Perchlorate: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 73: | Line 73: | ||
Over 40 phylogenetically and metabolically diverse microorganisms capable of perchlorate reduction have been isolated since 1996, including members of the [[Proteobacteria]] as well as two recently identified [[Firmicutes]], ''Moorella perchloratireducens'' and ''Sporomusa'' sp.<ref>{{cite journal | title = Microbial perchlorate reduction: rocket-fuelled metabolism | author = John D. Coates, Laurie A. Achenbach | journal = [[Nature Reviews Microbiology]] | volume = 2 | issue = 7 | pages = 569–580 | year = 2004 | pmid = 15197392| doi = 10.1038/nrmicro926}}</ref> |
Over 40 phylogenetically and metabolically diverse microorganisms capable of perchlorate reduction have been isolated since 1996, including members of the [[Proteobacteria]] as well as two recently identified [[Firmicutes]], ''Moorella perchloratireducens'' and ''Sporomusa'' sp.<ref>{{cite journal | title = Microbial perchlorate reduction: rocket-fuelled metabolism | author = John D. Coates, Laurie A. Achenbach | journal = [[Nature Reviews Microbiology]] | volume = 2 | issue = 7 | pages = 569–580 | year = 2004 | pmid = 15197392| doi = 10.1038/nrmicro926}}</ref> |
||
==Oxyanions of chlorine== |
===Oxyanions of chlorine=== |
||
Chlorine can assume [[oxidation state]]s of −1, +1, +3, +5, or +7, an additional oxidation state of +4 is seen in the neutral compound [[chlorine dioxide]] ClO<sub>2</sub>, which has a similar structure. Several other [[chlorine oxide]]s are also known. |
Chlorine can assume [[oxidation state]]s of −1, +1, +3, +5, or +7, an additional oxidation state of +4 is seen in the neutral compound [[chlorine dioxide]] ClO<sub>2</sub>, which has a similar structure. Several other [[chlorine oxide]]s are also known. |
||
Revision as of 07:13, 29 April 2014
| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Systematic IUPAC name
Perchlorate[1] | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| DrugBank | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.152.366 | ||
| 2136 | |||
| MeSH | 180053 | ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| ClO4− | |||
| Molar mass | 99.451 g mol−1 | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
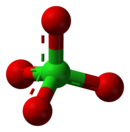
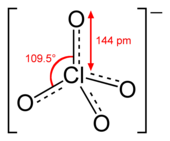
Perchlorates are the salts derived from perchloric acid—in particular when referencing the polyatomic anions found in solution, perchlorate is often written with the formula ClO4−. Perchlorates are often produced by natural processes but can also be produced artificially. They are used extensively within the pyrotechnics industry, and ammonium perchlorate is also a component of solid rocket fuel. Lithium perchlorate, which decomposes exothermically to produce oxygen, is used in oxygen "candles" on spacecraft, submarines, and in other situations where a reliable backup oxygen supply is needed. For example, oxygen "candles" are used in commercial aircraft during emergency situations to compensate for oxygen insufficiency. Most perchlorates are soluble in water,[2] except for potassium perchlorate which has the lowest solubility of any alkali metal perchlorate (1.5 g in 100 mL of water at 25 °C). Perchlorate contamination in the environment has been extensively studied as it has effects on human health. Perchlorate has been linked to its negative influence on the thyroid.
