Asturian language: Difference between revisions
Moving "Education" section |
Fixing data. This happened in 1798, ---> XVIII century. |
||
| Line 336: | Line 336: | ||
Other important writers were: [[Francisco Bernaldo de Quirós Benavides]] (1675), '''[[Josefa Jovellanos|Xosefa Xovellanos]]''' (1745), [[Xuan González Villar y Fuertes]] (1746), '''[[José Caveda y Nava|Xosé Caveda y Nava]]''' (1796), [[Juan María Acebal|Xuan María Acebal]] (1815), [[Teodoro Cuesta]] (1829, Xosé Benigno García González, ''[[Marcos del Torniello]]'' (1853), [[Bernardo Acevedo y Huelves]] (1849), '''[[Pín de Pría]]''' (1864), Galo Fernández, '''[[Fernán Coronas]]''' (1884), etc. |
Other important writers were: [[Francisco Bernaldo de Quirós Benavides]] (1675), '''[[Josefa Jovellanos|Xosefa Xovellanos]]''' (1745), [[Xuan González Villar y Fuertes]] (1746), '''[[José Caveda y Nava|Xosé Caveda y Nava]]''' (1796), [[Juan María Acebal|Xuan María Acebal]] (1815), [[Teodoro Cuesta]] (1829, Xosé Benigno García González, ''[[Marcos del Torniello]]'' (1853), [[Bernardo Acevedo y Huelves]] (1849), '''[[Pín de Pría]]''' (1864), Galo Fernández, '''[[Fernán Coronas]]''' (1884), etc. |
||
In the |
In the XVIII century, the erudite and intellectual [[Gaspar Melchor de Jovellanos]] was conscious of the historical and cultural value of what he termed “''our language''” and expressed the urgency for the compilation of a dictionary and a grammar and for the creation of a [[Academy of the Asturian Language|Language Academy]]. It took more than a century for the efforts of Asturian politicians to turn this into reality. |
||
In [[1974]], which was a symbolic year, a movement for acceptance and usage of the language surfaced once again in Asturias. Based on the ideas of the Asturian association named «[[Conceyu Bable]]», regarding Asturian language and culture, an argument was devised for the acceptance and modernization of the language that led to the development of an official institution for establishing Asturian language norms. In [[1980]] the [[Academy of the Asturian Language]] ([[1980]]), created with the approval of the [[Asturias|Regional Council of Asturias]] (the transitory government body of Asturias). |
In [[1974]], which was a symbolic year, a movement for acceptance and usage of the language surfaced once again in Asturias. Based on the ideas of the Asturian association named «[[Conceyu Bable]]», regarding Asturian language and culture, an argument was devised for the acceptance and modernization of the language that led to the development of an official institution for establishing Asturian language norms. In [[1980]] the [[Academy of the Asturian Language]] ([[1980]]), created with the approval of the [[Asturias|Regional Council of Asturias]] (the transitory government body of Asturias). |
||
Revision as of 11:17, 24 March 2013
| Asturian | |
|---|---|
| Astur-Leonese | |
| asturianu | |
| Native to | |
| Region | |
Native speakers | 110,000 (2007)[2] 450,000 L2 speakers (1994) |
| Dialects | |
| Latin | |
| Official status | |
| Regulated by | Academy of the Asturian Language (Asturian) |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-2 | ast |
| ISO 639-3 | ast |
| ELP | Asturian |
| Linguasphere | 51-AAA-ca |
 Linguistic area of asturian language | |
Asturian (/[invalid input: 'icon']æsˈtʊə.ri.ən/;[3] autonym: Asturianu; /astu'ɾjanu/[1]); is a Romance language of the West Iberian group, Astur-Leonese subgroup, spoken in Asturias (Spain). Asturian is also known as Astur-Leonese or Asturian-Leonese to refer to the language in its historical and current global expansion. The current number of speakers of Asturian is estimated about 100,000 first language speakers and 450,000 second language speakers.[4] There are three predominant variants in the asturleonese linguistic domain (Western, Central and Eastern), although in the case of Asturias, for historical and demographics reasons, the standard is based on the Central Asturian. Asturian has a grammar, a dictionary of the Asturian language, and a ortography. It's regulated by the Academy of the Asturian Language, and even though it is not an official language,[5] it's protected under the autonomous statute legislation and is an optional language at schools.[6]
History
Asturian is the autochthonous language of Asturias (Spain) and some parts of the provinces of León and Zamora (Spain) and the area surrounding the city of Miranda do Douro (Portugal) see this map[1].
