Tetramethylammonium pentafluoroxenate: Difference between revisions
Appearance
Content deleted Content added
Double sharp (talk | contribs) {{chem}} |
|||
| Line 40: | Line 40: | ||
[[Category:Xenon compounds]] |
[[Category:Xenon compounds]] |
||
[[Category:Quaternary ammonium compounds]] |
[[Category:Quaternary ammonium compounds]] |
||
[[fa:تترامتیلآمونیوم پنتافلوروزنات]] |
|||
[[fr:Pentafluoroxénate de tétraméthylammonium]] |
|||
[[ja:ペンタフルオロキセノン酸テトラメチルアンモニウム]] |
|||
[[zh:五氟合氙酸四甲基铵]] |
|||
Revision as of 05:10, 1 March 2013

| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Tetramethylammonium pentafluoridoxenonate(−)
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
| Properties | |||
| N(CH3)4XeF5 | |||
| Molar mass | 300.4308 g/mol | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
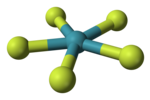
Tetramethylammonium pentafluoroxenate is the chemical compound with the formula N(CH3)4XeF5. The XeF−
5 ion it contains was the first example of a planar pentagonal AX5E2 species.[1] It was prepared by the reaction of N(CH3)4F with xenon tetrafluoride, N(CH3)4F being chosen because it can be prepared in anhydrous form and is readily soluble in organic solvents).[1] The anion is planar, with the fluorine atoms in a slightly distorted pentagonal coordination (Xe-F bond lengths ranging from 197.9 - 203.4 pm and Xe-F bond angles ranging from 71.5 - 72.3 °).[1] Other salts have been prepared with sodium, caesium and rubidium, and vibrational spectra shows that these contain the same planar ion.[1]
References
- ^ a b c d Christe K. O., Curtis E. C., Dixon D. A., Mercier H. P.,. Sanders J. C. P, Schrobilgen G. J. (1991). "The pentafluoroxenate(IV) anion, XeF5−: the first example of a pentagonal planar AX5 species". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 113 (9): 3351–3361. doi:10.1021/ja00009a021.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)