Vaitupu: Difference between revisions
Ohconfucius (talk | contribs) |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 52: | Line 52: | ||
| area_code_type = |
| area_code_type = |
||
| area_code = |
| area_code = |
||
| iso_code = |
| iso_code = TV-VAI |
||
| website = |
| website = |
||
| footnotes = |
| footnotes = |
||
Revision as of 00:29, 10 December 2013
Vaitupu | |
|---|---|
 Vaitupu atoll from space | |
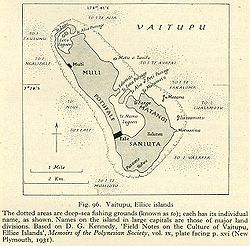 Map of Vaitupu, 1931 | |
| Country | Tuvalu |
| Area | |
• Total | 5.6 km2 (2.2 sq mi) |
| Population (2002) | |
• Total | 1,591 |
| • Density | 280/km2 (740/sq mi) |
| ISO 3166 code | TV-VAI |
Vaitupu is the largest atoll of the nation of Tuvalu. It is located at 7.48 degrees south and 178.83 degrees west. There are almost 1,600 people living on 5.6 km2 with the capital being Asau.
History
The exact date of Vaitupu's first settlement is unknown. According to oral history, the founder of the Vaitupuan community was a Samoan by the name of Telematua, who arrived in the 16th or 17th century.[1] However, it is possible that Tongans may have first reached the atoll during the mid-13th century. Vaitupu has maintained contacts with Tonga throughout its history, both peaceful (marriage alliances) and hostile (visits by Tongan slave-seekers). Vaitupu was also visited by I-Kiribati, and was thus far from isolated.[2] Vaitupu means 'the fountain of water'.
Obed Starbuck, a whaling captain, visited Vaitupu on the Loper in 1825, naming it 'Tracy Island'.[3] The United States Exploring Expedition under Charles Wilkes visited Vaitupu in 1841.[4]
Samoan pastors from the London Missionary Society successfully introduced Christianity in the 1860s. The pastors implemented religious regulations, outlawing many customary practices. They also introduced the Samoan language, as their Bibles were written in Samoan. Vaitupuans became literate in Samoan rather than in their own language.[5]
Vaitupuans celebrate Te Aso Fiafia (Happy Day) on 25 November of each year. Te Aso Fiafia commemorates 25 November 1887 which was the date on which the final instalment of a debt of $13,000 was repaid to H. M. Ruge and Company, a German trading firm that operated from Apia, Samoa. Vaitupu history is that Thomas William Williams, the Ruge agent, pretended to do his customers a favour by allowing them to obtain goods on credit.[6] In 1883 the debt of the Vaitupuans was $13,000 and H. M. Ruge and Company had threatened to seize the entire island unless the debt was repaid.[7] Neemia, a Vaitupuan pastor living in Samoa, returned and organised working parties to collect coconuts and prepare copra to sell to pay off the debt, with Henry Nitz, the Webber & Co agent on Vaitupu, contributing money to meet the final payment.[6] The Vaitupuans, with the help of their friends from Funafuti, repaid the debt by the due date.[8] Seven thousand dollars was repaid by 1886 and the balance was paid on 25 November 1887.[9]
Vaitupuan tradition is that chance favoured their efforts, a ship sent to collect the last payment sank, as did the second ship the trading schooner Vaitupulemele.[10] By the time a third ship arrived most of the money had been collected. However the trading schooner Vaitupulemele appears to have a different role in the history of Vaitupu. The creation of the debt that was repaid to Ruge & Co extended beyond the purchase of goods on credit to include the purchase price of the Vaitupulemele by the Vaitupu Company.[9] While T.M. Williams had been the Ruge agent, he later formed the Vaitupu Company with the Vaitupuan community and purchased the Vaitupulemele from Ruge & Co. However the schooner was lost during a voyage from Samoan and soon after Williams died, leaving no accounting for copra that had been shipped from Vaitupu.[9] In any event the Vaitupuans paid the full amount claimed by Ruge & Co, although that company soon after went into liquidation.[9]
Vaitupu Post Office opened around 1916.[11]
Population of Vaitupu
The population of Vaitupu from 1860–1900 is estimated to be 400 people.[12][13] Vaitupu is home to the second-largest population in Tuvalu, numbering 1,591 (2002 Census). Despite its relatively large size, Vaitupu became so overcrowded during the 1940s that a number of families migrated to Fiji to live on Kioa Island.[14] Neli Lifuka was instrumental in collecting the funds to purchase Kioa.[15][16]
Schools on Vaitupu
The primary school on Vaitupu is called Tolise.[17] There used to be a primary school called Elisefou (New Ellice) on Vaitupu. The school moved to Vaitupu in 1923 and closed in 1953 when the government primary school was established. Its first Headmaster, D. G. Kennedy, was a known disciplinarian who would not hesitate to discipline his students. The two most famous Tuvaluans from the school were Tuvalu's first Governor General, Sir Fiatau Penitala Teo and its first Prime Minister, Toaripi Lauti.
