Victoria (state): Difference between revisions
| Line 480: | Line 480: | ||
The [[Road transport in Victoria|Victorian road network]] services the population centres, with highways generally radiating from Melbourne and other major cities and rural centres with secondary roads interconnecting the highways to each other. Many of the highways are built to freeway standard ("M" freeways), while most are generally sealed and of reasonable quality. |
The [[Road transport in Victoria|Victorian road network]] services the population centres, with highways generally radiating from Melbourne and other major cities and rural centres with secondary roads interconnecting the highways to each other. Many of the highways are built to freeway standard ("M" freeways), while most are generally sealed and of reasonable quality. |
||
[[File: |
[[File:D2.5007 + C2.5111 bourke.JPG|thumb|230px|left|A current [[Trams in Melbourne|Melbourne]] [[C2-class Melbourne tram|C 2 class]] (Citadis) and a [[D-class Melbourne tram|D-class]] tram]] |
||
[[Rail transport in Victoria]] is provided by several private and public railway operators who operate over government-owned lines. Major operators include: [[Metro Trains Melbourne]] which runs an extensive, electrified, passenger system throughout Melbourne and suburbs; [[V/Line]] which is now owned by the Victorian Government, operates a concentrated service to major regional centres, as well as long distance services on other lines; [[Pacific National]], [[CFCLA]], [[El Zorro (railway)|El Zorro]] which operate freight services; [[Great Southern Railway (Australia)|Great Southern Railway]] which operates [[The Overland]] Melbourne—Adelaide; and [[CountryLink]] which operates [[XPT (Train)|XPTs]] Melbourne—Sydney. |
[[Rail transport in Victoria]] is provided by several private and public railway operators who operate over government-owned lines. Major operators include: [[Metro Trains Melbourne]] which runs an extensive, electrified, passenger system throughout Melbourne and suburbs; [[V/Line]] which is now owned by the Victorian Government, operates a concentrated service to major regional centres, as well as long distance services on other lines; [[Pacific National]], [[CFCLA]], [[El Zorro (railway)|El Zorro]] which operate freight services; [[Great Southern Railway (Australia)|Great Southern Railway]] which operates [[The Overland]] Melbourne—Adelaide; and [[CountryLink]] which operates [[XPT (Train)|XPTs]] Melbourne—Sydney. |
||
Revision as of 10:47, 18 April 2013
37°0′S 144°0′E / 37.000°S 144.000°E Template:Australia state or territory Victoria (abbreviated as Vic.) is a state in the south-east of Australia. Geographically the smallest mainland state, Victoria is bordered by New South Wales to the north, the Tasman Sea to the east, the Bass Strait and Tasmania to the south,[note 1] and South Australia to the west. Australia's most densely-populated state, most of Victoria's population is concentrated in the area surrounding Port Phillip, including the capital and largest city, Melbourne, which is also Australia's second-largest city overall.
Prior to European settlement, the area now constituting Victoria was inhabited by a large number of Aboriginal peoples, collectively known as the Koori. With Great Britain having claimed the entire Australian continent east of the 135th meridian east in 1788, Victoria was included in the wider colony of New South Wales. The first settlement in the area occurred in 1803 at Sullivan Bay, and much of what is now Victoria was included in the Port Phillip District in 1836, an administrative division of New South Wales. Victoria was officially created a separate colony in 1851, and achieved self-government in 1856. The Victorian gold rush in the 1850s and 1860s significantly increased both the population and wealth of the colony, and by the Federation of Australia in 1901, Melbourne had become the leading financial centre in Australasia. With Canberra still under construction, Melbourne also served as interim capital of Australia until 1927, with the Federal Parliament meeting in Parliament House.
Politically, Victoria has 37 seats in the Australian House of Representatives and 12 seats in the Australian Senate, with the majority belonging to the Labor Party. At state level, the Parliament of Victoria consists of the Legislative Assembly (the lower house) and the Legislative Council (the upper house). Victoria is currently governed by a coalition between the Liberal Party and the National Party, with the Liberals' Denis Napthine the current premier. The personal representative of the Queen of Australia in the state is the Governor of Victoria, currently Alex Chernov. Local government is concentrated in 79 municipal districts, including 33 cities, although a number of unincorporated areas still exist, which are administered directly by the state.
The economy of Victoria is largely based around the financial and property sectors, although the manufacturing, services, and retail sectors constitute the majority of the workforce. Victoria's total gross state product (GSP) is ranked second in Australia behind New South Wales, although Victoria is ranked sixth in terms of GSP per capita. Culturally, Melbourne is home to a number of museums and art galleries, and has also been described as the "sporting capital of Australia". The Melbourne Cricket Ground is the largest stadium in Australia, and the host of the 1956 Summer Olympics and the 2006 Commonwealth Games. The ground is also considered the "spiritual home" of Australian cricket and Australian rules football, and hosts the grand final of the Australian Football League (AFL) each year, usually drawing crowds of over 95,000 people. Victoria includes eight public universities, with the oldest, the University of Melbourne, having been founded in 1853.
Etymology
Victoria, like Queensland, was named after Queen Victoria, the monarch when it was established in 1851.
