Insulin pump: Difference between revisions
m missing red-linked image removed |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
* a disposable [[infusion set]], including a [[cannula]] for subcutaneous insertion (under the skin) and a tubing system to interface the insulin reservoir to the cannula. |
* a disposable [[infusion set]], including a [[cannula]] for subcutaneous insertion (under the skin) and a tubing system to interface the insulin reservoir to the cannula. |
||
Other configurations are possible. |
Other configurations are possible. For instance, more recent models may include disposable or semi-disposable designs for the pumping mechanism and may eliminate tubing from the infusion set. |
||
An insulin pump is an alternative to multiple daily injections of insulin by [[syringe#Standard U-100 insulin syringes|insulin syringe]] or an [[insulin pen]] and allows for [[intensive insulin therapy]] when used in conjunction with [[blood glucose monitoring]] and carb counting. |
An insulin pump is an alternative to multiple daily injections of insulin by [[syringe#Standard U-100 insulin syringes|insulin syringe]]s or an [[insulin pen]] and allows for [[intensive insulin therapy]] when used in conjunction with [[blood glucose monitoring]] and carb counting. |
||
==Dosing== |
==Dosing== |
||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
===Bolus shape=== |
===Bolus shape=== |
||
An insulin pump user |
An insulin pump user can influence the profile of the rapid-acting insulin by shaping the bolus. Users can experiment with bolus shapes to determine what is best for any given food, which means that they can improve control of [[blood sugar]] by adapting the bolus shape to their needs. |
||
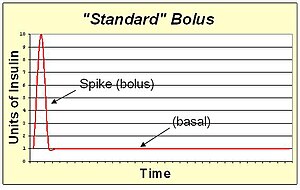
A '''standard bolus''' is an infusion of insulin pumped completely at the onset of the bolus. It |
A '''standard bolus''' is an infusion of insulin pumped completely at the onset of the bolus. It's the most similar to an injection. By pumping with a "spike" shape, the expected action is the fastest possible bolus for that type of insulin. The standard bolus is most appropriate when eating high carb low protein low fat meals because it will return blood sugar to normal levels quickly. |
||
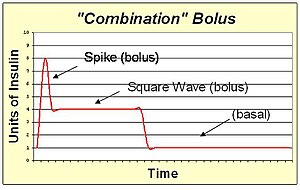
An '''extended bolus''' is a slow infusion of insulin spread out over time. By pumping with a "square wave" shape, the bolus avoids a high initial dose of insulin that may enter the blood and cause low blood sugar before digestion can facilitate sugar entering the blood. The extended bolus also extends the action of insulin well beyond that of the insulin alone. The extended bolus is appropriate when covering high fat high protein meals such as steak, which will be raising blood sugar for many hours past the onset of the bolus. The extended bolus is also useful for those with slow digestion (such as with gastroparesis or [[Coeliac disease]]). |
An '''extended bolus''' is a slow infusion of insulin spread out over time. By pumping with a "square wave" shape, the bolus avoids a high initial dose of insulin that may enter the blood and cause low blood sugar before digestion can facilitate sugar entering the blood. The extended bolus also extends the action of insulin well beyond that of the insulin alone. The extended bolus is appropriate when covering high fat high protein meals such as steak, which will be raising blood sugar for many hours past the onset of the bolus. The extended bolus is also useful for those with slow digestion (such as with gastroparesis or [[Coeliac disease]]). |
||
Revision as of 01:31, 4 January 2014
This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations. (March 2010) |


The insulin pump is a medical device used for the administration of insulin in the treatment of diabetes mellitus, also known as continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion therapy. The device configuration may vary depending on design. A traditional pump includes:
- the pump (including controls, processing module, and batteries)
- a disposable reservoir for insulin (inside the pump)
- a disposable infusion set, including a cannula for subcutaneous insertion (under the skin) and a tubing system to interface the insulin reservoir to the cannula.
Other configurations are possible. For instance, more recent models may include disposable or semi-disposable designs for the pumping mechanism and may eliminate tubing from the infusion set.
An insulin pump is an alternative to multiple daily injections of insulin by insulin syringes or an insulin pen and allows for intensive insulin therapy when used in conjunction with blood glucose monitoring and carb counting.