Like other Romance languages in the Iberian peninsula, it developed out of the break-up of unified Latin in the early Middle Ages. In historical terms Asturian became closely linked with the ancient Kingdom of Asturias (718–910) and the ensuing Asturian-Leonese or Leonese kingdom.
The language developed from Vulgar Latin with contributions from the pre-Roman languages which were spoken in the territory of the Astures, an ancient tribe of the Iberian peninsula.
The passage from Latin to Asturian was slow and progressive, and for a long period both co-existed in a diglossic relationship, in the Kingdom of Asturias first and that of Asturias and Leon later. In the 12th, 13th and part of the 14th centuries, the language used in official documents of the kingdom was Asturian. Many examples can be found of agreements, donations, wills, commercial contracts, etc. written in the language from that period onwards. Although there are no extent literary works written in Asturian in this period, it is known that some books, such as the "Llibru d'Alexandre", and also "Fueru d'Avilés" (1155)[7][8] had Asturian sources.
Castilian Spanish came to the area later, in the 14th century, when the central administration sent emissaries and functionaries to occupy political and ecclesiastical offices. Nowadays, Asturian codification of Astur-Leonese spoken in the Asturian Autonomous Community has become a modern language, after the birth of "Academy of the Asturian Language" in 1980. Mirandese is very close to Asturian.
Status and legislation
Much effort has been made since 1974 to protect and promote Asturian.[9] In 1994, there were 100,000 first-language speakers, and 450,000[10] second-language speakers able to speak or understand Asturian.[11] However, the situation of Asturian is critical, with a large decline in the number of speakers in the last 100 years.
- Law 1/93, of March 23, on the Use and Promotion of the Asturian Language
- Article 4 of Asturias 'Statute of Autonomy' provides:[1] The Asturian language will enjoy protection. Its use, teaching and diffusion in the media will be furthered, whilst its local dialects and voluntary apprenticeship will always be respected.
Thus, Asturian has an anomalous situation from the legal point of view. The Spanish Constitution, as far as the official recognition of languages in the autonomous communities is concerned, has not been fully applied. Nor have European and other international instruments on minority languages been applied. The ambiguity of the Statute of Autonomy, which recognises the existence of Asturian but does not put it on the same level than Spanish, leaves the door open to the de facto lack of protection of Asturian.
In a research from 1983,[12] the figure of 100,000 speakers of Asturian appeared to be a reasonable estimate. In addition, about 250,000 people declared they were able to understand the language. However, a similar survey was repeated in 1991 and the results were rather different. While in 1983 only 12% of the Asturian population declared they spoke the language, in 1991 the number of speakers within the population was 44% (about 450,000 people). About 80,000 and 60,000 people declare being able to read and write it. In addition to this, another 24% of the Asturian population understand the language. Thus, 68% of the people at least understand Asturian (Source: Llera Ramo, F.: Los Asturianos y la Llengua Asturiana. Conseyería d'Educación, Uviéu, 1994).
At the end of the 20th century, the Academia de la Llingua Asturiana made efforts to provide the language with most of the tools needed by a language to ensure its survival: a grammar, a dictionary, and periodicals. A new generation of Asturian writers have also championed the language. These developments give the Asturian language a greater hope of survival.