Production and use
Perchlorate salts are produced industrially by the oxidation of solutions of sodium chlorate by electrolysis. This method is used to prepare sodium perchlorate. Four perchlorates are of primary commercial interest: ammonium perchlorate (NH4ClO4), perchloric acid (HClO4), potassium perchlorate (KClO4), and sodium perchlorate (NaClO4). The main application is for rocket fuel.[3] Perchlorate is commercially produced as solid salts of ammonium, sodium, and potassium cations; it is used as an oxidizer in solid propellants for rockets, missiles, fireworks, and certain munitions and used in the manufacture of matches. Potassium perchlorate has, in the past, been used therapeutically to treat hyperthyroidism resulting from Graves' disease via interfering with accumulation of iodide in the thyroid, which results in the blocking of hormone production.[4]
Perchlorate can be produced artificially by humans or by natural processes. For example, electrolysis of chloric acid and following reaction with ammonium hydroxide of high purity produces products of perchloric acid and ammonium perchlorate in the artificial production of ammonium perchlorate by electrochemical process.[5] Further, perchlorate can be produced during natural processes like lightning storms and deposited onto surface soils. Many researchers have simulated the perchlorate production process via generation of an electrical discharge of chloride aerosol, followed by the exposure of the aerosol to high concentrations of ozone. As a further evidence of the origination of perchlorate from natural sources, researchers revealed the presence of perchlorate in rain and snow samples from Lubbock, Texas, and Florida. [6]
Chemical properties
The perchlorate ion is the least reactive oxidizer of the generalized chlorates. This appears to be a paradox, since higher oxidation numbers are expected to be progressively stronger oxidizers, and less stable. A table of reduction potentials of the four chlorates shows that, contrary to expectation, perchlorate is the weakest oxidant among the four in water.[7]
| Ion | Acidic reaction | E° (V) | Neutral/basic reaction | E° (V) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hypochlorite | H+ + HOCl + e− → ½Cl2(g) + H2O | 1.63 | ClO− + H2O + 2e− → Cl− + 2OH− | 0.89 |
| Chlorite | 3H+ + HOClO + 3e− → ½Cl2(g) + 2H2O | 1.64 | ClO2− + 2H2O + 4e− → Cl− + 4OH− | 0.78 |
| Chlorate | 6H+ + ClO3− + 5e− → ½Cl2(g) + 3H2O | 1.47 | ClO3− + 3H2O + 6e− → Cl− + 6OH− | 0.63 |
| Perchlorate | 8H+ + ClO4− + 7e− → ½Cl2(g) + 4H2O | 1.42 | ClO4− + 4H2O + 8e− → Cl− + 8OH− | 0.56 |
These data show that the perchlorate and chlorate are stronger oxidizers in acidic conditions than in basic conditions.
Gas phase measurements of heats of reaction (which allow computation of ΔHf°) of various chlorine oxides do follow the expected trend wherein Cl2O7 exhibits the largest endothermic value of ΔHf° (238.1 kJ/mol) while Cl2O exhibits the lowest endothermic value of ΔHf° (80.3 kJ/mol).[8]
The central chlorine in the perchlorate anion is a closed shell atom and is well protected by the four oxygens. Hence, perchlorate reacts sluggishly. Most perchlorate compounds, especially salts of electropositive metals such as sodium perchlorate or potassium perchlorate, are inert and are slow to react with organic compounds. This property is useful in many applications, such as flares, where ignition is required to initiate a reaction. Ammonium perchlorate is however dangerous, such as in the PEPCON disaster, which destroyed a large-scale production plant for ammonium perchlorate.
Over 40 phylogenetically and metabolically diverse microorganisms capable of perchlorate reduction have been isolated since 1996, including members of the Proteobacteria as well as two recently identified Firmicutes, Moorella perchloratireducens and Sporomusa sp.[9]
Oxyanions of chlorine
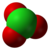
Chlorine can assume oxidation states of −1, +1, +3, +5, or +7, an additional oxidation state of +4 is seen in the neutral compound chlorine dioxide ClO2, which has a similar structure. Several other chlorine oxides are also known.
| Chlorine oxidation state | −1 | +1 | +3 | +5 | +7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | chloride | hypochlorite | chlorite | chlorate | perchlorate |
| Formula | Cl- | ClO− | ClO2− | ClO3− | ClO4− |
| Structure | 
|
|

|
Perchlorate Contamination in Environment
Natural source of perchlorate can be found in the nitrate deposit in Atacama Desert in northern Chile, but most of the detected perchlorate originates from disinfectants, bleaching agents, herbicides, and mostly from rocket propellants.[10] Perchlorate is the breakdown product between perchloric acid and its salt such as magnesium, sodium, potassium and ammonium perchlorate. Except for potassium perchlorate, perchlorate salts are soluble in water and dissociate into the perchlorate anion and the cation from the salt. Because perchlorate salts are readily soluble in both aqueous and non-aqueous solutions, when these salts are solvated, especially ammonium perchlorate, can undergo redox reactions and release gaseous products and release gaseous products and contaminate water and ground.[10] In addition, perchlorate is of concern because of uncertainties about toxicity and health effects at low levels in drinking water, impact on ecosystems, and indirect exposure pathways for humans due to accumulation in vegetables.[4]
Perchlorate Contamination in Drinking Water