History
After the founding of the colony of New South Wales in 1788, Australia was divided into an eastern half named New South Wales and a western half named New Holland, under the administration of the colonial government in Sydney. The first European settlement in the area later known as Victoria was established in October 1803 under Lieutenant-Governor David Collins at Sullivan Bay on Port Phillip. It consisted of 402 people (5 Government officials, 9 officers of marines, 2 drummers, and 39 privates, 5 soldiers' wives, and a child, 307 convicts, 17 convicts' wives, and 7 children).[1] They had been sent from England in HMS Calcutta under the command of Captain Daniel Woodriff, principally out of fear that the French, who had been exploring the area, might establish their own settlement and thereby challenge British rights to the continent.
In the year 1826 Colonel Stewart, Captain S. Wright, and Lieutenant Burchell were sent in H.M.S. Fly (Captain Wetherall) and the brigs Dragon and Amity, took a number of convicts and a small force composed of detachments of the 3rd and 93rd regiments. The expedition landed at Settlement Point (now Corinella), on the eastern side of the bay, which was the headquarters until the abandonment of Western Port at the instance of Governor Darling about twelve months afterwards.[2][3]
Victoria's next settlement was at Portland, on the west coast of what is now Victoria. Edward Henty settled Portland Bay in 1834.[4]
Melbourne was founded in 1835 by John Batman and John Pascoe Fawkner. From settlement the region around Melbourne was known as the Port Phillip District, a separately administered part of New South Wales.
Creation of separate colony of Victoria
On 1 July 1851, writs were issued for the election of the first Victorian Legislative Council, and the absolute independence of Victoria from New South Wales was established proclaiming a new Colony of Victoria.[5] Days later, still in 1851 gold was discovered near Ballarat, and subsequently at Bendigo. Later discoveries occurred at many sites across Victoria. This triggered one of the largest gold rushes the world has ever seen. The colony grew rapidly in both population and economic power. In ten years the population of Victoria increased sevenfold from 76,000 to 540,000. All sorts of gold records were produced including the "richest shallow alluvial goldfield in the world" and the largest gold nugget. Victoria produced in the decade 1851–1860 20 million ounces of gold, one third of the world's output[citation needed].

Immigrants arrived from all over the world to search for gold, especially from Ireland and China. Many Chinese miners worked in Victoria, and their legacy is particularly strong in Bendigo and its environs. Although there was some racism directed at them, there was not the level of anti-Chinese violence that was seen at the Lambing Flat riots in New South Wales. However, there was a riot at Buckland Valley near Bright in 1857. Conditions on the gold fields were cramped and unsanitary; an outbreak of typhoid at Buckland Valley in 1854 killed over 1,000 miners.
In 1854 at Ballarat there was an armed rebellion against the government of Victoria by miners protesting against mining taxes (the "Eureka Stockade"). This was crushed by British troops, but the discontents prompted colonial authorities to reform the administration (particularly reducing the hated mining licence fees) and extend the franchise. Within a short time, the Imperial Parliament granted Victoria responsible government with the passage of the Colony of Victoria Act 1855. Some of the leaders of the Eureka rebellion went on to become members of the Victorian Parliament.
The first foreign military action by the colony of Victoria was to send troops and a warship to New Zealand as part of the Māori Wars. Troops from New South Wales had previously participated in the Crimean War.
In 1901 Victoria became a state in the Commonwealth of Australia. As a result of the gold rush, Melbourne had by then become the financial centre of Australia and New Zealand. Between 1901 and 1927, Melbourne was the capital of Australia while Canberra was under construction. It was also the largest city in Australia at the time.[citation needed]
Government




| Composition of the Parliament of Victoria | ||
|---|---|---|
| Political Party |
Legislative Assembly |
Legislative Council |
| ALP | 43 | 16 |
| Liberal | 35 | 18 |
| National | 10 | 3 |
| Greens | 0 | 3 |
| Source: Victorian Electoral Commission | ||
Parliament
Victoria has a parliamentary form of government based on the Westminster System. Legislative power resides in the Parliament consisting of the Governor (the representative of the Queen), the executive (the Government), and two legislative chambers. The Parliament of Victoria consists of the lower house Legislative Assembly, the upper house Legislative Council and the Queen of Australia.
Eighty-eight members of the Legislative Assembly are elected to four-year terms from single-member electorates.
In November 2006, the Victorian Legislative Council elections were held under a new multi-proportional representation system. The State of Victoria was divided into eight electorates with each electorate represented by five representatives elected by Single Transferable Vote proportional representation. The total number of upper house members was reduced from 44 to 40 and their term of office is now the same as the lower house members—four years. Elections for the Victorian Parliament are now fixed and occur in November every four years. Prior to the 2006 election, the Legislative Council consisted of 44 members elected to eight-year terms from 22 two-member electorates.
Premier and cabinet
The Premier of Victoria is the leader of the political party or coalition with the most seats in the Legislative Assembly. The Premier is the public face of government and, with cabinet, sets the legislative and political agenda. Cabinet consists of representatives elected to either house of parliament. It is responsible for managing areas of government that are not exclusively the Commonwealth's, by the Australian Constitution, such as education, health and law enforcement. The current Premier of Victoria is Denis Napthine.
Governor
Executive authority is vested in the Governor of Victoria who represents and is appointed by Queen Elizabeth II. The post is usually filled by a retired prominent Victorian. The governor acts on the advice of the premier and cabinet. The current Governor of Victoria is Alex Chernov.