Dialectal variation
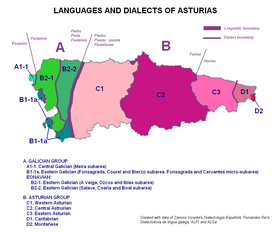

Asturias has also its own dialectal variation. Asturian is regulated by Academy of the Asturian Language and is mostly spoken in the Principality of Asturias (except for the westernmost part where Galician-Asturian is spoken). The dialects in adjoining areas of Castilla y León have continuity with the Asturian dialects; in that area they are referred to as Leonese. Attending only to purely linguistic criteria, the Asturian language is traditionally divided into three dialectal areas, which share their traits with the dialects spoken in León: [13] Western Asturian, Central Asturian, and Eastern Asturian. Intelligibility among the three dialects is adequate. Central Asturian has the most speakers (+80%) and has been taken as the basis for normative Asturian: the first Asturian grammar was published in 1998. The first normative dictionary was published in 2000.
Western Asturian
Western Asturian, is a linguistic variety in Western Asturian lands between the rivers Navia and Nalón, and western provinces of León, where is called Leonese as endonym, Zamora and Salamanca. Its area is defined by the following traits:
- – Female plurals in -as.
- – Maintenance of falling diphthongs /ei/ /ou/.
Central Asturian
Area between the Sella river and a full line from the mouth of the Nalón river, in Asturias, and north of León. It has been taken as the model for the written language. Its area is defined by these traits:
- – Female plurals in -es.
- – Compression of diphthongs /ou/, /ei/ in /o/ and /e/.
- – Neutral gender (Neutro de materia/Neuter of matter)[14] in adjetives applied to uncountable nouns. Examples: Lleche frío, carne tienro. This distinguishes it from the Western Asturian area.
Eastern Asturian
Eastern Asturian is a variant spoken between the Sella river and Llanes area, and the limit of Cabrales (Peñamellera Alta). This area is defined by the following traits:
- – Sound 'voiceless glottal fricative' (represented with the spelling ḥ) in words that usually begins in "f" in the rest of the linguistic domain. Examples: ḥoguera, ḥacer, ḥigos, ḥornu, instead of: foguera, facer, figos and fornu.
- – Female plurals in -as. Examples: ḥabas, ḥormigas, ḥiyas. (except in the towns closest to the eastern bank Seya where -es is kept: ḥabes, ḥormigues, ḥiyes, etc.)
- – Final transformation of -e in -i. Examples: xenti, tardi, ḥuenti.
- – In some areas, it retains the neutral gender (Neutro de materia/Neuter of matter),[14] closing -o in -u: agua friu, xenti güenu, ropa tendíu, carne guisáu, etc.
- – In some municipalities ('conceyos') bordering the Sella river, both east and west, appears in its pronominal system differentiating between direct pronouns me/te and indirect mi/ti. Examples: Busquéte (a ti) y alcontréte/Busquéti les llaves y alcontrétiles. Llévame (a mi)/Llévami la fesoria/h.osoria en carru.
Transitional varieties
The Asturian language has dialectal continuity with Cantabrian dialect to the east, and with Eonavian to the west:
- Cantabrian dialect or Montañés: the dialect is spoken in Eastern Asturian and some zones of Cantabria: Valley of Pas and the Valley of Soba. Cantabrian was listed in the UNESCO Red Book of the World’s Languages in Danger in 2009, in the Astur-Leonese linguistic group as a definitely endangered language.[15]
- Galician-Asturian or Eonavian: Controversy exists regarding the inclusion of Eonavian (spoken in the western end of Asturias, bordering Galicia) into the Galician language, as it has some traits in common with Western Asturian (spoken in the middle west of Asturias). There are those defending these linguistic varieties as dialects of transition to the Astur-Leonese group on the one hand, and those defending it as clearly Galician varieties on the other.
Linguistic description
Asturian belongs to Astur-Leonese linguistic group, which forms part of the Ibero-Romance languages, typologically and phylogenetically close to Galician-Portuguese, Castilian and less to Navarro-Aragonese. It's a typologically inflecting/Fusional language, head-initial and dependent-marking language and the basic order is SVO (declarative sentences without topicalization).
