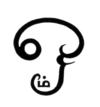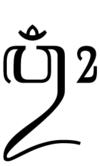Om: Difference between revisions
Om.sukanta (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Om.sukanta (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
{{Contains Indic text}} |
{{Contains Indic text}} |
||
{{Use Indian English|date=June 2013}} |
{{Use Indian English|date=June 2013}} |
||
[http://om-thegod.hpage.com/ '''The OM'''] |
|||
'''Om''' (written universally as {{script|Deva|ॐ}}; in [[Devanagari]] as {{script|Deva|ओं}} ''oṃ'' {{IPA-sa|õː|}}, {{script|Deva|औं}} ''auṃ'' {{IPA-sa|ə̃ũ|}}, or {{script|Deva|ओ३म्}} ''om'' {{IPA-sa|õːm|}}) is a [[mantra]] and mystical [[Sanskrit]] sound of [[Hindu]] origin (geographically India), sacred and important in various [[Dharmic]] religions such as [[Hinduism]], [[Buddhism]], [[Sanatana Dharma]] and [[Jainism]]. The syllable is also referred to as '''omkara''' ({{script|Deva|ओंकार}} ''{{IAST|oṃkāra}}'') or '''aumkara''' ({{script|Deva|औंकार}} ''{{IAST|auṃkāra}}''), literally "om syllable", and in [[Sanskrit]] it is sometimes referred to as ''{{IAST|praṇava}}'', literally "that which is sounded out loudly". |
'''Om''' (written universally as {{script|Deva|ॐ}}; in [[Devanagari]] as {{script|Deva|ओं}} ''oṃ'' {{IPA-sa|õː|}}, {{script|Deva|औं}} ''auṃ'' {{IPA-sa|ə̃ũ|}}, or {{script|Deva|ओ३म्}} ''om'' {{IPA-sa|õːm|}}) is a [[mantra]] and mystical [[Sanskrit]] sound of [[Hindu]] origin (geographically India), sacred and important in various [[Dharmic]] religions such as [[Hinduism]], [[Buddhism]], [[Sanatana Dharma]] and [[Jainism]]. The syllable is also referred to as '''omkara''' ({{script|Deva|ओंकार}} ''{{IAST|oṃkāra}}'') or '''aumkara''' ({{script|Deva|औंकार}} ''{{IAST|auṃkāra}}''), literally "om syllable", and in [[Sanskrit]] it is sometimes referred to as ''{{IAST|praṇava}}'', literally "that which is sounded out loudly". |
||
[http://om-thegod.hpage.com/ '''The OM'''] |
|||
Om is also written ओ३म् (''ō̄m'' {{IPA-sa|õːːm|}}), where ३ is ''pluta'' ("three times as long"), [[pluti|indicating a length]] of three [[morae]] (that is, the time it takes to say three syllables)—an [[vowel length|overlong]] [[nasalised]] [[close-mid back rounded vowel]]—though there are other enunciations adhered to in received traditions. It is placed at the beginning of most [[Hindu text]]s as a sacred incantation to be intoned at the beginning and end of a reading of the [[Vedas]] or prior to any prayer or [[mantra]]. It is used at the end of the invocation to the god being sacrificed to (''anuvakya'') as an invitation to and for the latter to partake of. |
Om is also written ओ३म् (''ō̄m'' {{IPA-sa|õːːm|}}), where ३ is ''pluta'' ("three times as long"), [[pluti|indicating a length]] of three [[morae]] (that is, the time it takes to say three syllables)—an [[vowel length|overlong]] [[nasalised]] [[close-mid back rounded vowel]]—though there are other enunciations adhered to in received traditions. It is placed at the beginning of most [[Hindu text]]s as a sacred incantation to be intoned at the beginning and end of a reading of the [[Vedas]] or prior to any prayer or [[mantra]]. It is used at the end of the invocation to the god being sacrificed to (''anuvakya'') as an invitation to and for the latter to partake of. |
||
[[Image:O3m AryaSamaj.PNG|thumb|ओ३म् - O3m - Aum - OM, the basis of all uttered sound.]] |
[[Image:O3m AryaSamaj.PNG|thumb|ओ३म् - O3m - Aum - OM, the basis of all uttered sound.]] |
||
Revision as of 14:02, 21 February 2014
This article may contain excessive or inappropriate references to self-published sources. (November 2010) |