Constitution
Victoria has a written constitution. Enacted in 1975, but based on the 1855 colonial constitution[dead link], it establishes the parliament as the state's law-making body for matters coming under state responsibility. The Victorian Constitution can be amended by the parliament of Victoria. Under new provisions to be enacted, changes to the Victorian Constitution will be subjected to a plebiscite of votes, voting in a referendum.
Politics
Premier Denis Napthine leads a Liberal/National Coalition that won the November 2010 Victorian state election under former leader Ted Baillieu.
The centre-left Australian Labor Party (ALP), the centre-right Liberal Party of Australia and the rural-based National Party of Australia are Victoria's major political parties. Traditionally, Labor is strongest in Melbourne's inner, working class and western and northern suburbs, Morwell, Ballarat, Bendigo and Geelong. The Liberals' main support lies in Melbourne's more affluent eastern and outer suburbs, and some rural and regional centres. The Nationals are strongest in Victoria's North Western and Eastern rural regional areas.
Federal government
Victorian voters elect 49 representatives to the Parliament of Australia, including 37 members of the House of Representatives and 12 members of the Senate. Since 2010, the ALP has held 22 Victorian house seats, the Liberals 12, the Nationals two and the Greens one. As of 1 July 2012, the Liberals have held four senate seats, the Nationals one, the ALP five, the Democratic Labor Party one, and the Greens also one.
Local government
Victoria is incorporated into 79 municipalities for the purposes of local government, including 39 shires, 32 cities, seven rural cities and one borough. Shire and city councils are responsible for functions delegated by the Victorian parliament, such as city planning, road infrastructure and waste management. Council revenue comes mostly from property taxes and government grants.[6]
Demographics

The 2011 Australian census reported that Victoria had 5,354,042 people resident at the time of the census.[7] The Australian Bureau of Statistics estimates that the population may well reach 7.2 million by 2050.
Victoria's founding Anglo-Celtic population has been supplemented by successive waves of migrants from southern and eastern Europe, Southeast Asia and, most recently, the Horn of Africa and the Middle East. Victoria's population is ageing in proportion with the average of the remainder of the Australian population.
About 72% of Victorians are Australian-born. This figure falls to around 66% in Melbourne but rises to higher than 95% in some rural areas in the north west of the state. Around two-thirds of Victorians claim Australian, Scottish, English or Irish ancestry. Less than 1% of Victorians identify themselves as Aboriginal. The largest groups of people born outside Australia came from the British Isles, China, Italy, Vietnam, Greece and New Zealand.
More than 75% of Victorians live in Melbourne, located in the state's south. The greater Melbourne metropolitan area is home to an estimated 4.17 million people.[8] Leading urban centres outside Melbourne include Geelong, Ballarat, Bendigo, Shepparton, Mildura, Warrnambool, Wodonga and the Latrobe Valley.
| Population growth estimates for Victoria | |
|---|---|
| 2007 | 5,087,000 |
| 2011 | 5,500,000 |
| 2016 | 6,000,000 |
| 2021 | 6,400,000 |
| 2026 | 6,800,000 |
| 2031 | 7,300,000 |
| Source: Dept of Planning and Community Development | |
Victoria is Australia's most urbanised state: nearly 90% of residents living in cities and towns. State Government efforts to decentralise population have included an official campaign run since 2003 to encourage Victorians to settle in regional areas,[9] however Melbourne continues to rapidly outpace these areas in terms of population growth.[10]
Age structure and fertility
The government predicts that nearly a quarter of Victorians will be aged over 60 by 2021. The 2011 census reveals that Australian median age has crept upward from 35 to 37 since 2001, which reflects the population growth peak of 1969–72.[11] In 2011, Victoria recorded a TFR of 1.88, the highest after 1978.[12]
Crime
The state of Victoria is divided into four geographical regions; North-West Metropolitan Region, Southern Metropolitan Region, Eastern Region, Western Region. In 2011-2012 there were 173 homicides within the state of Victoria.[13]
Religion
About 61.1% of Victorians describe themselves as Christian. Roman Catholics form the single largest religious group in the state with 26.7% of Victorian population, followed by Anglicans and members of the Uniting Church. Buddhism, the state's largest non-Christian, with 168,637 members as of the most recent census. Victoria is also home of 152,775 Muslims and 45,150 Jews. Hinduism is the fastest growing religion. Around 20% of Victorians claim no religion, and even amongst those who declare a religious affiliation, church attendance is low.[14]
In 2008, the levels of couples choosing to marry in a church had dropped to 36%; the other 64% chose to register their marriage with a civil celebrant.[15]
Education
Primary and secondary
Victoria's state school system dates back to 1872, when the colonial government legislated to make schooling both free and compulsory. The state's public secondary school system began in 1905. Before then, only private secondary schooling was available. Today, a Victorian school education consists of seven years of primary schooling (including one preparatory year) and six years of secondary schooling.
The final years of secondary school are optional for children aged over 17. Victorian children generally begin school at age five or six. On completing secondary school, students earn the Victorian Certificate of Education. Students who successfully complete their secondary education also receive a tertiary entrance ranking, or ATAR score, to determine university admittance.