Motufoua Secondary School was established in 1905. Over time the school has evolved and it is now is a boarding school for boys and girls that is administered by the Department of Education. In 2009 the student roll at Motufoua Secondary School was 550.[18] Vaitupu received worldwide attention in 2000, when a fire in a dormitory at the Motufoua school killed 18 girls and a female adult supervisor.[19][20] It was later discovered that the fire was caused by a student using a candle to read during the night.[21] The Prime Minister Ionatana Ionatana declared a national tragedy and quickly travelled to the island to witness the aftermath. A memorial service was held the following year in memory of the 18 girls and their matron who tragically lost their lives.[22] Tuvaluan leaders as well as parents of the victims attended the memorial service.[23]
In 2010 the largest diesel-solar photovoltaic (PV) hybrid electricity system in the South Pacific was installed at Motufoua Secondary School.[24] Prior to the instalment of the system the school relied upon a diesel powered generator, which needed to be turned off during the night. The hybrid system systems saves thousands of dollars in diesel costs and provides the school with a 24-hour supply of energy, with up to 200 kW per day.[25]
Geography
The island, which covers approximately 5.6 square kilometres, includes swamps, mangroves, a fringing coral reef and a large lagoon.
Vaitupu atoll consists of at least 9 isles, which are:
- Luasamotu
- Mosana (group of 2)
- Motutanifa
- Temotu
- Te Motu Olepa
- Tofia
- Vaitupu proper
- And at least 1 other isle
- There is at least 1 isle inhabited, which is Vaitupu proper.
- The biggest island is Vaitupu proper, followed by Tofia.
In the 2011 Tuvalu drought Vaitupu experienced the loss of coconut palm trees, pulaka and taro due to the high temperatures and arid soil.[26]
The community activities on Vaitupu include the Nafa Moa and Talo (Taro crops and chickens competition). In this contest the community is divided into two rival teams. Members of each team compete for who can grow the heavier taro or larger chickens; the climax comes with the weigh-off between the competitors, concluding a day of good-natured rivalry and fun.[27]
The only village on Vaitupu consists of the neighbourhoods Tumaseu and Asau. There is a church, Tolise Primary School, at least one guesthouse and a post office.
An aquaculture project has been established in the lagoon.
The small islet of Temoto in Loto Lagoon is home to a single family of 13 headed by the English born writer Lewis Wade.
Transportation and tourism
Today, Vaitupu can be accessed by either private boat or the government-operated MV Nivaga II after 8 hours at sea from the main island of Funafuti. The latter's return trip and dates of sailing are at irregular intervals. There is a wharf on Vaitupu but no harbour, meaning one must board a smaller boat from the MV Nivaga II to get to the shore. There are paths and small unpaved roads throughout the island. Only a few cars drive on Vaitupu. In the main village there is a guest house called Vivalia III located at the wharf near the main church.