Phonology
The transcript is consistent with the rules of the International Phonetic Alphabet.
Vowels
The system distinguishes five vowel phonemes of Asturian divided into three degrees of aperture (minimum, medium and maximum) and three situations (center, front and back).
| front (palatals) |
centrals | back (velars) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| close vowels (min aperture) |
i | - | u |
| mid vowels (mid aperture) |
e | - | o |
| open vowels (max aperture) |
- | a | - |
Consonants
Consonants labials dentals alveolars palatals velars occlusive voiceless p t tʃ k occlusive voiced b d ʝ g fricatives f θ s ʃ - nasals m - n ɲ - Laterals - - l ʎ - Flap alveolar - - r / ɾ - -
Notes:
- /n/ is pronounced like [ŋ] in coda position.
- /g/ usually pronounced as fricative voiced in initial word.
Writing
Since the earliest texts, the Latin alphabet was used in the Asturian language. In 1981, the Academia de la Llingua Asturiana published its orthographic rules.[16] However, in the Terra de Miranda (Portugal) different spelling rules are used.
Asturian orthographic rules in reading and writing practice shows clearly the model pursued in the written language that can be summarized by saying that it is based on a five-vowel system units /a e i o u/ with three aperture degrees and double location. Similarly, it has the following consonant units: /p t ĉ k b d y g f θ s š m n ņ l ḷ r ṙ/ . The model approaches to a written form where the phenomenon of -u metaphony is not frequent, nor the presence of decrescent diphthongs / ei, ou /, usually in the west area. Although they can be written, ḷḷ (che vaqueira, also represented formerly with spellings such as "ts") and the eastern 'ḥ' aspiration (also represented as "h.") corresponding to 'll' and 'f' don't appear in this model. Grammatically, the language offers triple gender distinction in the adjective, feminine plurals with -es, verb endings with -es, -en, -íes, íen, absence of compound tenses[16] (or periphrasis constructed with “tener”, etc.).
The model is not arbitrary, since it is provided as a rather common possibility in former writers, although the focus on the central varieties is a fact, the written form does not considers any spoken dialect as a main model. In the same way, the development of any local variety is accepted. In addition, speech with which students are familiar is mindful in teaching, necessary condition to achieving a proper pedagogy.
Alphabet
| Uppercase | A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | L | M | N | Ñ | O | P | R | S | T | U | V | X | Y | Z |
| Lowcase | a | b | c | d | e | f | g | h | i | l | m | n | ñ | o | p | r | s | t | u | v | x | y | z |
| Name | a | be | ce | de | e | efe | gue | hache | i | ele | eme | ene | eñe | o | pe | erre | ese | te | u | uve | xe | ye | zeta(*) |
| Phoneme | a | b | θ / k | d | e | f | g | - | i | l | m | n | ɲ | o | p | ɾ/r | s | t | u | b | ʃ | ʝ | θ |
- (*)also zeda, ceda
Digraphs
Asturian also has several digraphs, some of which have their own names.
| Diagraph | Name | Phoneme |
|---|---|---|
| ch | che | /t͡ʃ/ |
| gu + e, i | -- | /ɡ/ |
| ll | elle | /ʎ/ |
| qu + e, i | cu | /k/ |
| rr | erre doble | /r/ |
| ts | (te ese) | /t͡s/ (dialectal) |
| yy | (ye doble) | /kʲ/ (dialectal) |


Dialectal spellings
Furthermore, the letter h and the digraph ll can have their sound changed to represent dialectal pronunciation by underdotting the letters, resulting ḥ and digraph ḷḷ
| Normal | Pronunciation | Dotted | Pronunciation | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ll | /ʎ/ | ḷḷ | /t͡s/, /ɖʐ/, /ɖ/ and /ʈʂ/ | Ḷḷeite, Ḷḷinu |
| h | -- | ḥ | /h/, /x/ | ḥou, ḥenu, ḥuera |
- The 'ḥ' is commonly in the place names of Eastern Asturian, and in words that have the beginning in "f" in the rest of the linguistic domain,[17] while certain workarounds as "h." and "l.l" were used in the past to solve the lack of the real characters for printing.
