Neuromechanics: Difference between revisions
Jenna Fair (talk | contribs) |
Jenna Fair (talk | contribs) added education assignment box |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{ WAP assignment | course = Template:Course page | university = {{{Georgia Institute of Technology}}} | term = {{{Fall 2013}}} | project = {{{Neuroscience Wikipedia Page Project}}} }} |
|||
[[File:Human leg bones labeled.svg|thumb|right|Human leg bones labeled]] |
[[File:Human leg bones labeled.svg|thumb|right|Human leg bones labeled]] |
||
'''Lower limb neuromechanics''' is an interdisciplinary field which combines [[neuroscience]] and [[biomechanics]] to study human movement and its relation to the [[brain]], specifically in limbs below the waist. [[Lower limbs]] consist of four parts: [[human pelvis | hip bone girdle]], [[thigh]], [[lower leg]], and [[foot]]<ref name="O'Rahilly">{{cite book|last=O'Rahilly|first=Ronan|title=Basic Human Anatomy: A Regional Study of Human Structure|year=1982|publisher=W B Saunders Co|isbn=0721669905|url=https://www.dartmouth.edu/~humananatomy/index.html}}</ref> . |
'''Lower limb neuromechanics''' is an interdisciplinary field which combines [[neuroscience]] and [[biomechanics]] to study human movement and its relation to the [[brain]], specifically in limbs below the waist. [[Lower limbs]] consist of four parts: [[human pelvis | hip bone girdle]], [[thigh]], [[lower leg]], and [[foot]]<ref name="O'Rahilly">{{cite book|last=O'Rahilly|first=Ronan|title=Basic Human Anatomy: A Regional Study of Human Structure|year=1982|publisher=W B Saunders Co|isbn=0721669905|url=https://www.dartmouth.edu/~humananatomy/index.html}}</ref> . |
||
Revision as of 03:03, 26 September 2013

Lower limb neuromechanics is an interdisciplinary field which combines neuroscience and biomechanics to study human movement and its relation to the brain, specifically in limbs below the waist. Lower limbs consist of four parts: hip bone girdle, thigh, lower leg, and foot[1] .
Muscles signals stimulated by neurological impulses are collected using electromyography (EMG). Leg muscles that are commonly recorded through EMG are the gluteus maximus, quadriceps femoris, rectus femoris, vastus medialis, soleus, lateral gastrocnemius, medial gastrocnemius, and tibialis anterior.
Background

Neuroscience is the study of the nervous system. The nervous system is comprised of two sub-systems: the peripheral nervous system and the central nervous system[2].
The peripheral nervous system is then composed of three sub-systems: the somatic nervous system, the autonomic nervous system, and the visceral nervous system[3] . The autonomic nervous system is also broken down into the sympathetic nervous system, the parasympathetic nervous system, and the enteric nervous system. The nervous system responsible for voluntary motion, including lower limb motion, is the somatic nervous system[4]. Though the somatic nervous system is part of the peripheral nervous system, motion also involves use of elements of the central nervous system: the brain and the spinal cord[4] .
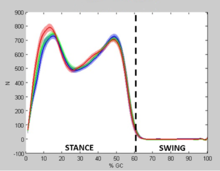
Biomechanics is the study of the structure and function of living systems such as humans, animals, and other organisms by means of mechanics. Lower limb biomechanics is concerned with the interactions of forces at the hip, knee, and ankle joints as well as the shear force and torsion on bone segments.
The gait cycle is a repetitive event that consists of one full step from heel-strike to the next heel-strike in the same foot. It can be divided into two phases: stance phase and swing phase[5]. Stance phase consists of the time during which the heel strikes the ground to the point in time at which the toe leaves the ground[5]. Swing phase consists of the rest of the gait cycle, the time between the toe leaving the ground to the next heel strike[5].
Inverted Pendulum Theory
Muscle Synergies
Adaptation
References
- ^ O'Rahilly, Ronan (1982). Basic Human Anatomy: A Regional Study of Human Structure. W B Saunders Co. ISBN 0721669905.
- ^ "What Are the Parts of the Nervous System?". National Institute of Health. Retrieved 25 September 2013.
- ^ Costanzo, Linda (2010). Physiology. McGraw Hill. ISBN 9781416062165.
- ^ a b Noback, Charles (2005). The Human Nervous System: Structure and Function. Springer. ISBN 1588290395.
- ^ a b c Perry, Jacqueline (2010). Gait Analysis: Normal and Pathological Function. Slack Incorporated. ISBN 1556427662.