Perchlorate is a toxic byproduct of the production of a rocket fuel and fireworks. Low levels of perchlorate have been detected in both drinking water and groundwater in 26 states in the U.S., according to the Environmental Protection Agency. In 2004, the chemical was also found in cow's milk in California with an average level of 1.3 parts per billion ("ppb" or µg/L), which may have entered the cows through feeding on crops that had exposure to water containing perchlorates.[11] According to the Impact Area Groundwater Study Program, the chemical has been detected at levels as high as 5 µg/L in Massachusetts, well over the state regulation of 2 µg/L.[12] Fireworks are also a source of perchlorate in lakes.[13]
The main source of perchlorate contamination comes from use of explosives such as fireworks and rocket propellants and other aerospace materials, and most of its detection comes from testing aerospace materials.[10] The removal and recovery of the perchlorate compounds in explosives and rocket propellants include high-pressure water washout, which generate aqueous ammonium perchlorate. Since 1998, perchlorate has been included in the contaminant candidate list (CCL), primarily due to its detection in California drinking water.[10] The source of perchlorate in California was can mainly be attributed to two manufacturers in Nevada which led to perchlorate release into Lake Mead and Colorado River, affecting its intact regions of Nevada, California and Arizona where water is used for consumption, irrigation and recreation.[10] Lake Mead is attributed as the source of 90% of perchlorate in Southern Nevada's drinking water and the sources of perchlorate in Lake Mead—and downstream in the Colorado River system—are two industrial complexes in the southeast portion of the Las Vegas Valley, where perchlorate is produced for industrial use. Perchlorate [14]Based on sampling, perchlorate is detected in 26 states and is affecting 20 million people, highest detection in Texas, southern California, New Jersey, and Massachusetts, but intensive sampling of the Great Plains and other middle state regions can increase the number of affected regions.[10]
Perchlorate minerals
In some places, perchlorate is detected because of contamination from industrial sites that use or manufacture it. In other places, there is no clear source of perchlorate. In those areas it may be naturally occurring. Natural perchlorate on Earth was first identified in terrestrial nitrate deposits of the Atacama Desert in Chile as early as in the 1880s[15] and for a long time considered a unique perchlorate source. The perchlorate released from the historic use of Chilean nitrate based fertilizer which were imported to the U.S. by the hundreds of tons in the early 19th century can still be found in some groundwater sources of the United States.[16] Recent improvements in analytical sensitivity using ion chromatography based techniques have revealed a more widespread presence of natural perchlorate, particularly in subsoils of Southwest USA,[17] salt evaporites in California and Nevada,[18] Pleistocene groundwater in New Mexico,[19] and even present in extremely remote places such as Antarctica.[20] The data from these studies and others indicate that natural perchlorate is globally deposited on Earth with the subsequent accumulation and transport governed by the local hydrologic conditions.
Despite its importance to environmental contamination, the specific source and processes involved in natural perchlorate production still remain poorly understood. Recent laboratory experiments in conjunction with isotopic studies[21] have implied that perchlorate may be produced on Earth by the oxidation of chlorine species through pathways involving ozone or its photochemical products.[22] Other studies have suggested that perchlorate can also be created by lightning activated oxidation of chloride aerosols (e.g., chloride in sea salt sprays),[23] and ultraviolet or thermal oxidation of chlorine (e.g., bleach solutions used in swimming pools) in water.[24][25][26]
Perchlorate is an environmental contaminant usually associated with the storage, manufacture, and testing of solid rocket motors, which use ammonium perchlorate as an oxidizer.[27] However, real-life contamination of perchlorate has been focused in the use of fertilizer and its perchlorate release into ground water. Fertilizer leaves perchlorate anions to leak into the ground water and threatens the water supplies of many regions in the US.[27] One of the main sources of perchlorate contamination from fertilizer use was found to come from the fertilizer derived from Chilean caliche, because Chile has rich source of naturally occurring perchlorate anion.[28] Perchlorate in the solid fertilizer ranged from 0.7 to 2.0 mg g−1, variation of less than a factor of 3 and it is estimated that sodium nitrate fertilizers derived from Chilean caliche contain approximately 0.5–2 mg g−1 of perchlorate anion.[28] The direct ecological effect of perchlorate is not well known and its impact can be influenced by several factors including rainfall and irrigation, dilution, natural attenuation, soil adsorption, and bioavailability.[28] Quantification of perchlorate concentrations in fertilizer components via ion chromatography revealed that in horticultural fertilizer components contained perchlorate ranging between 0.1 and 0.46%.[29] Perchlorate concentration was the highest in Chilean nitrate, ranging from 3.3 to 3.98%.[29]
Perchlorate is water-soluble, exceedingly mobile in aqueous systems, and can persist for many decades under typical groundwater and surface water conditions.[29] Perchlorate has been found in the water resources of several western states, including Lake Mead and the Colorado River, ranging from 4 to16 μg/L.[29] This water is used for drinking, irrigation, and recreation for approximately half of the population in Arizona, California, and Nevada.[29] Currently, an action level of 18 μg/L has been adopted by several affected states.[29] The potential for groundwater and surface water contamination via agricultural runoff is an obvious concern, and so EPA and other agencies have been analyzing fertilizers to quantitatively determine perchlorate content.[29]