Grammar

The grammar of Asturian resembles that of other Romance languages. Nouns have two genders (masculine and feminine), two numbers (singular and plural), and no cases. Adjectives can have a third gender (neuter), a grammatical phenomenon widely studied in the Asturian continuum and known as "matter-neutrality".[17] Verbs agree with their subjects in person (first, second, or third) and number, and additionally are conjugated to indicate mood (indicative, subjunctive, conditional, or imperative), tense (often present or past; different moods allow different possible tenses), and aspect (perfective or imperfective).[17]
Vocabulary
The vast majority of the words of the Asturias, as the other Romance languages, come from the Latin:
- Ablana, agua, falar, güeyu, home, llibru, muyer, pesllar, pexe, prau, suañar.
To this Latin basis, we must add words that entered in the Asturian lexicon background, from languages spoken before the arrival of the Latin (Substratum) or after (superstratum). To the influence of substratum and superstratum are added subsequent loans from other languages.
Substratum
- There is very little information about the language of the ancient astures, although it is possible that it was related with two Indo-European languages: Celtic and Lusitanian. The words of the ancient astures or other preIndo-European languages spoken in this area, are grouped under the name of prelatinian substratum. Several examples are:
- Bedul, boroña, brincar, bruxa, cándanu, cantu, carrascu, comba, cuetu, güelga, llamuerga, llastra, llócara, matu, peñera, riega, tapín, zucar...
- Also, many Celtic words were integrated into Latin, and later to the Asturian language.
- Bragues, camisa, carru, cerveza, sayu...
Superstratum
- The languages that came after Latin, were very important in the development of the Asturian language. In this case, they were particularly important Germanisms and Arabisms:
- Germanisms
- The Germanic peoples who stood in the Iberian Peninsula, especially Goths and Suevi, added words to Asturian like:
- Blancu, esquila, estaca, mofu, serón, espetar, gadañu o tosquilar.
- Arabisms
- The Arabisms could reach Asturian language directly, through contacts between the Asturian domain speakers with Arabs, or Southern Peninsula. In other cases could reach through the Castilian language. Some examples:
- Acebache, alfaya, altafarra, bañal, ferre, galbana, mandil, safase, xabalín, zuna, zucre
Loans
- The Asturian language also received much of its lexicon, from languages as Castilian, French, Occitan or Galician. In order of importance, the Spanish forms are in the first place on the list of loans to the Asturian. However in some cases, due to the great closeness between Castilian and the Asturian is quite difficult to know if a word is borrowed from Castilian, a common result to both languages from Latin, or a loan of the same Asturian into Castilian. Some Castilian forms in Asturian are:
Historical, social and cultural aspects
History of the literature


Some documents appear from as early as the 10th century containing the clear linguistic features of Asturian. However, it is from the 13th century onwards that it becomes possible to speak of a wealth of documentation in Asturian: writing by notaries, contracts, wills and the like. The importance of the Asturian language in the Middle Ages is revealed, for example, in the Fuero de Avilés (1085) (considered to be the first document written in Romanic) and the Fuero de Oviedo, in the Asturian version of the Fuero Juzgo as well .
All of these (XIII century) documents were legal in nature and acted as the laws for towns and cities or for the population at large. However, it is of note that by the second half of the XVI century documents were clearly coming to be written in the Castilian language, backed deliberately by the Trastámara Dynasty making the civil and ecclesiastical service of the Principality of Castilian origin. As a result, the Asturian language disappeared from written texts ('sieglos escuros' or Dark centuries) but continued to survive orally by being handed down from generation to generation. The only reference in this time is a work of Hernán Núñez (1555) about Proverbs and adages, «[...] ...in a large copy of rare languages, as Portuguese, Galician, Asturian, Catalan, Valencian, French, Tuscan...»[18]
Modern Asturian literature began in the XVII century with the clergyman Antón González Reguera (1605) and continued up until the XVIII century when it produced, according to Ruiz de la Peña (1981), a literature that could stand up to the best written in Asturias in the same period in the Castilian language.