Dosing


An insulin pump allows the replacement of slow-acting insulin for basal needs with a continuous infusion of rapid-acting insulin.
The insulin pump delivers a single type of rapid-acting insulin in two ways:[1]
- a bolus dose that is pumped to cover food eaten or to correct a high blood glucose level.
- a basal dose that is pumped continuously at an adjustable basal rate to deliver insulin needed between meals and at night.
Bolus shape
An insulin pump user can influence the profile of the rapid-acting insulin by shaping the bolus. Users can experiment with bolus shapes to determine what is best for any given food, which means that they can improve control of blood sugar by adapting the bolus shape to their needs.
A standard bolus is an infusion of insulin pumped completely at the onset of the bolus. It's the most similar to an injection. By pumping with a "spike" shape, the expected action is the fastest possible bolus for that type of insulin. The standard bolus is most appropriate when eating high carb low protein low fat meals because it will return blood sugar to normal levels quickly.
An extended bolus is a slow infusion of insulin spread out over time. By pumping with a "square wave" shape, the bolus avoids a high initial dose of insulin that may enter the blood and cause low blood sugar before digestion can facilitate sugar entering the blood. The extended bolus also extends the action of insulin well beyond that of the insulin alone. The extended bolus is appropriate when covering high fat high protein meals such as steak, which will be raising blood sugar for many hours past the onset of the bolus. The extended bolus is also useful for those with slow digestion (such as with gastroparesis or Coeliac disease).
A combination bolus/multiwave bolus is the combination of a standard bolus spike with an extended bolus square wave. This shape provides a large dose of insulin up front, and then also extends the tail of the insulin action. The combination bolus is appropriate for high carb high fat meals such as pizza, pasta with heavy cream sauce, and chocolate cake.
A super bolus is a method of increasing the spike of the standard bolus. Since the action of the bolus insulin in the blood stream will extend for several hours, the basal insulin could be stopped or reduced during this time. This facilitates the "borrowing" of the basal insulin and including it into the bolus spike to deliver the same total insulin with faster action than can be achieved with spike and basal rate together. The super bolus is useful for certain foods (like sugary breakfast cereals) which cause a large post-prandial peak of blood sugar. It attacks the blood sugar peak with the fastest delivery of insulin that can be practically achieved by pumping.
Bolus timing
Since the pump user is responsible to manually start a bolus, this provides an opportunity for the user to pre-bolus to improve upon the insulin pump's capability to prevent post-prandial hyperglycemia. A pre-bolus is simply a bolus of insulin given before it is actually needed to cover carbohydrates eaten.
There are two situations where a pre-bolus is helpful:
- A pre-bolus of insulin will mitigate a spike in blood sugar that results from eating high glycemic foods. Infused insulin analogs such as NovoLog and Apidra typically begin to impact blood sugar levels 15 or 20 minutes after infusion. As a result, easily digested sugars often hit the bloodstream much faster than infused insulin intended to cover them, and the blood sugar level spikes upward as a result. If the bolus were infused 20 minutes before eating, then the pre-bolused insulin would hit the bloodstream simultaneously with the digested sugars to control the magnitude of the spike.
- A pre-bolus of insulin can combine a meal bolus and a correction bolus when the blood sugar is above the target range before a meal. The timing of the bolus is a controllable variable to bring down the blood sugar level before eating again causes it to increase.
Similarly, a low blood sugar level or a low glycemic food might be best treated with a bolus after a meal is begun. The blood sugar level, the type of food eaten, and a person's individual response to food and insulin have an impact on the ideal time to bolus with the pump.
Basal rate patterns
The pattern for delivering basal insulin throughout the day can also be customized with a pattern to suit the pump user.
- A reduction of basal at night to prevent low blood sugar in infants and toddlers.
- An increase of basal at night to counteract high blood sugar levels due to growth hormone in teenagers.
- A pre-dawn increase to prevent high blood sugar due to the dawn effect in adults and teens.
- In a proactive plan before regularly scheduled exercise times such as morning gym for elementary school children or after-school basketball practice for high school children.
Basal rate determination
Basal insulin requirements will vary between individuals and periods of the day. The basal rate for a particular time period is determined by fasting while periodically evaluating the blood sugar level. Neither food nor bolus insulin must be taken for 4 hours before or during the evaluation period. If the blood sugar level changes dramatically during evaluation, then the basal rate can be adjusted to increase or decrease insulin delivery to keep the blood sugar level approximately steady.
