.0 |
| Tumblr | 1.0a |
| 1.0a | |
| Veevop | 2.0 |
| Vimeo | 1.0a |
| VK | 2.0 |
| Xero | 1.0a |
| 1.0[19] | |
| Yahoo! | 1.0a |
| Yammer | 2.0 |
| Yandex | 2.0 |
| Yelp | 1.0a |
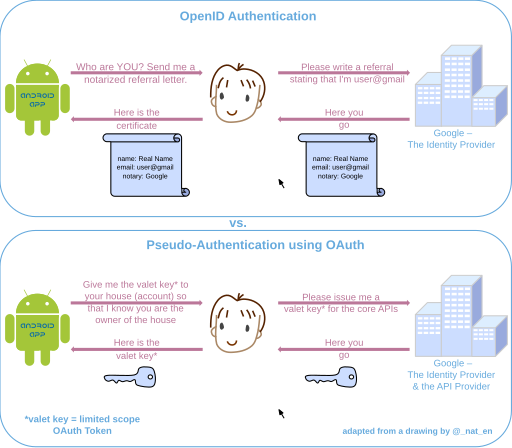
OpenID vs. pseudo-authentication using OAuth
The following drawing highlights the differences between using OpenID vs. OAuth for authentication. With OpenID, the process starts by the application asking the user for their identity (basically a log-in request by the application, to which the user typically provides an OpenID URI rather than actual credentials), whereas in the case of OAuth, the application specifically requests a limited access OAuth Token (valet key) to access the APIs (enter the house) on the user's behalf (which typically explicitly names the particular rights requested, and does not require the user to enter credentials at all). If the user can grant that access, the application can retrieve the unique identifier for establishing the profile (identity) using the APIs. In either case, the access to the Identity Provider will involve authentication to the Identity Provider, unless some session is already in effect. The net effect, in the OpenID case, is that the application allows the user access, because it trusts the OpenID Identity provider. The net effect, in the OAuth case, is that the API provider allows the application access because it trusts its own valet keys.
Controversy
In July 2012, Eran Hammer resigned his role of lead author for the OAuth 2.0 project, withdrew from the IETF working group, and removed his name from the specification. Hammer pointed to a conflict between the web and enterprise cultures, citing the IETF as a community that is "all about enterprise use cases", that is "not capable of simple". What is now offered is a blueprint for an authorisation protocol, he says, and "that is the enterprise way", providing a "whole new frontier to sell consulting services and integration solutions".[4]
In comparing OAuth 2.0 with 1.0, Hammer points out that it has become "more complex, less interoperable, less useful, more incomplete, and most importantly, less secure"... He explains how architectural changes for 2.0 unbound tokens from clients, removed all signatures and cryptography at a protocol level and added expiring tokens because tokens couldn't be revoked while complicating the processing of authorisation. Numerous items were left unspecified or unlimited in the specification because "as has been the nature of this working group, no issue is too small to get stuck on or leave open for each implementation to decide".[4]
Eran later gave a presentation at &yet elaborating on his views.[20]
David Recordon later also removed his name from the specifications for unspecified reasons. Dick Hardt took over the editor role, and the Framework was published in October 2012.[21]
See also
References
- ^ Chris Crum (2010-08-31). "Twitter Apps Go OAuth Today". WebProNews.com. Retrieved 2011-03-14.
- ^ "The OAuth 2.0 Authorization Framework". 2012-10.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ Eran Hammer (2010-05-15). "Introducing OAuth 2.0". Retrieved 2011-03-14.
- ^ a b c d "OAuth 2.0 and the Road to Hell". Eran Hammer. 28 July 2012. Retrieved 16 August 2012.
- ^ "Authentication - Facebook Developers". developers.facebook.com.
- ^ "Making auth easier: OAuth 2.0 for Google APIs". googlecode.blogspot.com. 2011-03-14.
- ^ Dare Obasanjo (2011-05-04). "Announcing Support for OAuth 2.0". windowsteamblog.com.
- ^ "RFC6749 - The OAuth 2.0 Authorization Framework". Dick Hardt. October 2012. Retrieved 10 October 2012.
- ^ "RFC6750 - The OAuth 2.0 Authorization Framework: Bearer Token Usage". Michael Jones, Dick Hardt. October 2012. Retrieved 10 October 2012.
- ^ "OAuth Security Advisory: 2009.1". 2009-04-23. Retrieved 2009-04-23.
- ^ OAuth Core 1.0a
- ^ "Is OAuth 2.0 Bad for the Web?". 2010-09-20. Retrieved 2010-09-21.
- ^ "an unwarranted bashing of Twitter's oAuth". 2011-08-03. Retrieved 2011-08-03.
- ^ "draft-ietf-oauth-v2-30". Dick Hardt, David Recordon. July 2012. Retrieved 12 November 2012.
- ^ http://develop.allplayers.com/oauth.html
- ^ http://developer.mixi.co.jp/appli/ns/mob/2-legged-oauth/
- ^ http://web.ods.openlinksw.com/odsdox/ods_oauth_server.html
- ^ http://www.plurk.com/API
- ^ https://dev.xing.com/docs/authentication
- ^ "OAuth 2.0 - Looking Back and Moving On". Eran Hammer. 23 October 2012. Retrieved 22 November 2012.
- ^ "RFC6749 - The OAuth 2.0 Authorization Framework". Dick Hardt. October 2012. Retrieved 10 October 2012.
External links
- RFC6749 at the IETF
- RFC6750 at the IETF
- RFC5849 at the IETF
- OAuth.net
- OAuth WG at the IETF
- OAuth Code Library Support on Google Groups
- OAuth Beginner's Guide and Resource Center on Hueniverse
- Google OAuth & Federated Login Research
- Yahoo! OAuth Quick Start Guide
- OAuth Checklist
- LIVE Demo of OAuth with Google, Yahoo