Bora Bora: Difference between revisions
→Tourism: removed 5 duplicate links |
|||
| Line 96: | Line 96: | ||
Most of the tourist destinations are aqua-centric; however it is possible to visit attractions on land such as WWII cannons. [[Air Tahiti]] has five or six flights daily to the [[Bora Bora Airport]] on Motu Mute from Tahiti (as well as from other islands). The island is served by Bora Bora Airport on Motu Mute in the north, with Air Tahiti providing daily flights to and from Papeete on Tahiti. |
Most of the tourist destinations are aqua-centric; however it is possible to visit attractions on land such as WWII cannons. [[Air Tahiti]] has five or six flights daily to the [[Bora Bora Airport]] on Motu Mute from Tahiti (as well as from other islands). The island is served by Bora Bora Airport on Motu Mute in the north, with Air Tahiti providing daily flights to and from Papeete on Tahiti. |
||
Although French and Tahitian are the main languages spoken by the inhabitants, people in contact with tourists generally have some command of English. Most visitors to Bora Bora are American, Japanese, or European.{{Citation needed|date=September 2010}} |
Although French and Tahitian are the main languages spoken by the inhabitants, people in contact with tourists generally have some command of English. Most visitors to Bora Bora are American, Japanese, or European.{{Citation needed|date=September 2010}} |
||
Public transport on the island is non-existent. Rental cars and bicycles are the recommended method of transport. There are also small fun-cars for hire in Vaitape. It is possible to rent (150$ per 4 hours) motor-driven boat to explore the lagoon. |
|||
[[Snorkeling]] and [[scuba diving]] in and around the lagoon of Bora Bora are popular activities. Many species of [[shark]]s and [[batoidea|rays]] inhabit the surrounding body of water. There are a few dive operators on the island offering manta ray dives and also shark-feeding dives. |
|||
In addition to the existing islands of Bora Bora (called motu), the new man-made motu of Motu Marfo has been added in the north-eastern corner of the lagoon on the property of the St. Regis Resort. |
In addition to the existing islands of Bora Bora (called motu), the new man-made motu of Motu Marfo has been added in the north-eastern corner of the lagoon on the property of the St. Regis Resort. |
||
Revision as of 13:34, 12 February 2013
This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these messages)
No issues specified. Please specify issues, or remove this template. |
 | |
| Geography | |
|---|---|
| Location | Pacific Ocean |
| Archipelago | Society Islands |
| Administration | |
France | |
| Demographics | |
| Population | 8,880[1] |

Bora Bora is an island in the Leeward group of the Society Islands of French Polynesia, an overseas collectivity of France in the Pacific Ocean. The island, located about 230 km (140 mi) northwest of Papeete, is surrounded by a lagoon and a barrier reef. In the centre of the island are the remnants of an extinct volcano rising to two peaks, Mount Pahia and Mount Otemanu, the highest point at 727 m (2,385 ft).
Bora Bora is a major international tourist destination, famous for its aqua-centric luxury resorts. The major settlement, Vaitape, is on the western side of the main island, opposite the main channel into the lagoon. Produce of the island is mostly limited to what can be obtained from the sea and the plentiful coconut trees, which were historically of economic importance for copra. According to a census performed in 2008, the permanent population of Bora Bora is 8,880.
Etymology
The original name of the island in the Tahitian language might be better rendered as Pora Pora, meaning First Born; an early transcription found in 18th- and 19th-century accounts, is "Bolabolla" or "Bollabolla". However, the discoverers misunderstood and thought the inhabitants said Bora Bora - the name stuck.
History

The island was first inhabited by Polynesian settlers around the 4th century. Its previous Polynesian name was Vava'u. As there is no B in the Tahitian language, it is actually called Pora Pora, but early visitors misheard it. The first European sighting was made by Jakob Roggeveen in 1722. James Cook sighted the island in 1770 and landed that same year. The London Missionary Society arrived in 1820 and founded a Protestant church in 1890. Bora Bora was an independent kingdom until 1888 when its last queen Teriimaevarua III was forced to abdicate by the French who annexed the island as a colony.
World War II
In World War II the U.S. chose Bora Bora as a South Pacific military supply base, and an oil depot, airstrip, seaplane base, and defensive fortifications were constructed. Known as "Operation Bobcat", it maintained a supply force of nine ships, 20,000 tons of equipment and nearly 7,000 men. Seven massive naval cannons were set up at strategic points around the island to protect it against potential military attack.
However, the island saw no combat as the American presence on Bora Bora went uncontested over the course of the war. Although the base was officially closed on 2 June 1946, many American personnel chose to remain on the island. [citation needed] The World War II airstrip, which was never able to accommodate large aircraft, was French Polynesia's only international airport until Faa'a International Airport was opened in Papeete, Tahiti in 1960.[2]
Commune of Bora Bora
Bora-Bora | |
|---|---|
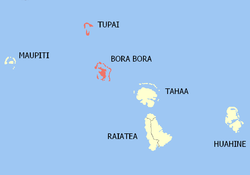 Location of the commune (in red) within the Leeward Islands | |
| Country | France |
| Overseas collectivity | French Polynesia |
| Subdivision | Leeward Islands |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Gaston Tong Sang |
Area 1 | 40.3 km2 (15.6 sq mi) |
| Population (August 2007 census) | 8,927 |
| • Density | 220/km2 (570/sq mi) |
| INSEE/Postal code | 98714 /98730 |
| Elevation | 0–727 m (0–2,385 ft) |
| 1 French Land Register data, which excludes lakes, ponds, glaciers > 1 km2 (0.386 sq mi or 247 acres) and river estuaries. | |
The commune of Bora-Bora is made up of the island of Bora Bora proper with its surrounding islets emerging from the coral reef, 29.3 km² (11.3 sq mi) in total, and of the atoll of Tupai (11 km2 (4.2 sq mi)*), located 20 kilometres (12 mi) north of Bora Bora. The atoll of Tupai has no permanent population apart from some workers in the coconut plantations.
The surrounding islets include: Motu Tapu, Motu Ahuna, Tevairoa, Motu Tane, Motu Mute, Motu Tufari, Motu Pitiaau, Sofitel Motu, Motu Toopua and Toopuaiti.
The commune is in the administrative subdivision of the Leeward Islands and divided into three districts: Vaitape, Faanui and Anau.
Administration
The administrative centre of the commune is the settlement of Vaitape, on the island of Bora Bora. The island is administratively part of the commune (municipality) of Bora-Bora, itself in the administrative subdivision of the Leeward Islands. The commune of Bora-Bora is made up of the island of Bora Bora proper with its surrounding islets emerging from the coral reef, 29.3 km² (11.3 sq mi) in total, and of the atoll of Tupai (11 km2 (4.2 sq mi)*), located 20 kilometres (12 mi) north of Bora Bora. The atoll of Tupai has no permanent population apart from about 50 workers in the coconut plantations. President of French Polynesia Gaston Tong Sang is the current mayor of Bora Bora in addition to being the President.[3]
Tourism