Victorian schools are either publicly or privately funded. Public schools, also known as state or government schools, are funded and run directly by the Victoria Department of Education [2]. Students do not pay tuition fees, but some extra costs are levied. Private fee-paying schools include parish schools run by the Roman Catholic Church and independent schools similar to British public schools. Independent schools are usually affiliated with Protestant churches. Victoria also has several private Jewish and Islamic primary and secondary schools. Private schools also receive some public funding. All schools must comply with government-set curriculum standards. In addition, Victoria has four government selective schools, Melbourne High School for boys, MacRobertson Girls' High School for girls, the coeducational schools John Monash Science School, Nossal High School and Suzanne Cory High School, and The Victorian College of the Arts Secondary School. Students at these schools are exclusively admitted on the basis of a selective entry test.
As of August 2010, Victoria had 1,548 public schools, 489 Catholic schools and 214 independent schools. Just under 540,800 students were enrolled in public schools, and just over 311,800 in private schools. Over 61 per cent of private students attend Catholic schools. More than 462,000 students were enrolled in primary schools and more than 390,000 in secondary schools. Retention rates for the final two years of secondary school were 77 per cent for public school students and 90 per cent for private school students. Victoria has about 63,519 full-time teachers.[16]
Tertiary education
Victoria has eight universities. The first to offer degrees, the University of Melbourne, enrolled its first student in 1855. The largest, Monash University, has an enrolment of nearly 56,000 students—more than any other Australian university. Both the University of Melbourne and Monash University are ranked highly among the world's best universities requiring a high entry score, or passing of mature age entrance exams for student admission into their courses.
The number of students enrolled in Victorian universities was 241,755 at 2004, an increase of 2% on the previous year. International students made up 30% of enrolments and account for the highest percentage of pre-paid university tuition fees. The largest number of enrolments were recorded in the fields of business, administration and economics, with nearly a third of all students, followed by arts, humanities, and social science, with 20% of enrolments.
Victoria has 18 government-run institutions of “technical and further education” (TAFE). The first vocational institution in the state was the Melbourne Mechanics' Institute (established in 1839), which is now the Melbourne Athenaeum. More than 1,000 adult education organisations are registered to provide recognised TAFE programs. In 2004, there were about 480,700 students enrolled in vocational education programs in the state.[17]

Libraries
The State Library of Victoria is the State's research and reference library. It is responsible for collecting and preserving Victoria's documentary heritage and making it available through a range of services and programs. Material in the collection includes books, newspapers, magazines, journals, manuscripts, maps, pictures, objects, sound and video recordings and databases.
In addition, local governments maintain local lending libraries, typically with multiple branches in their respective municipal areas.
Economy
| Victorian production and workers by economic activities | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Economic sector |
GSP produced |
Number of workers |
Percentage of workers |
| Finance, insurance and property |
30.5% | 319,109 | 15.3% |
| Community, social and personal services |
16.6% | 562,783 | 27.4% |
| Manufacturing | 15.4% | 318,218 | 15.3% |
| Wholesale and retail trade |
12.1% | 423,328 | 20.3% |
| Transport, utilities and communications |
10.6% | 133,752 | 6.4% |
| Construction | 6.2% | 136,454 | 6.6% |
| Government | 4% | 62,253 | 3% |
| Agriculture | 3.3% | 72,639 | 3.5% |
| Mining | 1.3% | 4,472 | 0.2% |
| Other | – | 49,208 | 2% |
| Source: Australian Bureau of Statistics. Figures are for 2004–2005 | |||
The state of Victoria is the second largest economy in Australia after New South Wales, accounting for a quarter of the nation's gross domestic product. The total gross state product (GSP) at current prices for Victoria was at just over A$293 billion, with a GSP per capita of A$52,872. The economy grew by 2.0 per cent in 2010, less than the Australian average of 2.3 per cent.
Finance, insurance and property services form Victoria's largest income producing sector, while the community, social and personal services sector is the state's biggest employer. Despite the shift towards service industries, the troubled manufacturing sector remains Victoria's single largest employer and income producer. As a result of job losses in declining sectors such as manufacturing, Victoria has the highest unemployment rate in Australia as of September 2009.[18]
Agriculture

During 2003–04, the gross value of Victorian agricultural production increased by 17% to $8.7 billion. This represented 24% of national agricultural production total gross value. As of 2004, an estimated 32,463 farms occupied around 136,000 square kilometres (52,500 sq mi) of Victorian land. This comprises more than 60% of the state's total land surface. Victorian farms range from small horticultural outfits to large-scale livestock and grain productions. A quarter of farmland is used to grow consumable crops.
More than 26,000 square kilometres (10,000 sq mi) of Victorian farmland are sown for grain, mostly in the state's west. More than 50% of this area is sown for wheat, 33% for barley and 7% for oats. A further 6,000 square kilometres (2,300 sq mi) is sown for hay. In 2003–04, Victorian farmers produced more than 3 million tonnes of wheat and 2 million tonnes of barley. Victorian farms produce nearly 90% of Australian pears and third of apples. It is also a leader in stone fruit production. The main vegetable crops include asparagus, broccoli, carrots, potatoes and tomatoes. Last year, 121,200 tonnes of pears and 270,000 tonnes of tomatoes were produced.