Template:Contains Indic text The OM Om (written universally as ॐ; in Devanagari as ओं oṃ [õː], औं auṃ [ə̃ũ], or ओ३म् om [õːm]) is a mantra and mystical Sanskrit sound of Hindu origin (geographically India), sacred and important in various Dharmic religions such as Hinduism, Buddhism, Sanatana Dharma and Jainism. The syllable is also referred to as omkara (ओंकार oṃkāra) or aumkara (औंकार auṃkāra), literally "om syllable", and in Sanskrit it is sometimes referred to as praṇava, literally "that which is sounded out loudly".
The OM Om is also written ओ३म् (ō̄m [õːːm]), where ३ is pluta ("three times as long"), indicating a length of three morae (that is, the time it takes to say three syllables)—an overlong nasalised close-mid back rounded vowel—though there are other enunciations adhered to in received traditions. It is placed at the beginning of most Hindu texts as a sacred incantation to be intoned at the beginning and end of a reading of the Vedas or prior to any prayer or mantra. It is used at the end of the invocation to the god being sacrificed to (anuvakya) as an invitation to and for the latter to partake of.

Name, phonology and written representation
The Sanskrit name for the syllable is praṇava, from a root nu "to shout, sound", verbal pra-nu- being attested as "to make a humming or droning sound" in the Brahmanas, and taking the specific meaning of "to utter the syllable om" in the Chāndogya Upanishad and the Shrauta Sutras. More rarely used terms are akṣara (lit. symbol, character) or ekākṣara (lit. one symbol, character), and in later times omkāra becomes prevalent.
Phonologically, the syllable is /aum/, which is regularly monophthongised to [õː] in Sanskrit. It is sometimes also written with pluti, as o3m (ओ३म्), notably by Arya Samaj. When occurring within a Sanskrit utterance, the syllable is subject to the normal rules of sandhi in Sanskrit grammar, however with the additional peculiarity that after preceding a or ā, the au of aum does not form vriddhi (au) but guna (o) per Pāṇini 6.1.95 (i.e. 'om').
The om symbol ![]() is a ligature of Devanagari ओ (U+0913) + ँ (U+0901) (oṃ, encoded in Unicode at U+0950 ॐ, the Tibetan script variant ༀ at U+0F00, the Tamil variant ௐ at U+0BD0, and the Chinese version 唵 at U+5535 or 吽 at U+543D).
is a ligature of Devanagari ओ (U+0913) + ँ (U+0901) (oṃ, encoded in Unicode at U+0950 ॐ, the Tibetan script variant ༀ at U+0F00, the Tamil variant ௐ at U+0BD0, and the Chinese version 唵 at U+5535 or 吽 at U+543D).
-
Devanagari as per the Vedic scripts
-
Tamil script
-
Om in Jain script
Hinduism

| Part of a series on |
| Hinduism |
|---|
 |
The syllable "om" is first described as all-encompassing mystical entity in the Upanishads. Today, in all Hindu art and all over Nepal and India, 'om' can be seen virtually everywhere, a common sign for Hinduism and its philosophy and theology. Hindus believe that as creation began, the divine, all-encompassing consciousness took the form of the first and original vibration manifesting as sound "OM".[1] Before creation began it was "Shunyākāsha", the emptiness or the void. Shunyākāsha, meaning literally "no sky", is more than nothingness, because everything then existed in a latent state of potentiality. The vibration of "OM" symbolises the manifestation of God in form ("sāguna brahman"). "OM" is the reflection of the absolute reality, it is said to be "Adi Anadi", without beginning or the end and embracing all that exists.[1] The mantra "OM" is the name of God, the vibration of the Supreme. When taken letter by letter, A-U-M represents the divine energy (Shakti) united in its three elementary aspects: Bhrahma Shakti (creation), Vishnu Shakti (preservation) and Shiva Shakti (liberation, and/or destruction).[1]
Early Vedantic literature
The syllable is mentioned in all the Upanishads, specially elaborated upon in the Taittiriya, Chāndogya and Māndukya Upanishad set forth as the object of profound religious meditation, the highest spiritual efficacy being attributed not only to the whole word but also to the three sounds a (a-kāra), u (u-kāra), m (ma-kāra), of which it consists. A-kara means form or shape like earth, trees, or any other object. U-kāra means formless or shapeless like water, air or fire. Ma-kāra means neither shape nor shapeless (but still exists) like the dark energy content of the Universe. When we combine all three syllables we get AUM which is a combination of A-kāra, U-kāra, and Ma-kāra.[2]
The Katha Upanishad states:
- "The goal, which all Vedas declare, which all austerities aim at, and which humans desire when they live a life of conscience, I will tell you briefly it is aum"
- "The one syllable [evākṣara, viz. aum] is indeed Brahman. This one syllable is the highest. Whosoever knows this one syllable obtains all that he desires.
- "This is the best support; this is the highest support. Whosoever knows this support is adored in the world of Brahma." (1.2.15–17)[3]
The Chāndogya Upanishad (1.1.1-1) states:
- om ity-etad akṣaram udgītham upāsīta / aum iti hy udgāyati / tasyopavyākhyānam
- "The udgi:tā ["the chanting", that is, the syllable om] is the best of all essences, the highest, deserving the highest place, the eighth."
The Bhagavad Gi:tā (8.13) states that:
- Uttering the monosyllable Aum, the eternal world of Brahman, One who departs leaving the body (at death), he attains the Supreme Goal (i.e., he reaches God).
In Bhagavad Gi:tā (9.17): Lord Krishna says to Arjuna – "I am the father of this universe, the mother, the support and the grandsire. I am the object of knowledge, the purifier and the syllable oṃ. I am also the Ṛig, the Sāma and the Yajur Vedas."
The Bhagvad Gi:tā (17.23) has:
- om tatsatiti nirdesho brahmanstrividhah samratah
- "OM, tat and sat has been declared as the triple appellation of Brahman, who is Truth, Consciousness and Bliss."
In the following sūtra it emphasises, "The repetition of Om should be made with an understanding of its meaning".[4]
Puranic Hinduism


