Anatomical terms of bone: Difference between revisions
→Rounded: add |
m →Rounded |
||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
====Rounded==== |
====Rounded==== |
||
A ''[[:wikt:condyle|condyle]]''' ({{IPAc-en|ˈ|k|ɒ|n|d|əl}} or {{IPAc-en|ˈ|k|ɒ|n|d|aɪ|l}}; |
A ''[[:wikt:condyle|condyle]]''' ({{IPAc-en|ˈ|k|ɒ|n|d|əl}} or {{IPAc-en|ˈ|k|ɒ|n|d|aɪ|l}};<ref>[http://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/condyle Entry "condyle"] in ''[http://www.merriam-webster.com/ Merriam-Webster Online Dictionary]''.</ref> is the round prominence at the end of a bone, most often part of a joint - an articulation with another bone. {{sfn|OED|1989|loc="Condyle"}} The ''[[:wikt:Epicondyle|epicondyle]]'' refers to a projection near a condyle, particularly the [[medial epicondyle]] of the [[humerus]]. {{sfn|OED|1989|loc="Epicondyle"}} These terms derive from {{lang-la|condylus}}, from "knuckle" ({{lang-el|kondylos}}), with "epi" referring to "Upon" {{sfn|OED|1989|loc="Condyle, Epicondyle, Epi-"}} |
||
An ''eminence'' refers to a relatively small projection or bump, particularly of bone, such as the [[medial eminence]]. {{sfn|OED|1989|loc="eminence"}} |
An ''eminence'' refers to a relatively small projection or bump, particularly of bone, such as the [[medial eminence]]. {{sfn|OED|1989|loc="eminence"}} |
||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
Both ''tubercle'' and ''tuberosity'' refer to a projection or bump with a roughened surface, with a 'tubercle' generally smaller than a 'tuberosity'. These terms are derived from [[Tuber]], originally from the Latin "swelling" ({{lang-la|Tuber}}) {{sfn|OED|1989|loc="Tuberous, Tubercle"}} |
Both ''tubercle'' and ''tuberosity'' refer to a projection or bump with a roughened surface, with a 'tubercle' generally smaller than a 'tuberosity'. These terms are derived from [[Tuber]], originally from the Latin "swelling" ({{lang-la|Tuber}}) {{sfn|OED|1989|loc="Tuberous, Tubercle"}} |
||
A ''ramus'' refers to an extension of bone, such as the [[ramus of the mandible]] in the [[Human jaw|jaw]] or [[Superior pubic ramus]]. Ramus is derived from "branch" ({{lang-la|Ramus}}) {{sfn|OED|1989|loc="ramus"}} and may also be used to refer to nerves, such as the [[ |
A ''ramus'' refers to an extension of bone, such as the [[ramus of the mandible]] in the [[Human jaw|jaw]] or [[Superior pubic ramus]]. Ramus is derived from "branch" ({{lang-la|Ramus}}) {{sfn|OED|1989|loc="ramus"}} and may also be used to refer to nerves, such as the [[ramus communicans]]. |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
====Pointed==== |
====Pointed==== |
||
Revision as of 08:11, 6 March 2014
Many anatomical terms describing to bone are anatomical terminology, often derived from Greek and Latin, that serve to describe bone.
Protrusions
Process, tubercle, condyle, epicondyle, malleolus, eminence
Articulations
Rounded
A condyle' (/ˈkɒndəl/ or /ˈkɒndaɪl/;[1] is the round prominence at the end of a bone, most often part of a joint - an articulation with another bone. [2] The epicondyle refers to a projection near a condyle, particularly the medial epicondyle of the humerus. [3] These terms derive from Template:Lang-la, from "knuckle" (Template:Lang-el), with "epi" referring to "Upon" [4]
An eminence refers to a relatively small projection or bump, particularly of bone, such as the medial eminence. [5]
A process refers to a relatively large projection or prominent bump,An eminence refers to a relatively small projection or bump, particularly of bone, such as the medial eminence. [6] as does a promontory such as the sacral promontory. [7]
Both tubercle and tuberosity refer to a projection or bump with a roughened surface, with a 'tubercle' generally smaller than a 'tuberosity'. These terms are derived from Tuber, originally from the Latin "swelling" (Template:Lang-la) [8]
A ramus refers to an extension of bone, such as the ramus of the mandible in the jaw or Superior pubic ramus. Ramus is derived from "branch" (Template:Lang-la) [9] and may also be used to refer to nerves, such as the ramus communicans.