Perchlorate on Mars
In May 2008, the Wet Chemistry Laboratory (WCL) on board the 2007 Phoenix Mars Lander performed the first wet chemical analysis of martian soil. The analyses on three samples, two from the surface and one from depth of 5 cm, revealed a slightly alkaline soil and low levels of salts typically found on Earth. Unexpected though was the presence of ~ 0.6% by weight perchlorate (ClO4−), most likely as a Mg(ClO4)2 phase.[30] The salts formed from perchlorates discovered at the Phoenix landing site act as "anti-freeze" and will substantially lower the freezing point of water. Based on the temperature and pressure conditions on present-day Mars at the Phoenix lander site, conditions would allow a perchlorate salt solution to be present in liquid form for a few hours each day during the summer.[31]
The possibility that the perchlorate was a contaminant brought from Earth has been eliminated by several lines of evidence. The Phoenix retro-rockets used ultra pure hydrazine and launch propellants consisted of ammonium perchlorate. Sensors on board Phoenix found no traces of ammonium, and thus the perchlorate in the quantities present in all three soil samples is indigenous to the martian soil.
In 2006, a mechanism was proposed for the formation of perchlorates that is particularly relevant to the discovery of perchlorate at the Mars Phoenix lander site. It was shown that soils with high concentrations of chloride converted to perchlorate in the presence of sunlight and/or ultraviolet light. The conversion was reproduced in the lab using chloride-rich soils from Death Valley.[32] Other experiments have demonstrated the formation of perchlorate is associated with wide band gap semiconducting oxides.[33]
Further findings by the Mars Curiosity rover in 2012-2013 support perchlorates as being widespread,[34][35] and even inspired a Science article titled "Pesky Perchlorates All Over Mars".[36]
Perchlorate clean up
There have been many attempts to eliminate perchlorate contamination. Current remediation technologies for perchlorate have negative downsides of extreme costs and difficulty in operation.[37] Thus, there have been interests in developing systems that would offer economic and green alternatives to the established remediation technologies.[37] For example, the MIOX Product Development team of MIOX Corporation, by collaborating with Dr. Benjamin Stanford at Hazen and Sawyer, PC, will be endeavoring to develop electrochemical methods, which will remove inorganic disinfection by-products such as perchlorate and chlorate from water.[37]
Ex situ and in situ treatments
Numerous technologies remove perchlorate, including ex situ and in situ treatments. Ex situ treatments include ion exchange using perchlorate-selective or nitrite-specific resins, bioremediation using packed-bed or fluidized-bed bioreactors, and membrane technologies via electrodialysis and reverse osmosis.[38] In addition, ex situ technology of liquid phase carbon adsorption is employed, where granular activated carbon (GAC) is used in eliminating low levels of perchlorate and pretreatment may be required in arranging GAC for perchlorate elimination.[38] Furthermore, in situ treatments, such as bioremediation via perchlorate-selective microbes and permeable reactive barrier, are also being used to treat perchlorate.[38] In situ technology of phytoremediation could also be utilized, even though perchlorate phytoremediation mechanism is not fully founded yet.[38]
Health effects
Perchlorate is a potent competitive inhibitor of the thyroid sodium-iodide symporter.[39] Thus, it has been used to treat hyperthyroidism since the 1950s.[40] At very high doses (70,000–300,000 ppb) the administration of potassium perchlorate was considered the standard of care in the United States, and remains the approved pharmacologic intervention for many countries.
In large amounts perchlorate interferes with iodine uptake into the thyroid gland. In adults, the thyroid gland helps regulate the metabolism by releasing hormones, while in children, the thyroid helps in proper development. The NAS, in its 2005 report, Health Implications of Perchlorate Ingestion, emphasized that this effect, also known as Iodide Uptake Inhibition (IUI) is not an adverse health effect. However, in January 2008, California's Department of Toxic Substances Control stated that perchlorate is becoming a serious threat to human health and water resources.[41] In 2010, the Environmental Protectional Agency's (EPA) Office of the Inspector General determined that the EPA's own perchlorate reference dose of 24.5 parts per billion protects against all human biological effects from exposure. This finding was due to a significant shift in policy at the EPA in basing its risk assessment on non-adverse effects such as IUI instead of adverse effects. The Office of the Inspector General also found that because the EPA's perchlorate reference dose is conservative and protective of human health further reducing perchlorate exposure below the reference dose does not effectively lower risk.[42]
According to some groups, perchlorate affects only the thyroid gland. Because it is neither stored nor metabolized, any effects of perchlorate on the thyroid gland are fully reversible.[43] Less clear are the effects of perchlorate on fetuses, newborns, and children.