More than 14 million sheep and 5 million lambs graze over 10% of Victorian farms, mostly in the state's north and west. In 2004, nearly 10 million lambs and sheep were slaughtered for local consumption and export. Victoria also exports live sheep to the Middle East for meat and to the rest of the world for breeding. More than 108,000 tonnes of wool clip was also produced—one-fifth of the Australian total.
Victoria is the centre of dairy farming in Australia. It is home to 60% of Australia's 3 million dairy cattle and produces nearly two-thirds of the nation's milk, almost 6.4 million litres. The state also has 2.4 million beef cattle, with more than 2.2 million cattle and calves slaughtered each year. In 2003–04, Victorian commercial fishing crews and aquaculture industry produced 11,634 tonnes of seafood valued at nearly A$109 million. Blacklipped abalone is the mainstay of the catch, bringing in A$46 million, followed by southern rock lobster worth A$13.7 million. Most abalone and rock lobster is exported to Asia.
Manufacturing
Machinery and equipment manufacturing is the state's most valuable manufacturing activity, followed by food and beverage manufacturing and petroleum, coal and chemical manufacturing. More than 15% Victorian workers are employed in manufacturing industries. Victoria has 318,000 manufacturing workers. The state is marginally behind New South Wales in the value of manufacturing output.
Major industrial plants belong to the car manufacturers Ford, Toyota and Holden; Alcoa's Portland and Point Henry aluminium smelters; oil refineries at Geelong and Altona; and a major petrochemical facility at Laverton.
Victoria also plays an important role in providing goods for the defence industry. Melbourne is the centre of manufacturing in Victoria, followed by Geelong. Energy production has aided industrial growth in the Latrobe Valley.
Mining

Mining in Victoria contributes around A$3 billion to the gross state product (~1%) but employs less than 1% of workers. The Victorian mining industry is concentrated on energy producing minerals, with brown coal, petroleum and gas accounting for nearly 90% of local production. The oil and gas industries are centred off the coast of Gippsland in the state's east, while brown coal mining and power generation is based in the Latrobe Valley.
In the 2005/2006 fiscal year, the average gas production was over 700 million cubic feet (20,000,000 m3) per day (M cuft/d) and represented 18% of the total national gas sales, with demand growing at 2% per year.[19]
In 1985, oil production from the offshore Gippsland Basin peaked to an annual average of 450,000 barrels (72,000 m3) per day. In 2005–2006, the average daily oil production declined to 83,000 bbl (13,200 m3)/d, but despite the decline Victoria still produces almost 19.5% of crude oil in Australia.[20]
Brown coal is Victoria's leading mineral, with 66 million tonnes mined each year for electricity generation in the Latrobe Valley, Gippsland.[21] The region is home to the world's largest known reserves of brown coal.
Despite being the historic centre of Australia's gold rush, Victoria today contributes a mere 1% of national gold production. Victoria also produces limited amounts of gypsum and kaolin.
Service industry
The service industries sector is the fastest growing component of the Victorian economy. It includes the wide range of activities generally classified as community, social and personal services; finances, insurance and property services, government services, transportation and communication, and wholesale and retail trade. Most service industries are located in Melbourne and the state's larger regional centres.
As of 2004–05, service industries employed nearly three-quarters of Victorian workers and generated three-quarters of the state's GSP. Finance, insurance and property services, as a group, provide a larger share of GSP than any other economic activity in Victoria. More than a quarter of Victorian workers are employed by the community, social and personal services sector.[22]
Tourism


Some major tourist destinations in Victoria are:
- The metropolis of Melbourne, particular its inner city suburbs (known also for shopping tourism) and the attractions of the city centre such as Crown Casino, Melbourne Zoo, Melbourne Museum, the Melbourne Aquarium, ScienceWorks, Healesville Sanctuary, Werribee Open Range Zoo, tourism precincts such as Melbourne Docklands, Southbank and St Kilda as well as cultural and sporting tourist icons such as The Arts Centre, National Gallery of Victoria, the Melbourne Cricket Ground, also known as the MCG, and the Eureka Tower, with the highest observation deck in the Southern Hemisphere, Skydeck 88.
- Victoria has more than 2000 kilometres of coastline with hundreds of beaches.[23]
- The Goldfields region featuring the historic cities of Ballarat, Beechworth, Bendigo, Castlemaine, Maldon and Daylesford.
- Natural attractions, such as The Twelve Apostles, Wilsons Promontory, The Grampians, the Fairy Penguins (particularly at Phillip Island and St Kilda), the Buchan Caves and the Gippsland Lakes.
- The Dandenong Ranges (in particular the Puffing Billy Railway).
- Towns along the Murray River and Riverina including Echuca and Mildura including waterskiing.
- Geelong and the Australian International Airshow
- The Bellarine Peninsula which features historic resort towns such as Queenscliff.
- The Surf Coast which features famous beaches such as Bells Beach, Torquay and Lorne
- Mornington Peninsula, particularly for its wineries and secluded beaches, Arthur's Seat and the coastal attractions of Portsea and Sorrento.
- Yarra Valley (in particular Healesville Sanctuary and wineries).
- Great Ocean Road, which features The Twelve Apostles, historic towns of Port Fairy and Portland, cliffs and whale watching and resort towns such as Lorne.
- The Victorian Alpine Region, part of the Australian Alps, particularly for skiing
- The Central Victorian Highlands, 'Highcountry' are very well known for winter sports and bushwalking
- Wine regions across the entire state.