For instance, to determine an individual's morning basal requirement, they must skip breakfast. On waking, they would test their blood glucose level periodically until lunch. Changes in blood glucose level are compensated with adjustments in the morning basal rate. The process is repeated over several days, varying the fasting period, until a 24-hour basal profile has been built up which keeps fasting blood sugar levels relatively steady. Once the basal rate is matched to the fasting basal insulin need, the pump user will then gain the flexibility to skip or postpone meals such as sleeping late on the weekends or working overtime on a weekday.
Many factors can change insulin requirements and require an adjustment to the basal rate:
- continued beta cell death following diagnosis of type 1 diabetes (honeymoon period)
- growth spurts particularly during puberty
- weight gain or loss
- any drug treatment that affects insulin sensitivity (e.g. corticosteroids)
- eating, sleeping, or exercise routine changes
- whenever the control over hyperglycemia is degrading
- and according to the seasons.
A pump user should be educated by their diabetes care professional about basal rate determination before beginning pump therapy.
Temporary basal rates
Since the basal insulin is provided as a rapid-acting insulin, the basal insulin can be immediately increased or decreased as needed with a temporary basal rate. Examples when this is helpful include:
- As a passenger during a long car drive, when more insulin is needed due to inactivity.
- While driving on an extended trip, to reduce the risk of hypoglycemia, a lower temporary basal rate may be programmed.
- During and after spontaneous exercise or sports activities, when the body needs less insulin.
- During illness or stress, when basal demand increases due to insulin resistance.
- When blood ketones are present, when additional insulin is needed.
- When on an extended fast (such as Ramadan, Lent, or Yom Kippur) when basal requirements may be lower.
- During menses, when additional basal insulin is needed.
Advantages of pumping insulin
- Users report better quality of life (QOL) compared to using other devices for administering insulin. The improvement in QOL is reported in type 1 and insulin-requiring type 2 diabetes subjects on pumps.[2]
- The use of rapid-acting insulin for basal needs offers relative freedom from a structured meal and exercise regime previously needed to control blood sugar with slow-acting insulin.[citation needed]
- Programmable basal rates allow for scheduled insulin deliveries of varying amounts at different times of the day. This is especially useful in controlling events such as Dawn phenomenon.[citation needed]
- Many users feel that bolusing insulin from a pump is more convenient and discreet than injection.[citation needed]
- Insulin pumps make it possible to deliver more precise amounts of insulin than can be injected using a syringe. This supports tighter control over blood sugar and Hemoglobin A1c levels, reducing the chance of long-term complications associated with diabetes. This is predicted to result in a long-term cost savings relative to multiple daily injections.[3]
- Many modern "smart" pumps have a "bolus wizard" that calculates how much bolus insulin you need taking into account expected carbohydrate intake, blood sugar level, and still-active insulin.[citation needed]
- Insulin pumps can provide an accurate record of insulin usage through their history menus. On many insulin pumps, this history can be uploaded to a computer and graphed for trend analysis.[citation needed]
- Neuropathy is a troublesome complication of diabetes resistant to usual treatment. There are reports of alleviation or even total disappearance of resistant neuropathic pain with the use of insulin pumps.[4]
- Recent studies of use of insulin pumps in Type 2 diabetes have shown profound improvements in HbA1c, sexual performance, and neuropathy pain.[5]
Disadvantages of pumping insulin
- Insulin pumps, cartridges, and infusion sets may be far more expensive than syringes used for insulin injection.[citation needed]
- Since the insulin pump needs to be worn most of the time, pump users need strategies to participate in activities that may damage the pump, such as rough sports and activities in the water. Some users may find that wearing the pump all the time (together with the infusion set tubing) is uncomfortable or unwieldy.[citation needed]
- An episode of diabetic ketoacidosis may occur if the pump user does not receive sufficient fast acting insulin for many hours. This can happen if the pump battery is discharged, if the insulin reservoir runs empty, the tubing becomes loose and insulin leaks rather than being injected, or if the cannula becomes bent or kinked in the body, preventing delivery. Therefore pump users typically monitor their blood sugars more frequently to evaluate the effectiveness of insulin delivery.[citation needed]