Some studies suggest that perchlorate has pulmonary toxic effects as well. Studies have been performed on rabbits where perchlorate has been injected intratracheally. The lung tissue was then removed and analyzed, and it was found that perchlorate injected lung tissue showed multiple adverse effects when compared to the control group that had been intratracheally injected with saline. These effects included inflammatory infiltrates, alveolar collapse, subpleural thickening, and lymphocyte proliferation.[44]
Toxic effects of perchlorate have also been studied in a survey of industrial plant workers who had been exposed to perchlorate, compared to a control group of other industrial plant workers who had no known exposure to perchlorate. After undergoing multiple tests, workers exposed to perchlorate were found to have a significant systolic blood pressure rise compared to the workers who were not exposed to perchlorate, as well as a significant decreased thyroid function compared to the control workers.[45]
A study involving healthy adult volunteers determined that at levels above 0.007 milligrams per kilogram per day (mg/(kg·d)), perchlorate can temporarily inhibit the thyroid gland's ability to absorb iodine from the bloodstream ("iodide uptake inhibition", thus perchlorate is a known goitrogen).[46] The EPA converted this dose into a reference dose of 0.0007 mg/(kg·d) by dividing this level by the standard intraspecies uncertainty factor of 10. The agency then calculated a "drinking water equivalent level" of 24.5 ppb by assuming a person weighs 70 kilograms (154 pounds) and consumes 2 liters (68 ounces) of drinking water per day over a lifetime.[47]
In 2006, a study by Blount, et al. reported a statistical association between environmental levels of perchlorate and changes in thyroid hormones of women with low iodine. The study authors were careful to point out that hormone levels in all the study subjects remained within normal ranges. The authors also indicated that they did not originally normalize their findings for creatinine, which would have essentially accounted for fluctuations in the concentrations of one-time urine samples like those used in this study.[48] When the Blount research was re-analyzed with the creatinine adjustment made, the study population limited to women of reproductive age, and results not shown in the original analysis, any remaining association between the results and perchlorate intake disappeared.[49] Soon after the revised Blount Study was released, NAS panelist Dr. Robert Utiger, a physician with the Harvard Institutes of Medicine, testified before Congress and stated: "I continue to believe that that reference dose, 0.007 milligrams per kilo (24.5 ppb,) which includes a factor of 10 to protect those who might be more vulnerable, is quite adequate."[50]
At a 2013 presentation of a previously unpublished study, it was suggested that environmental exposure to perchlorate in pregnant women with hypothyroidism may be associated with significant risk of low IQ in their children. [51]
Treatment of aplastic anemia
In the early 1960s, potassium perchlorate was implicated in the development of aplastic anemia—a condition where the bone marrow fails to produce new blood cells in sufficient quantity—in thirteen patients, seven of whom died.[52] Subsequent investigations have indicated the connection between administration of potassium perchlorate and development of aplastic anemia to be "equivocable at best", which means that the benefit of treatment, if it is the only known treatment, outweighs the risk, and it appeared a contaminant poisoned the 13.[53]
Regulatory issues in the U.S.
On February 11, 2011, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) issued a "regulatory determination" that perchlorate meets the Safe Drinking Water Act criteria for regulation as a contaminant. The agency found that perchlorate may have an adverse effect on the health of persons and is known to occur in public water systems with a frequency and at levels that it presents a public health concern. As a result of EPA's regulatory determination, it began a process to determine what level of contamination is the appropriate level for regulation. The EPA prepared, as part of its regulatory determination, extensive responses to submitted public comments. The "docket ID" for EPA's regulatory action is EPA-HQ-OW-2009-0297 and can be found on regulations.gov.