Other popular tourism activities are gliding, hang-gliding, hot air ballooning and scuba diving.
Major events also play a big part in tourism in Victoria, particularly cultural tourism and sports tourism. Most of these events are centred around Melbourne, but others occur in regional cities, such as the V8 Supercars and Australian Motorcycle Grand Prix at Phillip Island, the Grand Annual Steeplechase at Warrnambool and the Australian International Airshow at Geelong and numerous local festivals such as the popular Port Fairy Folk Festival, Queenscliff Music Festival, Bells Beach SurfClassic and the Bright Autumn Festival.
Geology and geography

Victoria's northern border is the southern bank of the Murray River. It also rests at the southern end of the Great Dividing Range, which stretches along the east coast and terminates west of Ballarat. It is bordered by South Australia to the west and shares Australia's shortest land border with Tasmania. The official border between Victoria and Tasmania is at 39°12' S, which passes through Boundary Islet in the Bass Strait for 85 metres.[24][25]
Victoria contains many topographically, geologically and climatically diverse areas, ranging from the wet, temperate climate of Gippsland in the southeast to the snow-covered Victorian alpine areas which rise to almost 2,000 metres (6,500 ft), with Mount Bogong the highest peak at 1,986 m; (6,516 ft). There are extensive semi-arid plains to the west and northwest. There is an extensive series of river systems in Victoria. Most notable is the Murray River system. Other rivers include: Ovens River, Goulburn River, Patterson River, King River, Campaspe River, Loddon River, Wimmera River, Elgin River, Barwon River, Thomson River, Snowy River, Latrobe River, Yarra River, Maribyrnong River, Mitta River, Hopkins River, Merri River and Kiewa River. The state symbols include the Pink Heath (state flower), Leadbeater's Possum (state animal) and the Helmeted Honeyeater (state bird).
The state's capital, Melbourne, contains approximately 70% of the state's population and dominates its economy, media, and culture. For other cities and towns, see List of localities (Victoria) and Local Government Areas of Victoria.
Climate
| Average monthly maximum temperature in Victoria | ||||
| Month | Melbourne | Mildura | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| January | 25.8 °C | 32.8 °C | ||
| February | 25.8 °C | 32.7 °C | ||
| March | 23.8 °C | 29.3 °C | ||
| April | 20.2 °C | 24.1 °C | ||
| May | 16.6 °C | 19.6 °C | ||
| June | 14.0 °C | 16.0 °C | ||
| July | 13.4 °C | 15.4 °C | ||
| August | 14.9 °C | 17.7 °C | ||
| September | 17.2 °C | 21.1 °C | ||
| October | 19.6 °C | 25.0 °C | ||
| November | 21.8 °C | 29.0 °C | ||
| December | 24.1 °C | 31.7 °C | ||
| Source: Bureau of Meteorology | ||||
Victoria has a varied climate despite its small size. It ranges from semi-arid and hot in the north-west, to temperate and cool along the coast. Victoria's main land feature, the Great Dividing Range, produces a cooler, mountain climate in the centre of the state.
Victoria's southernmost position on the Australian mainland means it is cooler and wetter than other mainland states and territories. The coastal plain south of the Great Dividing Range has Victoria's mildest climate. Air from the Southern Ocean helps reduce the heat of summer and the cold of winter. Melbourne and other large cities are located in this temperate region. Autumn months are mild and bring colorful foliage across many parts of the state in April and May.
The Mallee and upper Wimmera are Victoria's warmest regions with hot winds blowing from nearby deserts. Average temperatures top 30 °C (86 °F) during summer and 15 °C (59 °F) in winter. Victoria's highest maximum temperature of 48.8 °C (119.9 °F) was recorded in Hopetoun on 7 February 2009, during the 2009 southeastern Australia heat wave.[26]
The Victorian Alps in the northeast are the coldest part of Victoria. The Alps are part of the Great Dividing Range mountain system extending east-west through the centre of Victoria. Average temperatures are less than 9 °C (48 °F) in winter and below 0 °C (32 °F) in the highest parts of the ranges. The state's lowest minimum temperature of −11.7 °C (10.9 °F) was recorded at Omeo on 13 June 1965, and again at Falls Creek on 3 July 1970.[26]
Rainfall
Victoria is the wettest Australian state after Tasmania. Rainfall in Victoria increases from south to north, with higher averages in areas of high altitude. Median annual rainfall exceeds 1,800 millimetres (71 in) in some parts of the northeast but is less than 250 millimetres (10 in) in the Mallee.
Rain is heaviest in the Otway Ranges and Gippsland in southern Victoria and in the mountainous northeast. Snow generally falls only in the mountains and hills in the centre of the state. Rain falls most frequently in winter, but summer precipitation is heavier. Rainfall is most reliable in Gippsland and the Western District, making them both leading farming areas. Victoria's highest recorded daily rainfall was 375 millimetres (14.7 in) at Tanybryn in the Otway Ranges on 22 March 1983.[26]
- Average temperatures and precipitation for Victoria
-
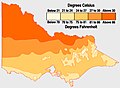
Average January temperatures:
Victoria's north is almost always hotter than coastal and mountainous areas. -
Average July temperatures:
Victoria's hills and ranges are coolest during winter. Snow also falls there. -
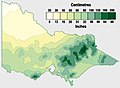
Average yearly precipitation:
Victoria's rainfall is concentrated in the mountainous north-east and coast.
| Source: Bureau of Meteorology, Department of Primary Industries, Australian Natural Resources Atlas |
Transport
Victoria has the highest population density in any state in Australia, with population centres spread out over most of the state; only the far northwest and the Victorian Alps lack permanent settlement.