- Possibility of insulin pump malfunctioning, and having to resort back to multiple daily injections until a replacement becomes available. However most pump manufacturers will usually have a program that will get a new pump to the user within 24 hours or allow the user to buy a second pump as a backup for a small fee. Additionally the pump itself will make many safety checks throughout the day, in some cases up to 4,000,000 and may have a second microprocessor dedicated to this.[citation needed]
- Users may experience scar tissue buildup around the inserted cannula, resulting in a hard bump under the skin after the cannula is removed. The scar tissue does not heal particularly fast, so years of wearing the pump and changing the infusion site will cause the user to start running out of viable "spots" to wear the pump. In addition, the areas with scar tissue buildup generally have lower insulin sensitivity and may affect basal rates and bolus amounts. In some extreme cases the insulin delivery will appear to have no/little effect on lowering blood glucose levels and the site must be changed.[citation needed]
- Users may experience allergic reactions and other skin irritation from the adhesive on the back of an infusion set. Experience may vary according to the individual, the pump manufacturer, and the type of infusion set used.[citation needed]
- A larger supply of insulin may be required in order to use the pump. Many units of insulin can be "wasted" while refilling the pump's reservoir or changing an infusion site. This may affect prescription and dosage information.[citation needed]
History of insulin pumps
In 1963 Dr. Arnold Kadish designed the first insulin pump worn as a backpack.[6] A more wearable version was devised by Dean Kamen in 1976. Kamen formed a company called "AutoSyringe" to market the product, which he sold to Baxter Health Care in 1981.[7]
The insulin pump was first endorsed in the United Kingdom in 2003, by the National Institute for Clinical Excellence.
Acceptability
Use of insulin pumps is increasing throughout the world because of:
- easy delivery of multiple insulin injections for those using intensive insulin therapy.
- accurate delivery of very small boluses, helpful for infants.
- growing support among doctors and insurance companies due to the benefits contributing to reducing the incidence of long-term complications.
- improvements in blood glucose monitoring. New meters require smaller drops of blood, and the corresponding lancet poke in the fingers is smaller and less painful. These meters also support alternate site testing for the most routine tests for practically painless testing. This compensates for the need for pump users to test blood sugar more frequently.
- support groups demonstrating techniques for adapting insulin pump use to sports, exercise, and water sports. Expert help is becoming common in user groups and books. The pump can be effectively combined with partial basal insulin from the pump and partial basal insulin from a long-acting insulin such as Lantus and Levemir. This is becoming known as the untethered regimen.
Recent developments

New insulin pumps are becoming "smart" as new features are added to their design. These simplify the tasks involved in delivering an insulin bolus.
- insulin on board: This calculation is based on the size of a bolus, the time elapsed since the completion of the bolus, and a programmable metabolic rate. The pump software will estimate the insulin remaining in the bloodstream and relay it to the user. This supports the process of performing a new bolus before the effects of the last bolus are complete and, thereby, helps prevent the user from overcompensating for high blood sugar with unnecessary correction boluses.
- bolus calculators: Pump software helps by calculating the dose for the next insulin bolus. The user enters the grams of carbohydrates to be consumed, and the bolus "wizard" calculates the units of insulin needed. It adjusts for the most recent blood glucose level and the insulin on board, and then suggests the best insulin dose to the user to approve and deliver.
- custom alarms: The pump can monitor for activities during specific times of day and alarm the user if an expected activity did not occur. Examples include a missed lunch bolus, a missed blood glucose test, a new blood glucose test 15 minutes after a low blood glucose test, etc. The alarms are customized for each user.
- touch bolus: For persons with visual impairments, this button on the pump can be used to bolus for insulin without using the display. This works with a system of beeps to confirm the bolus parameters to the pump user. This feature is described as 'touch', 'audio', or 'easy' bolus depending on brand. The feature was first introduced in the mid- to late 1990s.[citation needed]
- interface to personal computers: Since the late 1990s, most pumps can interface with personal computers for managing and documenting pump programming and/or to upload data from the pump. This simplifies record keeping and can be interfaced with diabetes management software.
- integration with blood glucose meters: Blood glucose data can be manually entered into the pump to support the bolus wizard for calculation of the next insulin bolus. Some pumps support an interface between the insulin pump and a blood glucose meter.
