Scandium(III) trifluoromethanesulfonate: Difference between revisions
Appearance
Content deleted Content added
m r2.7.3) (Robot: Modifying fa:تریفلوئورومتانسولفونات اسکاندیم(III) |
m Bot: Migrating 1 interwiki links, now provided by Wikidata on d:q6364879 |
||
| Line 54: | Line 54: | ||
[[fa:تریفلوئورومتانسولفونات اسکاندیم(III)]] |
[[fa:تریفلوئورومتانسولفونات اسکاندیم(III)]] |
||
[[sr:Skandijum(III) trifluorometansulfonat]] |
|||
Revision as of 19:04, 14 March 2013

| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Scandium trifluoromethanesulfonate
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.157.499 |
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C3F9O9S3Sc | |
| Molar mass | 492.16 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Scandium trifluoromethanesulfonate, commonly called scandium triflate, is a chemical compound with formula Sc(SO3CF3)3, a salt consisting of scandium cations Sc3+ and triflate SO3CF3− anions.
Scandium triflate is used as a reagent in organic chemistry as a Lewis acid.[1] Compared to other Lewis acids this reagent is stable towards water and can often be used in an organic reaction as a true catalyst rather than one used in stoichiometric amounts. The compound is prepared by reaction of scandium oxide with trifluoromethanesulfonic acid.
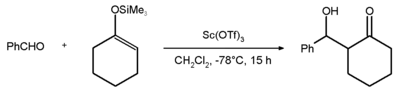
An example of the use of scandium triflate is the Mukaiyama aldol addition reaction between benzaldehyde and the silyl enol ether of cyclohexanone with an 81% chemical yield.[2]
References
- ^ Deborah Longbottom (1999). "SYNLETT Spotlight 12: Scandium Triflate". Synlett. 1999 (12): 2023. doi:10.1055/s-1999-5997.
- ^ S. Kobayashi (1999). "Scandium Triflate in Organic Synthesis". Eur. J. Org. Chem. 1999: 15–27. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1099-0690(199901)1999:1<15::AID-EJOC15>3.0.CO;2-B.
Wikimedia Commons has media related to Scandium(III) triflate.