Prior to issuance of its regulatory determination, the U.S. EPA issued a recommended Drinking Water Equivalent Level (DWEL) for perchlorate of 24.5 µg/L. In early 2006, EPA issued a "Cleanup Guidance" for this same amount. Both the DWEL and the Cleanup Guidance were based on a thorough review of the existing research by the National Academy of Science (NAS).[54] This followed numerous other studies, including one that suggested human breast milk had an average of 10.5 µg/L of perchlorate.[55] Both the Pentagon and some environmental groups have voiced questions about the NAS report, but no credible science has emerged to challenge the NAS findings. In February 2008, U.S. Food and Drug Administration said that U.S. toddlers on average are being exposed to more than half of the U.S. EPA's safe dose from food alone.[56] In March 2009, a Centers for Disease Control study found 15 brands of infant formula contaminated with perchlorate. Combined with existing perchlorate drinking water contamination, infants could be at risk for exposure to perchlorate above the levels considered safe by E.P.A.[57]
The US Environmental Protection Agency has issued substantial guidance and analysis concerning the impacts of perchlorate on the environment as well as drinking water.[1] California has also issued guidance regarding perchlorate use.[2]
Several states in the U.S. have enacted drinking water standard for perchlorate including Massachusetts in 2006. California's legislature enacted AB 826, the Perchlorate Contamination Prevention Act of 2003, requiring California's Department of Toxic Substance Control (DTSC) to adopt regulations specifying best management practices for perchlorate and perchlorate-containing substances. The Perchlorate Best Management Practices were adopted on December 31, 2005, and became operative on July 1, 2006. [3] California issued drinking water standards in 2007. Several other states, including Arizona, Maryland, Nevada, New Mexico, New York, and Texas have established non-enforceable, advisory levels for perchlorate.
In 2003, a federal district court in California found that the Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation and Liability Act (CERCLA) applied because perchlorate is ignitable and therefore a "characteristic" hazardous waste. (see Castaic Lake Water Agency v. Whittaker, 272 F. Supp. 2d 1053, 1059–61 (C.D. Cal. 2003)).
One example of perchlorate related problems was found at the Olin Flare Facility, Morgan Hill, California—Perchlorate contamination beneath a former flare manufacturing plant in California was first discovered in 2000, several years after the plant had closed. The plant had used potassium perchlorate as one of the ingredients during its 40 years of operation. By late 2003, the state of California and the Santa Clara Valley Water District had confirmed a groundwater plume currently extending over nine miles through residential and agricultural communities.
The Regional Water Quality Control Board and the Santa Clara Valley Water District have engaged in a major outreach effort that has received extensive press and community response. A well testing program is underway for approximately 1,200 residential, municipal, and agricultural wells in the area. Large ion exchange treatment units are operating in three public water supply systems that include seven municipal wells where perchlorate has been detected. The potentially responsible parties, Olin Corporation and Standard Fuse Incorporated, are supplying bottled water to nearly 800 households with private wells. The Regional Water Quality Control Board is overseeing potentially responsible party (PRP) cleanup efforts.[4]
References
- ^ "Perchlorate - PubChem Public Chemical Database". The PubChem Project. USA: National Center for Biotechnology Information.
- ^ Draft Toxicological Profile for Perchlorates, Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, September, 2005.
- ^ Helmut Vogt, Jan Balej, John E. Bennett, Peter Wintzer, Saeed Akbar Sheikh, Patrizio Gallone "Chlorine Oxides and Chlorine Oxygen Acids" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry 2002, Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a06_483
- ^ a b Sridhar Susarla, C. W. Collette, A. W. Garrison, N. L. Wolfe, S. C. McCutcheon "Perchlorate Identification in Fertilizers" in Environmental Science and Technology 1999, American Chemical Society. doi:10.1021/es990577k
- ^ R.L. Dotson. "A novel electrochemical process for the production of ammonium perchlorate" in Journal of Applied Electrochemistry September 1993, Volume 23, Issue 9, pp 897-904. Kluwer Academic Publishers.
- ^ Kathleen Sellers, Katherine Weeks, William R. Alsop, Stephen R. Clough, Marilyn Hoyt, Barbara Pugh, Joseph Robb. "Perchlorate: Environmental Problems and Solutions" 2007, p 9. Taylor & Francis Group, LLC.
- ^ Cotton, F. Albert; Wilkinson, Geoffrey (1988), Advanced Inorganic Chemistry (5th ed.), New York: Wiley-Interscience, p. 564, ISBN 0-471-84997-9
- ^ Wagman, D. D.; Evans, W. H.; Parker, V. P.; Schumm, R. H.; Halow, I.; Bailey, S. M.; Churney, K. L.; Nuttall, R. L. J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data Vol. 11(2); &169;1982 by the American Chemical Society and the American Institute of Physics.
- ^ John D. Coates, Laurie A. Achenbach (2004). "Microbial perchlorate reduction: rocket-fuelled metabolism". Nature Reviews Microbiology. 2 (7): 569–580. doi:10.1038/nrmicro926. PMID 15197392.