- The Medtronic Diabetes Minimed Paradigm series of insulin pumps allow for radio frequency (RF) communication. This enables the pump to receive data from a Lifescan (in the US) or Bayer (in other countries) blood glucose meter. The RF link also supports a continuous blood glucose sensor known as the Paradigm REAL-Time Continuous Glucose Monitor that wirelessly provides an interstitial glucose value every 5 minutes on the pump screen. The Medtronic REAL-Time System is the first to link a continuous monitor with an insulin pump system.
- The Animas Ping is a pump/blood glucose meter combo that connect to each other using radio frequency. They both can work independently of each other and each have their own history storage. The main purpose of the connection between the pump and the meter is that it allows boluses to be made from the meter or the pump. This is particularly useful when correcting for a high blood sugar as the meter remembers readings and automatically enters them in correction boluses if they are less than 15 minutes old.
- The DANA Diabecare IISG insulin pump has blood glucose meter in it. After blood glucose check with the integrated glucometer, the user can use bolus wizard and deliver a required bolus.
- The Insulet OmniPod has a separate remote, also known as a Personal Diabetes Monitor (PDM), that features a built-in meter that uses Freestyle test strips. This eliminates the need to carry and manage a separate meter or transfer blood glucose results from device to device.
- full featured remote: Insulet's "OmniPod" has a separate electronic display and controls. This remote, or PDM, features a built-in meter that uses Freestyle test strips. The Animas OneTouch Ping pump has a meter remote included based on the Lifescan OneTouch UltraSmart meter that can be used as a glucose meter and a pump remote control.
- simple remote: The Medtronic pumps offer an optional RF remote control that allows the user to deliver a discrete bolus or stop insulin delivery when the pump is concealed or inaccessible. This feature was introduced in 1999.
- bluetooth remote:The Accu-Chek Combo Insulin Pump System, offers a two-way Bluetooth wireless connection between the pump and the blood glucose meter. This gives the patient full control over the pump, and a full check on the pump’s status and activity.
- tubeless pod: The OmniPod is attached directly to the skin by its infusion set, eliminating the tube from the pump.
- touch screen interface: The Tandem Diabetes Care t:slim Insulin Pump uses a color touch screen built around a streamlined user interface more common on consumer electronics.[8]
- rechargeable battery: The Tandem Diabetes Care t:slim Insulin Pump uses an internal, rechargeable battery commonly used by cell phones. Other insulin pumps use disposable dry cell batteries (i.e. AAAs). The t:slim® is recharged via a mini USB cable.[8]
- pre-filled insulin cartridge: The Asante Snap Pump uses pre-filled insulin cartridges so users avoid the time consuming refill process and contamination risk.[9]
Future developments
- When insulin pump technology is combined with a continuous blood glucose monitoring system, the technology seems promising for real-time control of the blood sugar level. Currently there are no mature algorithms to automatically control the insulin delivery based on feedback of the blood glucose level. When the loop is closed, the system may function as an artificial pancreas.
- Insulin pumps are being used for infusing pramlintide (brand name Symlin, or synthetic amylin) with insulin for improved postprandial glycemic control compared to insulin alone.
- Dual hormone insulin pumps that infuse either insulin or glucagon. In event of hypoglycemia, the glucagon could be triggered to increase the blood glucose. This would be particularly valuable in a closed loop system under the control of a glucose sensor.