Other important writers were: Francisco Bernaldo de Quirós Benavides (1675), Xosefa Xovellanos (1745), Xuan González Villar y Fuertes (1746), Xosé Caveda y Nava (1796), Xuan María Acebal (1815), Teodoro Cuesta (1829, Xosé Benigno García González, Marcos del Torniello (1853), Bernardo Acevedo y Huelves (1849), Pín de Pría (1864), Galo Fernández, Fernán Coronas (1884), etc.
In the XVIII century, the erudite and intellectual Gaspar Melchor de Jovellanos was conscious of the historical and cultural value of what he termed “our language” and expressed the urgency for the compilation of a dictionary and a grammar and for the creation of a Language Academy. It took more than a century for the efforts of Asturian politicians to turn this into reality.
In 1974, which was a symbolic year, a movement for acceptance and usage of the language surfaced once again in Asturias. Based on the ideas of the Asturian association named «Conceyu Bable», regarding Asturian language and culture, an argument was devised for the acceptance and modernization of the language that led to the development of an official institution for establishing Asturian language norms. In 1980 the Academy of the Asturian Language (1980), created with the approval of the Regional Council of Asturias (the transitory government body of Asturias).
Besides this, there was unprecedented literary activity, a production that breaks away from the system of subordination, of costumbrism and gender limitation: «el Surdimientu» (Awakening). Authors such as Manuel Asur (Cancios y poemes pa un riscar), Xuan Bello (El llibru vieyu), Adolfo Camilo Díaz (Añada pa un güeyu muertu), Pablo Antón Marín Estrada (Les hores), Xandru Fernández (Les ruines), Lourdes Álvarez, Martín López-Vega, Miguel Rojo, Lluis Antón González and dozens more writers appeared, amongst others who wrote in the language of these territories in line with contemporary trends and guidelines, breaking away from the Asturian-Leonese tradition of rural themes, moral messages and dialogue-style writing, to put Asturian language literature on the map.
Nowadays the Asturian language is a living reality within the territory of Asturias, with about 150 annual publications[19], while small communities speaking Asturian can also be found in areas that do not belong administratively to the Principality.
Toponimy

Traditional and popular place names of the towns of the Principality is enjoying significant progress in recent years, in the context of the "Ley de Uso" (law on usage of Asturian) and the «Principality’s 2003-07 plan for Establishment of the Language»[20], with the work of the Xunta Asesora de Toponimia[21], which with its validation of, and research into, the names of those villages, towns, conceyos (municipalities) and cities that have requested it, has been able to achieve official status for them — of which there are 50 out of 78 conceyos at the moment (2012), with a further 28 conceyos at varied stages in the process—. In Leonese areas, there have been no officially recognized Asturian-Leonese names for the towns, and no research has been undertaken into this or any record of possible names has been made.
Education
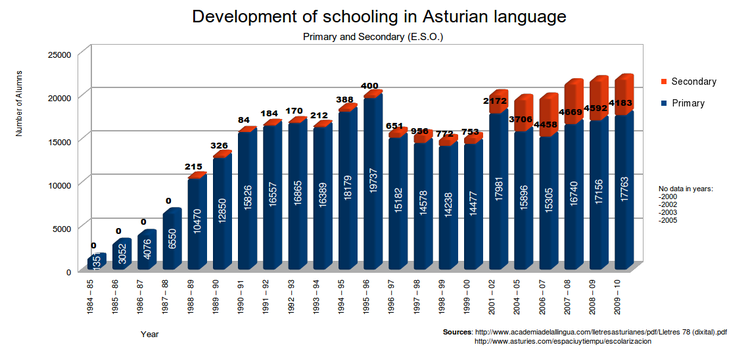
Primary and Secondary
Although Spanish (Castillian) is the official language used in all schools in Asturias, in many of them children are allowed to take Asturian language classes from the ages of 6 to 16. Optional classes are offered from ages 16 to 19. The Central area of Asturias (Nalón and Caudal comarcas), has the highest schooling in Asturian language, with almost 80% of students in primary, plus 30% in secondary.[22] Gijón/Xixón comarca, remains with percentages above 52% and 13% in Primary and Secondary zones are continuously growing as Oviedo/Uviéu, Eo-Navia and Oriente (Eastern comarca).