Today the island is almost entirely dependent on tourism. Over the last few years several resorts have been built on motu (small islands, from Tahitian) surrounding the lagoon. Thirty years ago, Hotel Bora Bora built the first over-the-water bungalows on stilts over the lagoon and today, over-water bungalows are a standard feature of most Bora Bora resorts. The quality of those bungalows ranges from comparably cheap, basic accommodations to very luxurious and expensive places to stay. The only camping on the island is Bora Bora Camping at the southern point of Motu Piti Aau.
Most of the tourist destinations are aqua-centric; however it is possible to visit attractions on land such as WWII cannons. Air Tahiti has five or six flights daily to the Bora Bora Airport on Motu Mute from Tahiti (as well as from other islands). The island is served by Bora Bora Airport on Motu Mute in the north, with Air Tahiti providing daily flights to and from Papeete on Tahiti.
Although French and Tahitian are the main languages spoken by the inhabitants, people in contact with tourists generally have some command of English. Most visitors to Bora Bora are American, Japanese, or European.[citation needed]
Public transport on the island is non-existent. Rental cars and bicycles are the recommended method of transport. There are also small fun-cars for hire in Vaitape. It is possible to rent (150$ per 4 hours) motor-driven boat to explore the lagoon.
Snorkeling and scuba diving in and around the lagoon of Bora Bora are popular activities. Many species of sharks and rays inhabit the surrounding body of water. There are a few dive operators on the island offering manta ray dives and also shark-feeding dives.
In addition to the existing islands of Bora Bora (called motu), the new man-made motu of Motu Marfo has been added in the north-eastern corner of the lagoon on the property of the St. Regis Resort.
Climate
| Climate data for Bora-Bora | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 30 (86) |
29 (85) |
30 (86) |
30 (86) |
29 (85) |
29 (84) |
28 (82) |
28 (83) |
28 (83) |
29 (85) |
30 (86) |
29 (85) |
29 (85) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 23 (74) |
23 (74) |
24 (75) |
24 (75) |
24 (76) |
24 (75) |
23 (73) |
23 (74) |
23 (73) |
24 (75) |
24 (75) |
24 (75) |
24 (75) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 470 (18.6) |
260 (10.4) |
130 (5.1) |
210 (8.4) |
33 (1.3) |
48 (1.9) |
210 (8.1) |
56 (2.2) |
200 (7.7) |
64 (2.5) |
180 (7.2) |
400 (15.7) |
2,261 (89.1) |
| Average rainy days (≥ 0.02) | 17 | 16 | 18 | 13 | 9 | 6 | 5 | 1 | 5 | 5 | 6 | 8 | 109 |
| Source 1: Weatherbase[4] | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: [5] | |||||||||||||
Most rainfall occurs during the summer months (November to April) and is accompanied by high humidity, although clear days are not unknown in the middle of January.[citation needed]
Gallery
-
Aerial view of Bora Bora
-
Mount Otemanu
-
The French frigate Floréal, stationed in Bora-Bora lagoon
-
Maohi Protestant Church in Anau
-
Coca-Cola Machine in Vaitape
-
Bora Bora
-
Bora Bora
-
Matira Beach and Lagoon
-
Flag of Bora Bora
See also
References
- ^ Population of the commune of Bora-Bora minus about 50 workers living in the coconut plantations on the atoll of Tupai.
- ^ "Our History". Our History. Office of Post and Telecommunications. Retrieved 18 April 2011.
- ^ "President of French Polynesia steps down". The Australian. 8 February 2009. Retrieved 12 February 2009.
- ^ "Weatherbase: Historical Weather for Bora-Bora, French Polynesia". Weatherbase. 2011. Retrieved 24 November 2011.
- ^ http://worldclimateguide.co.uk/climateguides/frenchpolynesia/vaitapebora-bora.php