- Ultrafast insulins. These insulins are absorbed more quickly than the currently available Humalog, Novolog, and Apidra which have a peak at about 60 minutes.[10] Faster insulin uptake would theoretically coordinate with meals better, and allow faster recovery from hyperglycemia if the insulin infusion is suspended. Ultrafast insulins are in development by Biodel,[11] Halozyme, and Novo Nordisk.[12]
Hypoglycemia and new developments
An important step forward is the MySentry system for an automated alert in case of nocturnal hypoglycemia, the development of algorithms for suspension of pump action in case of sensor detected imminent hypoglycemia, and the availability of stable glucagon solutions which will enable automated glucagon delivery from a second sensor activated pump. </ref>
Security
In August 2011, an IBM researcher, Jay Radcliffe, demonstrated a security flaw in insulin pumps. Radcliffe was able to hack the wireless interface used to control the pump remotely.[13] Pump manufacturer Medtronic later said security research by McAfee uncovered a flaw in its pumps that could be exploited.[14]
Choosing a pump
When the time comes to select an insulin pump, there are numerous options. The "perfect" pump varies by person. Factors such as weight, color, cost, canula insertion angles, special features, and easy usage play a vital role in the selection process. Patient factors relevant to infusion set selection include patient’s age, immune system function, body characteristics, activities, personal preferences, and history of diabetic ketoacidosis.[15]
Popular pumps include the Asante Snap, Tandem t:slim, Animas One Touch Ping, Medtronic MiniMed, and OmniPod.[16] The process of selecting a pump usually involves the patient meeting with representatives from companies they are interested in. It is recommended for patients to do as much research as possible. All pumps have the same goal, and each takes a different route. On-line tools have been developed to assist with pump choice.[17]
Bibliography
- Chapter 6 of Understanding Diabetes a.k.a. "The Pink Panther Book" by H. Peter Chase
- "Strike The Spike! Strategies for Combatting After-Meal Highs:" an instructional presentation by Gary Scheiner
References
- ^ http://www.diabetes.co.uk/insulin/Insulin-pumps.html Insulin pumps
- ^ Kesavadev J, Kumar A, Ahammed S, Jothydev S (2008). "Experiences with Insulin Pump in 52 Patients with Type 2 Diabetes in India". DiabetesPro. American Diabetes Association. 2021-PO.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Conget Donlo I, Serrano Contreras D, Rodríguez Barrios JM, Levy Mizrahi I, Castell Abat C, Roze S (2006). "[Cost-utility analysis of insulin pumps compared to multiple daily doses of insulin in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus in Spain]". Rev. Esp. Salud Publica (in Spanish; Castilian). 80 (6): 679–95. PMID 17147307.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) CS1 maint: unrecognized language (link) - ^ Kesavadev J, Rasheed SA. "Dramatic Response of Painful Peripheral Neuropathy with Insulin Pump in Type 2 Diabetes". DiabetesPro. American Diabetes Association. 2097-PO.
- ^ Kesavadev J, Balakrishnan S, Ahammed S, Jothydev S (2009). "Reduction of glycosylated hemoglobin following 6 months of continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion in an Indian population with type 2 diabetes" (PDF). Diabetes Technol. Ther. 11 (8): 517–21. doi:10.1089/dia.2008.0128. PMID 19698065.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ https://wiki.engr.illinois.edu/display/BIOE414/The+History+of+Insulin+Pumps
- ^ http://www.diabeteswellbeing.com/who-invented-the-insulin-pump.html
- ^ a b www.tandemdiabetes.com
- ^ http://www.diabetesmine.com/2013/03/oh-snap-asante-insulin-pump-isnt-a-pearl-anymore.html
- ^ [1], Humalog prescribing information.
- ^ [2], Linjeta duration of action .
- ^ [3], Novo pipeline .
- ^ Insulin Pumps Vulnerable to Hacking
- ^ "Exclusive: Medtronic probes insulin pump risks". Reuters. 25 October 2011.
- ^ http://www.diabeteseducator.org/export/sites/aade/_resources/pdf/research/12-30-11-AADE_Insulin_WhitePaper_Print.pdf
- ^ http://www.diabetesnet.com/diabetes-technology/insulin-pumps/current-pumps/pump-comparison
- ^ http://insulinpump.com/
- Steiner SS, Li M, Hauser R, Pohl R. 2010 Stabilized glucagon formulation for bihormonal pump use. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2010 Nov 1;4(6):1332-7
- Kaiserman K, Buckingham BA, et al 2013 Acceptability and utility of the mySentry remote glucose monitoring system. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2013 Mar 1;7(2):356-61.
- Russell SJ, El-Khatib FH, Nathan DM, Magyar KL, Jiang J, Damiano ER. 2012 Blood glucose control in type 1 diabetes with a bihormonal bionic endocrine pancreas. Diabetes Care. 2012 Nov;35(11):2148-55.
- Phillip M, Battelino Tet al 2013 Nocturnal glucose control with an artificial pancreas at a diabetes camp. N Engl J Med. 2013 Feb 28;368(9):824-33.