In Purānic Hinduism, om is the mystic name for the Hindu Trimurti, and represents the union of the three gods, viz. a for Brahma, u for Vishnu and m for Mahadev which is another name of Shiva. The three sounds also symbolise the three Vedas, namely (Rigveda, Samaveda, Yajurveda).
According to Hindu philosophy (see Māndukya Upanishad), the letter A represents creation, when all existence issued forth from Brahma's golden nucleus; the letter U refers to Vishnu the God of the middle who preserves this world by balancing Brahma on a lotus above himself, and the letter M symbolises the final part of the cycle of existence, when Brahma falls asleep and Shiva has to breathe in so that all existing things have to disintegrate and are reduced to their essence to him. More broadly, om is said to be the primordial sound that was present at the creation of the universe. It is said to be the original sound that contains all other sounds, all words, all languages and all mantras.
The Māndukya Upanishad is entirely devoted to the explanation of the syllable. The syllable consists of three phonemes, a (Vaishvanara),[5] u (Hiranyagarbha), and m (Ishvara), which symbolise the beginning, duration, and dissolution of the universe and the associated gods Brahma, Vishnu, and Shiva, respectively.[6]
Advaita

In Advaita philosophy it is frequently used to represent three subsumed into one, a triune, a common theme in Hinduism. It implies that our current existence is mithyā and maya, "falsehood", that in order to know the full truth we must comprehend beyond the body and intellect the true nature of infinity. Essentially, upon moksha (mukti, samādhi) one is able not only to see or know existence for what it is, but to become it. When one gains true knowledge, there is no split between knower and known: one becomes knowledge/consciousness itself. In essence, Om is the signifier of the ultimate truth that all is one.
Jainism