General election, 2010
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nonpartisan | Apisai Ielemia |
597 | ||
| Nonpartisan | Taukelina Finikaso |
541 | ||
| Nonpartisan | Ionatana Peia | 403 | ||
Notable local persons
Reverend Sir Filoimea Telito, GCMG, MBE became a teacher at Motufoua Secondary School. After completing theological studies, he returned to Motufoua to serve as Pastor. Later he became Principal of Motufoua, then in April 2005 he was appointed to be the Governor-General of Tuvalu.[29]
Taukelina Finikaso represents Vaitupu in the Parliament of Tuvalu. He served as Minister of Communications and Works in the Government of Tuvalu from 2006 to 2010 and was appointed the Foreign Minister on 5 August 2013 following Enele Sopoaga becoming prime minister.[30]
Apisai Ielemia has served as Prime Minister of Tuvalu from 2006 to 2010. He represents Vaitupu in the Parliament of Tuvalu.
See also
References
- ^ Kalaaki Laupepa, Hugh Laracy (ed.) (1983). "Chapter 11 – Vaitupu". Tuvalu: A History. Institute of Pacific Studies, University of the South Pacific and Government of Tuvalu. p. 78.
{{cite book}}:|first1=has generic name (help); Cite has empty unknown parameter:|chapterurl=(help) - ^ Donald G. Kennedy, Field Notes on the Culture of Vaitupu, Ellice Islands, Journal of the Polynesian Society, vol.38, 1929, pp.2–5
- ^ Keith S. Chambers & Doug Munro, The Mystery of Gran Cocal: European Discovery and Mis-Discovery in Tuvalu, 89(2) (1980) The Journal of the Polynesian Society, 167–198
- ^ Tyler, David B. – 1968 The Wilkes Expedition. The First United States Exploring Expedition (1838–42). Philadelphia: American Philosophical Society
- ^ Donald G. Kennedy, Field Notes on the Culture of Vaitupu, Ellice Islands, Journal of the Polynesian Society, vol.38, 1929, pp.5–6
- ^ a b Kalaaki Laupepa, Hugh Laracy (ed.) (1983). "Chapter 11 – Vaitupu". Tuvalu: A History. Institute of Pacific Studies, University of the South Pacific and Government of Tuvalu. p. 82.
{{cite book}}:|first1=has generic name (help); Cite has empty unknown parameter:|chapterurl=(help) - ^ Doug Munro and Teloma Munro (1985). The Rise and Fall of the Vaitupu Company: An Episode in the Commercial History of Tuvalu. 20 (4) Journal of Pacific History 174-90.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|chapterurl=(help) - ^ Tito Isala and Doug Munro (1987 & 2008). Te Aso Fiafia: Te Tala o Te Kamupane Vaitupu 1877–1887. South Pacific Books/Institute of Pacific Studies.
{{cite book}}: Check date values in:|year=(help); Cite has empty unknown parameter:|chapterurl=(help)CS1 maint: year (link) - ^ a b c d "The 'Ownership' of Niulakita, 1880–1896". Tuvalu: A History. Institute of Pacific Studies, University of the South Pacific and Government of Tuvalu. 1983. pp. 196–197.
{{cite book}}:|first1=has generic name (help);|first1=missing|last1=(help); Cite has empty unknown parameter:|chapterurl=(help) - ^ "New Zealand Herald, Rōrahi XVI, Putanga 5545, 25 Hereturikōkā 1879, Page 4". Shipping News. 1879.
{{cite web}}: Cite has empty unknown parameters:|chapterurl=and|month=(help) - ^ Premier Postal History. "Post Office List". Premier Postal Auctions. Retrieved 5 July 2013.
- ^ W.F. Newton, The Early Population of the Ellice Islands, 76(2) (1967) The Journal of the Polynesian Society, 197–204.