- ^ a b c d e f Kucharzyk, Katarzyna. "Development of drinking water standards for perchlorate in the United States". Elsevier B.V.
- ^ Associated Press. "Toxic chemical found in California milk". MSNBC. June 22, 2004.
- ^ http://www.mass.gov/dep/water/dwstand.pdf
- ^ Fireworks Displays Linked To Perchlorate Contamination In Lakes
- ^ https://www.lvvwd.com/wq/facts_perchlorate.html
- ^ Ericksen, G. E. Geology and origin of the Chilean nitrate deposits;U.S. Geological Survey Prof. Paper 1188; USGS: Reston, VA,1981, 37 pp.
- ^ Böhlke, J. K.;Hatzinger, P. B.; Sturchio, N. C.; Gu, B.; Abbene, I.; Mroczkowski, S. J.,Atacama perchlorate as an agricultural contaminant in groundwater: Isotopic andchronologic evidence from Long Island, New York. Environmental science & technology 2009, 43 (15), 5619-5625.
- ^ Rao, B.; Anderson, T. A.;Orris, G. J.; Rainwater, K. A.; Rajagopalan, S.; Sandvig, R. M.; Scanlon, B.R.; Stonestrom, S. A.; Walvoord, M. A.; Jackson, W. A. Widespread NaturalPerchlorate in Unsaturated zones of the Southwest United States" Environ. Sci. Technol 2007, 41, 4522-4528
- ^ Orris, G. J.; Harvey, G. J.; Tsui, D. T.; Eldridge, J. E. Preliminaryanalyses for perchlorate in selected natural materials and theirderivative products; USGS Open File Report 03-314; USGS, U.S.Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, 2003.
- ^ Plummer, L. N.; Bo¨hlke, J. K.; Doughten, M. W. Perchlorate in Pleistocene and Holocene groundwater in North-Central New Mexico" Environ. Sci. Technol 2005, 39, 4586-4593.
- ^ Böhlke, John Karl, Neil C. Sturchio, Baohua Gu, Juske Horita, Gilbert M. Brown, W. Andrew Jackson, Jacimaria Batista, and Paul B. Hatzinger. "Perchlorate isotope forensics." Analytical Chemistry 77, no. 23 (2005) 7838-7842.
- ^ Rao, B.; Anderson, T. A.;Redder, A.; Jackson, W. A. Perchlorate Formation by Ozone Oxidation of AqueousChlorine/Oxy-Chlorine Species: Role of ClxOy Radicals" Environ. Sci. Technol 2010, 44, 2961-2967
- ^ Dasgupta,P. K.; Martinelango, P. K.; Jackson, W. A.; Anderson, T. A.; Tian, K.; Tock, R.W.; Rajagopalan, S., The origin of naturally occurring perchlorate: the role ofatmospheric processes. Environmental science& technology 2005, 39 (6), 1569-1575.
- ^ Rao, B.; Estrada, N; Mangold, J.; Shelly, M.; Gu, B.; Jackson, W. A. Perchlorate production byphotodecomposition of aqueous chlorine. Environ.Sci. Technol., 2012, doi:10.1021/es3015277
- ^ Stanford, B. D., Pisarenko, A. N., Snyder, S. A., & Gordon, G. (2011). Perchlorate, bromate, and chlorate in hypochlorite solutions: Guidelines for utilities. Journal American Water Works Association, 103(6), 71.
- ^ William E. Motzer (2001). "Perchlorate: Problems, Detection, and Solutions". Environmental Forensics. 2 (4): 301–311. doi:10.1006/enfo.2001.0059.