In Jainism, om is regarded to be a condensed form of reference to the Pañca-Parameṣṭhi, by their initials A+A+A+U+M (o3m). The Dravyasamgraha quotes a Prakrit line:
- ओम एकाक्षर पञ्चपरमेष्ठिनामादिपम् तत्कथमिति चेत "अरिहंता असरीरा आयरिया तह उवज्झाया मुणियां"
- oma ekākṣara pañca-parameṣṭhi-nāmā-dipam tatkabhamiti ceta "arihatā asarīrā āyariyā taha uvajjhāyā muṇiyā"
- "Om" is one syllable made from the initials of the five parameshthis. It has been said: "Arihant, Ashiri, Acharya, Upajjhaya, Muni" .
Thus, ओं नमः (oṃ namaḥ) is a short form of the Navkar Mantra.
Buddhism
Esoteric Buddhists place om at the beginning of their Vidya-Sadaksari ("om mani padme hum") as well in as most other mantras and dharanis. Moreover, as a seed syllable (a bija mantra) aum is considered holy in Esoteric Buddhism.
In Buddhist texts of East Asian provenance, om is often written as the Chinese character 唵 (pinyin ǎn) or 嗡 (pinyin wēng).
A key distinction should be made here between Buddhism as it arose in Nepal, and Buddhism after the migration of the teachings to Tibet under the guidance of Padmasambhava. In its original form, Buddhism in Nepal was characterised mainly by types of mindfulness meditation and did not involve the chanting of om or of mantras. The chanting of om is not mentioned even a single time in the Pali Canon (oldest known teachings attributed to The Buddha) or Visuddhimagga (ancient commentary on The Pali Canon).
Modern literature
Eben Alexander III (born December, 1953 in Charlotte, North Carolina) is a neurosurgeon and the author of the best-selling Proof of Heaven: A Neurosurgeon's Journey into the Afterlife, in which he shares his thoughts on his near-death experience and whether science can explain that heaven really does exist. In his book Eben says " "I will occasionally use Om as the pronoun for God","OM" was the sound I remembered hearing associated with that omniscient,omnipotent,and unconditionally loving god".
"Onkar" in Sikhism

Ik Onkar, in modern Punjabi spelt out as ਇੱਕ ਓਅੰਕਾਰ, but iconically represented as [ੴ] Error: {{Lang}}: unrecognized language tag: p (help) in the Guru Granth Sahib (although sometimes spelt out in full as ਏਕੰਕਾਰੁ) is the statement of the uniqueness of God in Sikhism,[7] and is commonly translated simply as "one God".[8] Within the phrase, "ik" is the Punjabi word for "one", and "onkar" figuratively means "God" but literally means "creator of Om";[9] the suffix "-kar" derived from the verb "create", "work", or "action".[10] Thus, although "Om" is referenced, Sikhism uses it only to starkly emphasize its monotheism without subscribing to its philosophy in and of itself.[9]
Modern reception
The Brahmic script om-ligature has become widely recognised in western counterculture since the 1960s. As to its precise graphic form, the Vedic or Indian om is what most Westerners are used to, and the Tibetan alphabet om is less widespread in popular culture.[11] Even Tibetan handicrafts made in India tend to use the Nepali-script om for recognisability.
References
- ^ a b c Paramhans Swami Maheshwarananda, The hidden power in humans, Ibera Verlag, page 15., ISBN 3-85052-197-4
- ^ Satyarth Prakāsh by Swāmi Dayānand Saraswati
- ^ :sarve vedā yat padam āmananti / tapām̐si sarvāṇi ca yad vadanti / yad icchanto brahmacaryaṃ caranti / tat te padaṃ saṃgraheṇa bravīmy / om ity-etat //
- etad dhy evākṣaraṃ brahma / etad dhy evākṣaraṃ param / etad dhy evākṣaraṃ jñātvā / yo yad icchati / tasya tat //
- etad ālambanaṃ śreṣṭham / etad ālambanaṃ param / etad ālambanaṃ jñātvā / brahmaloke mahīyate //
- ^ Yoga Sutras of Patanjali, English translation by Bon Giovanni. (sacred-texts.com)
- ^ Mandukya Upanishad
- ^ Werner, Karel (1994). A Popular Dictionary of Hinduism. Curzon Press. ISBN 0-7007-1049-3.
- ^ Wazir Singh, Aspects of Guru Nanak's philosophy (1969), p. 20: "the 'a,' 'u,' and 'm' of aum have also been explained as signifying the three principles of creation, sustenance and annihilation. ... aumkār in relation to existence implies plurality, ... but its substitute Ekonkar definitely implies singularity in spite of the seeming multiplicity of existence. ..."
- ^ Singh, Khushwant (2002). "The Sikhs". In Kitagawa, Joseph Mitsuo (ed.). The religious traditions of Asia: religion, history, and culture. London: RoutledgeCurzon. p. 114. ISBN 0-7007-1762-5.
{{cite book}}: External link in|chapterurl=|chapterurl=ignored (|chapter-url=suggested) (help) - ^ a b Doniger, Wendy (1999). Merriam-Webster's encyclopedia of world religions. Merriam-Webster. p. 500. ISBN 978-0-87779-044-0. Retrieved 2011-08-24.
- ^ "Sri Granth: Advanced Gurbani Search". SriGranth.org. Retrieved 2011-08-24.
- ^ Messerle, Ulrich. "Graphics of the Sacred Symbol OM".