University
The current charter of the University of Oviedo expressly indicates in Article 6 that: “The University of Oviedo, due to its historical, social and economic links with the Principality of Asturias, will devote particular attention to the cultural aspects and collective interests of Asturias. The Asturian Language will be treated appropriately in accordance with legislation. Nobody will be discriminated against for using it”.[25]
In other words, Asturian can be used at the university in line with the Use of Asturian Act. However, practice shows that this is a minority activity and is preferred for subjects related to the philological study of Asturian (linguistic, socio-linguistic, educational, etc.). The Scientific Memoranda of the University show the increased presence of courses and scientific work that employ Asturian. In the courses based in the Department of Philology and Educational Sciences, there are distinct subjects[26] relating to the Asturian language that show an acceptance and demand among students.
Also, with the new Bologna process people will be able to study Asturian Philology in the same way as Spanish Philology [2], and school-teachers will be able to do a speciality in the Asturian language. But these two possibilities can only be studied in the University of Oviedo (Asturias).
Internet
Many internet pages use the Asturian language; Government[27] the council's pages, blogs,[28] music groups' pages, Social networking services[29] and more.
Ubuntu offers Asturian as a full operating system language.[30][31] Also Debian and Fedora is offered in asturian language. Supply of software products in Asturian language is large: Firefox, Thunderbird, LibreOffice, VLC, Gnome, Chromium, KDE, etc. (...see more [3])
See also
- Leonese language
- Mirandese language
- List of Asturian language authors
- Cantabrian dialect
- Extremaduran language
- Ramón Menéndez Pidal
References
- ^ a b c Art. 1 de la Ley 1/1998, de 23 de marzo, de uso y promoción del bable/asturiano/Law 1/93, of March 23, on the Use and Promotion of the Asturian Language.
- ^ Asturian at Ethnologue (17th ed., 2013)

- ^ Asturian Dictionary.com Unabridged. Random House, Inc. (Retrieved 15 March 2013).
- ^ Ethnologue report for Asturian
- ^ http://www.elcomerciodigital.com/gijon/20090112/local/asturias/miembro-andecha-astur-enfrenta-200901121726.html
- ^ See: Euromosaic report
- ^ http://cvc.cervantes.es/lengua/thesaurus/pdf/04/TH_04_003_141_0.pdf
- ^ http://arqueologiaypatrimonio.blogspot.com.es/2009/12/el-ayuntamiento-adquiere-una.html
- ^ Bauske 1995
- ^ PROEL Report
- ^ Llera Ramo 1994
- ^ http://www.unioviedo.es/reunido/index.php/RFA/article/download/9260/9111
- ^ http://www.uoc.edu/euromosaic/web/document/asturia/an/i1/i1.html
- ^ a b Xulio Viejo Fdz. Univerdad de Oviedo Based on a work of ANDRÉS DIAZ, R. 1993: "Emplegu del neutru n'asturianu", Lletres Asturianes 49, págs.49-84, IDEM 1994: "Aspeutos morfolóxicos del neutru n'asturianu", Editorial Complutense, Madrid, págs. 9-30, IDEM 1998: "Concordancias y referencias neutras en asturiano", Atti del XX/Congresso Internaziomale di Linguistica e Filologia Romanza (Palermo 18-24 settembre 1995), Max Niemeyer, Tübingen, v.II, págs. 39-47. Cite error: The named reference "neutro/materia" was defined multiple times with different content (see the help page).