A facet refers to a small, flattened articular surface. [citation needed]
Pointed
| crest|| A prominent ridge.
| line|| A long, thin projection, often with a rough surface. Also known as a ridge.
| spine|| A relatively long, thin projection or bump.
Special
These terms are used to describe bony protuberances in specific parts of the body.
The Malleolus (Template:Lang-la) is the bony prominence on each side of the ankle. [10] These are known as the medial and lateral malleolus. Each leg is supported by two bones, the tibia on the inner side (medial) of the leg and the fibula on the outer side (lateral) of the leg. The medial malleolus is the prominence on the inner side of the ankle, formed by the lower end of the tibia. The lateral malleolus is the prominence on the outer side of the ankle, formed by the lower end of the fibula.
The trochanters are parts of the femur, to which muscles attach. [11] It may refer to the greater, lesser, or third trochanter
Cavities
Openings
The following terms are used to describe cavities that connect to other areas:
A foramen (/fəˈreɪmən/;[12][13] pl. foramina, /fəˈræmənə/) is any opening, particularly referring to those in bone. [14] Foramina inside the body of humans and other animals typically allow muscles, nerves, arteries, veins, or other structures to connect one part of the body with another.
A canal is a long, tunnel-like foramen, usually a passage for notable nerves or blood vessels.
Blind-ended
The following terms are used to describe cavities that do not connect to other areas:
A fossa (/ˈfɒsə/;[15][16] plural fossas /ˈfɒsəz/, or fossae (/ˈfɒsiː/ or /ˈfɒsaɪ/); from the Latin "fossa", ditch or trench) is a depression or hollow, usually in a bone, such as the hypophyseal fossa, the depression in the sphenoid bone.[17]
A a meatus /miːˈeɪtəs/[18][19] is a short canal that opens to another part of the body. [20] [a]
A fovea (Template:Lang-la) is a small pit, usually on the head of a bone. The most well-known example of a fovea is the fovea centralis, a depression in the retina of the eye.
Walls
The following terms are used to describe the walls of a cavity:
A labyrinth refers to the bony labyrinth and membranous labryinth, components of the inner ear, due to their fine and complex structure. [21]
A sinus refers to a bony cavity, usually within a the skull. [22]
Relationship with other bones
Articulation
| articular process|| A projection that contacts an adjacent bone. |- | articulation|| The region where adjacent bones contact each other — a joint. |- | suture|| Articulation between cranial bones.
Features of Long Bones

Gross features
Head, neck, body, base
Internal regions
| Bone feature | Definition |
|---|---|
| diaphysis | The long, relatively straight main body of a long bone; region of primary ossification. Also known as the shaft. |
| epiphysis | The end regions of a long bone; regions of secondary ossification. |
| epiphyseal plate | Also known as the growth plate or physis. In a long bone it is a thin disc of hyaline cartilage that is positioned transversely between the epiphysis and metaphysis. In the long bones of humans, the epiphyseal plate disappears by twenty years of age. |
| head | The proximal articular end of the bone. |
| metaphysis | The region of a long bone lying between the epiphysis and diaphysis. |
| neck | The region of bone between the head and the shaft. |
Cortex, medulla
Regions
Head, Neck, Body, Base
Types of bone
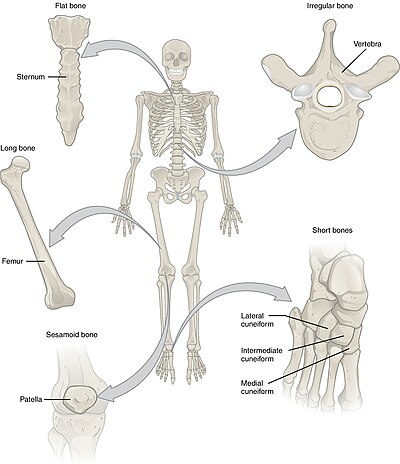
Long Bones
