Shadowgraph: Difference between revisions
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
=== Shadowgram === |
=== Shadowgram === |
||
According to F. |
According to F. U. Weinerberg,<ref>Weinberg, F.J., ''Optics of flames: including methods for the study of refractive index fields in combustion and aerodynamics'', London:Buttworks, 1963.</ref> the result of applying the shadowgraph technique should be known as a ''shadowgram''. A shadowgram is not a focused image, rather it is a mere shadow. In the shadowgram, the differences in light intensity are proportional to the second spatial derivative ([[Laplacian]]) of the [[refractive index]] field in the transparent medium under study. Once the distance from the transparent disturbance to the cast shadow becomes too large, then the shadow no longer constitutes a useful representation of the disturbance that caused it. |
||
=== Cartoons === |
=== Cartoons === |
||
Revision as of 02:00, 2 September 2013
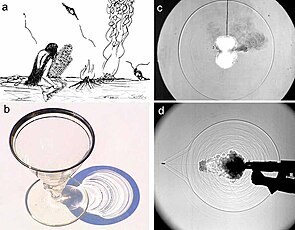
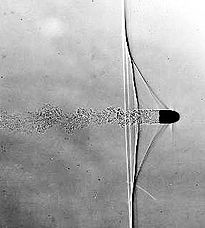
Shadowgraph is an optical method that reveals non-uniformities in transparent media like air, water, or glass. It is related to, but simpler than, the schlieren and schlieren photography methods that perform a similar function. Shadowgraph is a type of flow visualisation.
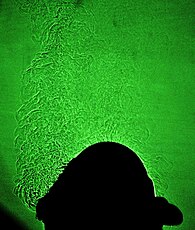
In principle, we cannot directly see a difference in temperature, a different gas, or a shock wave in the transparent air. However, all these disturbances refract light rays, so they can cast shadows. The plume of hot air rising from a fire, for example, can be seen by way of its shadow cast upon a nearby surface by the uniform sunlight.
Sunlight shadowgraph
This technique is as old as nature itself. For example, some aquatic predators detect their transparent prey by way of their shadows cast upon the ocean floor. Nevertheless it was Robert Hooke[1] who first scientifically demonstrated the sunlight shadowgraph and Jean-Paul Marat[2] who first used it to study fire. A modern account of shadowgraphy is given by G.S. Settles.[3]
Applications
Applications of shadowgraphy in science and technology are very broad. It is used in aeronautical engineering to see the flow about high-speed aircraft and missiles, as well as in combustion research, ballistics, explosions, and in the testing of glass.
Shadowgram
According to F. U. Weinerberg,[4] the result of applying the shadowgraph technique should be known as a shadowgram. A shadowgram is not a focused image, rather it is a mere shadow. In the shadowgram, the differences in light intensity are proportional to the second spatial derivative (Laplacian) of the refractive index field in the transparent medium under study. Once the distance from the transparent disturbance to the cast shadow becomes too large, then the shadow no longer constitutes a useful representation of the disturbance that caused it.
Cartoons
The Shadowgraph, and shadowgram have been used in animation, where they reinforce the cartoon's realism. One first use was made by Disney Studios on the Three Blind Mouseketeers (1936) Silly Symphonies.[5]
Postcards
Additionally the term Shadowgraph was used by English postcard publishers E.T.W. Dennis & Sons Ltd. of London and Scarborough for a series of 'Hold up to the Light' postcards in the 1950s. In these a saucy image can be seen through what seems an innocent picture when a light is shone through the card.[6]
Gallery
|
|
See also
References
- ^ Hooke, R., "Of a New Property in the Air," Micrographia, Observation LVIII,217-219, London(1665).
- ^ Marat, J.-P., Recherches physiques sur le feu, Paris, France:Cl. Ant. Jombert, 1780.
- ^ Settles, G. S., Schlieren and shadowgraph techniques: Visualizing phenomena in transparent media, Berlin:Springer-Verlag, 2001.
- ^ Weinberg, F.J., Optics of flames: including methods for the study of refractive index fields in combustion and aerodynamics, London:Buttworks, 1963.
- ^ Russel Merritt & JB Kaufman, Walt Disney's Silly Symphonies : A Companion to the classic cartoons series, Italy:La Cinecita del Friuli, 2006, ISBN 88-86155-27-1 p 46
- ^ "MetroPostcard Publishers D". Metropolitan Postcard Club of New York City. Retrieved 2008-10-02.