- ^ UNESCO Interactive Atlas of the World’s Languages in Danger, where cantabrian language is listed in the Astur-Leonese linguistic group.
- ^ a b [http://www.academiadelallingua.com/diccionariu/normes.pdf Normes ortográfiques de la Llingua Asturiana Cite error: The named reference "Normes" was defined multiple times with different content (see the help page).
- ^ a b c Academia de la Llingua Asturiana, Gramática de la Llingua Asturiana, tercera edición, Oviedo: Academia de la Llingua Asturiana (2001), ISBN 84-8168-310-8, http://www.academiadelallingua.com/diccionariu/gramatica_llingua.pdf Cite error: The named reference "Gramática de la llingua" was defined multiple times with different content (see the help page).
- ^ Los refranes o proverbios en Romance, Hernán Nuñez, pag 12
- ^ Catalog of publications in 2011
- ^ Decretu 98/2002, de 18 de xunetu pel que s'establez el procedimientu de recuperación y afitamientu de la toponimia asturiana
- ^ Xunta asesora de Toponimia. 38/2002, de 4 d'abril, pel que se regula la Xunta Asesora de Toponimia del Principau d'Asturies
- ^ http://archivo.lavozdeasturias.es/html/263549.html (2006)
- ^ http://www.asturies.com/espaciuytiempu/escolarizacion
- ^ http://www.academiadelallingua.com/lletresasturianes/pdf/Lletres%2078%20%28dixital%29.pdf
- ^ http://www.crue.org/export/sites/Crue/legislacion/documentos/estatutosuniversidades/Oviedo.pdf
- ^ http://directo.uniovi.es/catalogo/FichaAsignatura.asp?asignatura=2123 http://directo.uniovi.es/catalogo/FichaAsignatura.asp?asignatura=2123, Conocimiento global de la realidad la lengua asturiana, de su unidad e independencia al margen de los fenómenos de variación interna y de su integración en el marco hispano-románico, a partir de un enfoque esencialmente histórico y diacrónico.
- ^ Government of the Principality of Asturias - Official Website
- ^ Blog Channel in Asturian language
- ^ Ximielga.me Social networking service in Asturian
- ^ http://www.jonobacon.org/2009/09/30/ubuntu-in-your-language
- ^ Stats of Translations in Ubuntu 12.10
Bibliography
- Template:Es Llera Ramo, F. (1994) Los Asturianos y la Lengua Asturiana: Estudio Sociolingüístico para Asturias-1991. Oviedo: Consejería de Educación y Cultura del Principado de Asturias ISBN 84-7847-297-5.
- Wurm, Stephen A. (ed) (2001) Atlas of the World's Languages in Danger of Disappearing. Unesco ISBN 92-3-103798-6.
- Transclusion error: {{En}} is only for use in File namespace. Use {{langx|en}} or {{in lang|en}} instead. M.Teresa Turell (2001). Multilingualism in Spain: Sociolinguistic and Psycholinguistic Aspects of Linguistic Minority Groups. ISBN 1-85359-491-1
- Transclusion error: {{En}} is only for use in File namespace. Use {{langx|en}} or {{in lang|en}} instead. Mercator-Education (2002): European Network for Regional or Minority Languages and Education. "The Asturian language in education in Spain" ISSN 1570-1239
External links
- Academia de la Llingua Asturiana – the official Asturian language academy
- Dirección Xeneral de Política Llingüística del Gobiernu del Principáu d'Asturies – Bureau of Asturian Linguistic Politics (Government of the Principality of Asturias)
- Ethnologue report for Asturian
- Asturian grammar in English
- Asturian–English dictionary
- Xunta pola Defensa de la Llingua Asturiana
- Real Instituto de Estudios Asturianos – Royal Institute of Asturian Studies (RIDEA or IDEA), founded 1945.
- A short Asturian–English–Japanese phrasebook incl. sound file
- Aconceyamientu de Xuristes pol Asturianu The Advisory Council of Lawyers for Asturian