- ^ Richard Bedford, Barrie Macdonald & Doug Monro, Population Estimates for Kiribati and Tuvalu (1980) 89(1) J. of the Polynesian Society 199
- ^ G. M. White (1965). Kioa: an Ellice community in Fiji. Project for the Comparative Study of Cultural Change and Stability in Displaced Communities in the Pacific, 1962–63: Oregon University, Department of Anthropology.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|chapterurl=(help) - ^ Lifuka, Neli; edited and introduced by Klaus-Friedrich Koch (1978). Logs in the current of the sea : Neli Lifuka's story of Kioa and the Vaitupu colonists. Australian National University Press/Press of the Langdon Associates. ISBN 0708103626.
{{cite book}}:|last1=has generic name (help); Cite has empty unknown parameter:|chapterurl=(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Michael Goldsmith, Review of Klaus-Friedrich Koch, Logs in the Current of the Sea, Journal of the Polynesian Society, 87:4 (1978), 361–62
- ^ "Opening of Tolise & Motufoua Athletics Championship 2011". Tuvalu Athletics Association (TAA). 2011. Retrieved 20 November 2012.
- ^ Salanieta Bakalevu (Project Coordinator), David Manuella, Tuvalu USP Campus (June 2011). "Open Schooling as a Strategy for Second‐chance Education in the Pacific: A desk study report" (PDF). Commonwealth of Learning (COL) / University of the South Pacific. pp. 96–100. Retrieved 20 November 2012.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) CS1 maint: year (link) - ^ Keith-Reid, Robert (10 March 2000). "Schoolgirls die in horror blaze". The Independent (London). Retrieved 20 November 2012.
- ^ "19 Die in Tuvalu Dormitory Blaze". CBS news (US). 10 March 2000. Retrieved 20 November 2012.
- ^ Seluka, Marica (March 2000). "Motufoua Fire Tragedy – The Story from Tuvalu". Tuvalu Philatelic Bureau Newsletter/Tuvalu Online. Retrieved 20 November 2012.
- ^ "Tuvalu to Issue Stamps for Motufoua Fire Victims". Tuvalu Online. 27 February 2001. Retrieved 20 November 2012.
- ^ Resture, Jane (March 2000). "Photographs of Clive Smith taken at the Motufoua Memorial Service 9th March 2001". Tuvalu Philatelic Bureau Newsletter/ Tuvalu Online. Retrieved 20 November 2012.
- ^ "Motufoua Secondary School solar project – Battery buffered, grid parallel PV solar system". EcoGeneration. May/June 2010. Retrieved 18 October 2011.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ "Off-grid power supply for Motufoua Secondary School" (PDF). SMA Solar Technology. 2011. Retrieved 20 November 2012.
- ^ Panapa, Tufoua (2012). "Ethnographic Research on Meanings and Practices of Health in Tuvalu: A Community Report" (PDF). Report to the Tuvaluan Ministries of Health and Education: Ph D Candidate Centre for Development Studies – "Transnational Pacific Health through the Lens of Tuberculosis" Research Group. Department of Anthropology, The University of Auckland, N.Z. Retrieved 16 March 2013.
- ^ Panapa, Tufoua (2012). "Ethnographic Research on Meanings and Practices of Health in Tuvalu: A Community Report" (PDF). Report to the Tuvaluan Ministries of Health and Education: Ph D Candidate Centre for Development Studies – "Transnational Pacific Health through the Lens of Tuberculosis" Research Group. Department of Anthropology, The University of Auckland, N.Z. pp. 42–44. Retrieved 16 March 2013.
- ^ Cannon, Brian (16 September 2010). "Tuvalu Election Results". Tuvalu News. Tuvaluislands.com. Retrieved 17 September 2010.
- ^ "State Funeral of the late former Governor General of Tuvalu, Reverend Sir Filoimea Telito, GCMG, MBE" (PDF). Tuvalu Philatelic Bureau Newsletter (TPB: 01/2011). 25 July 2011. Retrieved 20 November 2012.
- ^ "Enele Sopoaga Sworn-in Today as Tuvalu's New PM". Islands Business. 5 August 2013. Retrieved 5 August 2013.