The Victorian road network services the population centres, with highways generally radiating from Melbourne and other major cities and rural centres with secondary roads interconnecting the highways to each other. Many of the highways are built to freeway standard ("M" freeways), while most are generally sealed and of reasonable quality.

Rail transport in Victoria is provided by several private and public railway operators who operate over government-owned lines. Major operators include: Metro Trains Melbourne which runs an extensive, electrified, passenger system throughout Melbourne and suburbs; V/Line which is now owned by the Victorian Government, operates a concentrated service to major regional centres, as well as long distance services on other lines; Pacific National, CFCLA, El Zorro which operate freight services; Great Southern Railway which operates The Overland Melbourne—Adelaide; and CountryLink which operates XPTs Melbourne—Sydney.
There are also several smaller freight operators and numerous tourist railways operating over lines which were once parts of a state-owned system. Victorian lines mainly use the 5 ft 3 in (1,600 mm) broad gauge. However, the interstate trunk routes, as well as a number of branch lines in the west of the state have been converted to 4 ft 8+1⁄2 in (1,435 mm) standard gauge. Two tourist railways operate over 2 ft 6 in (762 mm) narrow gauge lines, which are the remnants of five formerly government-owned lines which were built in mountainous areas.
Melbourne has the world's largest tram network,[27] currently operated by Yarra Trams. As well as being a popular form of public transport, over the last few decades trams have become one of Melbourne's major tourist attractions. There are also tourist trams operating over portions of the former Ballarat and Bendigo systems. There are also tramway museums at Bylands and Haddon.
Melbourne Airport is the major domestic and international gateway for the state. Avalon Airport is the state's second busiest airport, which complements Essendon and Moorabbin Airports to see the remainder of Melbourne's air traffic. Hamilton Airport, Mildura Airport, Mount Hotham and Portland Airport are the remaining airports with scheduled domestic flights. There are no fewer than 27 other airports in the state with no scheduled flights.
The Port of Melbourne is the largest port for containerised and general cargo in Australia,[28] and is located in Melbourne on the mouth of the Yarra River, which is at the head of Port Phillip. Additional seaports are at Westernport, Geelong, and Portland.
Utilities
Energy
Victoria's major utilities include a collection of brown-coal-fired power stations, particularly in the Latrobe Valley. One of these is Hazelwood Power Station, which is number 1 in the worldwide List of least carbon efficient power stations.
Water
Victoria's water infrastructure includes a series of dams and reservoirs, predominantly in Central Victoria, that hold and collect water for much of the state. The water collected is of a very high quality and requires little chlorination treatment, giving the water a taste more like water collected in a rainwater tank. In regional areas however, such as in the west of the state, chlorination levels are much higher.
The Victorian Water Grid consists of a number of new connections and pipelines being built across the State. This allows water to be moved around Victoria to where it is needed most and reduces the impact of localised droughts in an era thought to be influenced by climate change. Major projects already completed as part of the Grid include the Wimmera Mallee Pipeline and the Goldfields Superpipe.[29]
Sport


Victoria is the home of Australian rules football, with ten of the eighteen clubs of the Australian Football League based in Victoria, and the traditional Grand Final held at the Melbourne Cricket Ground usually on the last Saturday in September.
Victoria's cricket team, the Victorian Bushrangers play in the national Sheffield Shield cricket competition. Victoria is represented in the National Rugby League by the Melbourne Storm and in Super Rugby by the Melbourne Rebels. It is also represented in Football (soccer) by Melbourne Victory and Melbourne Heart in the A-League.
Melbourne has held the 1956 Summer Olympics, 2006 Commonwealth Games and the FINA World Swimming Championship.
Melbourne is also home to the Australian Open tennis tournament in January each year, the first of the world's four Grand Slam tennis tournaments, and the Australian Formula One Grand Prix.
Victoria's Bells Beach hosts one of the world's longest-running surfing competition, the Bells Beach SurfClassic, which is part of The ASP World Tour.
Netball is a big part of sport in Victoria. The Melbourne Vixens represent Victoria in the ANZ Championship. Some of the worlds best netballers such as Sharelle McMahon, Renae Hallinan, Madison Browne, Julie Corletto and Bianca Chatfield come from Victoria.
Possibly Victoria's most famous island, Phillip Island, is home of the Phillip Island Grand Prix Circuit which hosts the Australian motorcycle Grand Prix which features MotoGP (the world's premier motorcycling class), as well as the Australian round of the World Superbike Championship and the domestic V8 Supercar racing, which also visits Sandown Raceway and the rural Winton Motor Raceway circuit.
Australia's most prestigious footrace, the Stawell Gift, is an annual event.
Victoria is also home to the Aussie Millions poker tournament, the richest in the Southern hemisphere.
The Melbourne Spring Racing Carnival is one of the biggest horse racing events in the world and is one of the world's largest sporting events. The main race is for the $6 million Melbourne Cup, and crowds for the carnival exceed 700,000.