A long bone is one that is cylindrical in shape, being longer than it is wide. However, the term describes the shape of a bone, not its size. Long bones are found in the arms (humerus, ulna, radius) and legs (femur, tibia, fibula), as well as in the fingers (metacarpals, phalanges) and toes (metatarsals, phalanges). Long bones function as levers; they move when muscles contract.[23]
Short Bones
A short bone is one that is cube-like in shape, being approximately equal in length, width, and thickness. The only short bones in the human skeleton are in the carpals of the wrists and the tarsals of the ankles. Short bones provide stability and support as well as some limited motion.[23]
Flat Bones
The term “flat bone” is somewhat of a misnomer because, although a flat bone is typically thin, it is also often curved. Examples include the cranial (skull) bones, the scapulae (shoulder blades), the sternum (breastbone), and the ribs. Flat bones serve as points of attachment for muscles and often protect internal organs.[23]
Irregular Bones
An irregular bone is one that does not have any easily characterized shape and therefore does not fit any other classification. These bones tend to have more complex shapes, like the vertebrae that support the spinal cord and protect it from compressive forces. Many facial bones, particularly the ones containing sinuses, are classified as irregular bones.[23]
Sesamoid Bones
A sesamoid bone is a small, round bone that, as the name suggests, is shaped like a sesame seed. These bones form in tendons (the sheaths of tissue that connect bones to muscles) where a great deal of pressure is generated in a joint. The sesamoid bones protect tendons by helping them overcome compressive forces. Sesamoid bones vary in number and placement from person to person but are typically found in tendons associated with the feet, hands, and knees. The patellae (singular = patella) are the only sesamoid bones found in common with every person.[23]
Notes
- ^ (The plural forms of "meatus" are: meatus, as a Latin form (of the fourth declension noun class, which the word belongs to); or meatuses, as a normally derived English plural; or often, and incorrectly, meati, by false analogy with the very common Latin -us/-i forms (such as alumnus/alumni), i.e., the second declension noun class.)
Images to be placed out
-
Maybe?
References
This Wikipedia entry incorporates text from the freely licenced Connexions [1] edition of Anatomy & Physiology [2] text-book by OpenStax College
- ^ Entry "condyle" in Merriam-Webster Online Dictionary.
- ^ OED 1989, "Condyle".
- ^ OED 1989, "Epicondyle".
- ^ OED 1989, "Condyle, Epicondyle, Epi-".
- ^ OED 1989, "eminence".
- ^ OED 1989, "process".
- ^ OED 1989, "promontory".
- ^ OED 1989, "Tuberous, Tubercle".
- ^ OED 1989, "ramus".
- ^ OED 1989, "Malleolus".
- ^ OED 1989, "Trochanter".
- ^ OED 2nd edition, 1989.
- ^ Entry "foramen" in Merriam-Webster Online Dictionary.
- ^ OED 1989, "Foramen".
- ^ OED 2nd edition, 1989.
- ^ Entry "fossa" in Merriam-Webster Online Dictionary.
- ^ Venieratos D, Anagnostopoulou S, Garidou A., A new morphometric method for the sella turcica and the hypophyseal fossa and its clinical relevance.;Folia Morphol (Warsz). 2005 Nov;64(4):240-7. PMID 16425149
- ^ OED 2nd edition, 1989, as /miːˈeɪtəs/.
- ^ Entry "meatus" in Merriam-Webster Online Dictionary.
- ^ OED 1989, "meatus".
- ^ OED 1989, "labyrinth".
- ^ OED 1989, "sinus".
- ^ a b c d e "Anatomy & Physiology". Openstax college at Connexions. Retrieved November 16, 2013.
- Books
- The Oxford English dictionary. Oxford: Clarendon Press. 1989. ISBN 9780198611868.
{{cite book}}:|first=missing|last=(help)











