Aza-Diels–Alder reaction: Difference between revisions
Kwamikagami (talk | contribs) m Kwamikagami moved page Aza Diels–Alder reaction to Aza-Diels–Alder reaction |
m Bot: Migrating 2 interwiki links, now provided by Wikidata on d:q2042393 |
||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
[[Category:Name reactions]] |
[[Category:Name reactions]] |
||
[[nl:Aza-Diels-Alder-reactie]] |
|||
[[zh:氮杂双烯狄尔斯–阿尔德反应]] |
|||
Revision as of 12:14, 14 March 2013
The aza-Diels–Alder reaction converts imines and dienes to tetrahydropyridines. This organic reaction is a modification of the Diels–Alder reaction. The nitrogen atom can be part of the diene or the dienophile.
The imine is often generated in situ from an amine and formaldehyde. An example is the reaction of cyclopentadiene with benzylamine to an aza norbornene.[1]

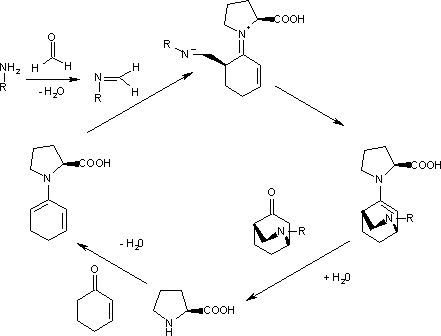
In the enantioselective Diels–Alder (DA) reaction of an aniline, formaldehyde and a cyclohexenone catalyzed by (S)-proline even the diene is masked.[2]

The catalytic cycle starts with the reactions of the aromatic amine with formaldehyde to the imine and the reaction of the ketone with proline to the diene. The second step, an endo trig cyclisation, is driven to one of the two possible enantiomers (99% ee) because the imine nitrogen atom forms a hydrogen bond with the carboxylic acid group of proline on the Si face. Hydrolysis of the final complex releases the product and regenerates the catalyst.
See also
References
- ^ N-benzyl-2-azanorbornene Paul A. Grieco and Scott D. Larsen Organic Syntheses, Coll. Vol. 8, p.31; Vol. 68, p.206 Article
- ^ Direct Catalytic Enantioselective Aza-Diels-Alder Reactions Henrik Sundén, Ismail Ibrahem, Lars Eriksson, Armando Córdova Angewandte Chemie International Edition 4877 2005 Abstract