Major professional teams include:
- Australian Football: Melbourne Demons, Carlton Blues, Essendon Bombers, Collingwood Magpies, St Kilda Saints, Richmond Tigers, Hawthorn Hawks, North Melbourne Kangaroos, Western Bulldogs, Geelong Cats
- Basketball: Melbourne Tigers
- Cricket: Victoria Bushrangers, Melbourne Renegades, Melbourne Stars
- Football (soccer): Melbourne Victory, Melbourne Heart
- Netball: Melbourne Vixens
- Rugby League: Melbourne Storm
- Rugby Union: Melbourne Rebels
See also
- Australia
- Outline of Australia
- Index of Australia-related articles
- Template:Wikipedia books link
- 2003 Melbourne thunderstorm
- Atlas of Victorian Birds
Geography:
Lists:
Notes
- ^ Due to a previous surveying error, Victoria and Tasmania share a land border on Boundary Islet. At 85 metres (93 yd) in length, the border is the smallest between any Australian state or territory.
References
- ^ "CORRESPONDENCE". The Advertiser (Adelaide, SA : 1889 - 1931). Adelaide, SA: National Library of Australia. 14 October 1901. p. 7. Retrieved 17 January 2012.
- ^ "ATTEMPTED COLONISATION AT WESTERN PORT". Mornington Standard (Vic. : 1889 - 1908). Vic.: National Library of Australia. 12 August 1905. p. 5 Edition: MORNING. Retrieved 24 January 2012.
- ^ Corinella - Victoria's Best Kept Secret
- ^ James Boyce (2011) 1835: The Founding of Mebourne and the Conquest of Australia, Black Inc, p.12
- ^ "Anniversary of the Week". The Argus (Melbourne, Vic. : 1848 - 1956). Melbourne, Vic.: National Library of Australia. 4 July 1930. p. 2 Supplement: Saturday Camera Supplement. Retrieved 26 January 2012.
- ^ Victorian Parliamentary Library, Department of Victorian Communities, Australian Electoral Commission
- ^ Australian Bureau of Statistics (31 October 2012). "Victoria". 2011 Census QuickStats. Retrieved 12 February 2013.
- ^ "3218.0 - Regional Population Growth, Australia, 2011". ABS website. Australian Bureau of Statistics. 31 July 2012. Retrieved 29 August 2012.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Provincial Victoria – About
- ^ Colebatch, Tim (24 April 2009). "Pressure grows as Melbourne rockets to 4 million". The Age. Australia.
- ^ Australian Bureau of Statistics (31 October 2012). "Victoria". 2011 Census QuickStats. Retrieved 24 February 2013.
- ^ 3301.0 – Births, Australia, 2009
- ^ http://www.police.vic.gov.au/crimestats/crimestats2011-12.pdf
- ^ 2011 Census Community Profile Series : Victoria
- ^ Statistics report for 2008 from the Victorian Registry of Births, Deaths and Marriages
- ^ 4221.0 Schools, Australia 2010, Australian Bureau of Statistics, 17 March 2011.
- ^ Australian Bureau of Statistics, Department of Education and Training (Victoria), Department of Education, Science and Training (Commonwealth), National Centre for Vocational Education Research
- ^ Business & Finance News – Yahoo!7 Finance
- ^ Department of Primary Industries[dead link]
- ^ DEPARTMENT OF PRIMARY INDUSTRIES: Oil and Gas[dead link]
- ^ Australian Bureau of Statistics: Year Book Australia, 2004 – Profile of major commodities
- ^ Australian Bureau of Statistics, Department of Primary Industries
- ^ WA Today: Waves of fancy: Victoria's best beaches
- ^ "Victoria Tasmania border". Archived from the original on 2 January 2006. Retrieved 7 March 2006.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|org=ignored (help) - ^ Boundary Islet on street-directory.com.au
- ^ a b c "Rainfall and Temperature Records: National" (PDF). Bureau of Meteorology. Retrieved 14 November 2009.
- ^ DoI (2008). [1]. Retrieved 28 April 2008. [dead link]
- ^ "DoI media release – 'GOVERNMENT OUTLINES VISION FOR PORT OF MELBOURNE FREIGHT HUB' – 14 August 2006". Retrieved 26 July 2007.
- ^ "Department of Sustainability & Environment, "Expansion of the Water Grid", http://www.ourwater.vic.gov.au/programs/water-grid, accessed 27 January 2011".
Further reading—Victorian frontier history
- Jan Critchett, (1990), A distant field of murder: Western district frontiers, 1834-1848, Melbourne University Press (Carlton, Vic. and Portland, Or.) ISBN 052284389
- Ian D Clark (1990) Aboriginal languages and clans: An historical atlas of western and central Victoria, 1800-1900, Dept. of Geography & Environmental Science, Monash University (Melbourne), ISBN 0-909685-41-X
- Ian D Clark (1995), Scars in the landscape: A register of massacre sites in western Victoria, 1803-1859, Australian Institute of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Studies (Canberra), ISBN 0-85575-281-5
- Ian D Clark (2003) ‘That’s my country belonging to me’ - Aboriginal land tenure and dispossession in nineteenth century Western Victoria, Ballarat Heritage Services, Ballarat.