- ^ a b Matthew L. Magnuson, Edward T. Urbansky, Catherine A. Kelty, "Determination of Perchlorate at Trace Levels in Drinking Water by Ion-Pair Extraction with Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry" Analytical Chemistry 72, no. 1 (2000)
- ^ a b c .T. Urbansky *, S.K. Brown, M.L. Magnuson, C.A. Kelty, "Perchlorate levels in samples of sodium nitrate fertilizer derived from Chilean caliche" Environmental Pollution 112 (2001)
- ^ a b c d e f g Sridhar Susarla ,* T. W. Collette , A. W. Garrison , N. L. Wolfe , and S. C. McCutcheon "Perchlorate Identification in Fertilizers" Environmental Science and Technology 33 (1999)
- ^ Hecht, M. H., S. P. Kounaves, R. Quinn; et al. (2009). "Detection of Perchlorate & the Soluble Chemistry of Martian Soil at the Phoenix Mars Lander Site". Science. 325 (5936): 64–67. Bibcode:2009Sci...325...64H. doi:10.1126/science.1172466. PMID 19574385.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Chevrier, V. C., Hanley, J., and Altheide, T.S. (2009). "Stability of perchlorate hydrates and their liquid solutions at the Phoenix landing site, Mars". Geophysical Research Letters. 36 (10): L10202. Bibcode:2009GeoRL..3610202C. doi:10.1029/2009GL037497.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Miller, Glen. "Photooxidation of chloride to perchlorate in the presence of desert soils and titanium dioxide". American Chemical Society. March 29, 2006
- ^ Jennifer D. Schuttlefield, Justin B. Sambur, Melissa Gelwicks, Carrick M. Eggleston, and B. A. Parkinson "Photooxidation of Chloride by Oxide Minerals: Implications for Perchlorate on Mars" J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, vol. 133, pp. 17521–17523. doi:10.1021/ja2064878
- ^ Adam Mann. "Look What We Found on Mars - Curiosity Rover Serves Up Awesome Science". Slate (magazine). 26 September 2013.
- ^ Chang, Kenneth (1 October 2013). "Hitting Pay Dirt on Mars". New York Times. Retrieved 2 October 2013.
- ^ Richard A. Kerr. "Pesky Perchlorates All Over Mars". Science (journal). 12 April 2013. Vo. 340 No. 6129 P. 138. doi:10.1126/science.340.6129.138-b
- ^ a b c "Eliminating Water Contamination by Inorganic Disinfection Byproducts". Hazen and Sawyer. Hazen and Sawyer.
- ^ a b c d "Technical Fact Sheet – Perchlorate" (PDF). US EPA. US EPA.
- ^ Braverman, L. E.; He X.; Pino S.; et al. (2005). "The effect of perchlorate, thiocyanate, and nitrate on thyroid function in workers exposed to perchlorate long-term". J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 90 (2): 700–706. doi:10.1210/jc.2004-1821. PMID 15572417.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Godley, A. F.; Stanbury, J. B. (1954). "Preliminary experience in the treatment of hyperthyroidism with potassium perchlorate". J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 14 (1): 70–78. doi:10.1210/jcem-14-1-70. PMID 13130654.
{{cite journal}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|month=(help) - ^ California Department of Toxic Substances Control Jan 26, 2008
- ^ Scientific Analysis of Perchlorate (Report). United States Environmental Protection Agency, Office of the Inspector General. 19 April 2010.
What We Found
- ^ J. Wolff (1998). "Perchlorate and the Thyroid Gland". Pharmacological Reviews. 50 (1): 89–105. PMID 9549759.
- ^ Wu F., Chen H., Zhou X., Zhang R., Ding M., Liu Q., Peng KL. Pulmonary fibrosis effect of ammonium perchlorate exposure in rabbit. Taylor & Francis Group, LLC. Arch Environ Occup Health. 2013;68(3):161-5. PubMed PMID 23566323
- ^ Chen HX, Shao YP, Wu FH, Li YP, Peng KL. [Health survey of plant workers for an occupational exposure to ammonium perchlorate]. Zhonghua Lao Dong Wei Sheng Zhi Ye Bing Za Zhi. 2013 Jan;31(1):45-7. PubMed PMID 23433158
- ^ Greer, M. A., Goodman, G., Pleuss, R. C., Greer, S. E. (2002). "Health effect assessment for environmental perchlorate contamination: The dose response for inhibition of thyroidal radioiodide uptake in humans" (free online). Environmental Health Perspectives. 110 (9): 927–937. doi:10.1289/ehp.02110927. PMC 1240994. PMID 12204829.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ US EPA Memorandum Jan 26, 2006
- ^ Benjamin C. Blount, James L. Pirkle, John D. Osterloh, Liza Valentin-Blasini, and Kathleen L. Caldwell (2006). "Urinary Perchlorate and Thyroid Hormone Levels in Adolescent and Adult Men and Women Living in the United States". Environmental Health Perspectives. 114 (12): 1865–71. doi:10.1289/ehp.9466. PMC 1764147. PMID 17185277.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Tarone; et al. (2010). "The Epidemiology of Environmental Perchlorate Exposure and Thyroid Function: A Cmprehensive Review". Journal of Occupational and Environmental Medicine. 52 (June): 653–60. doi:10.1097/JOM.0b013e3181e31955. PMID 20523234.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help) - ^ "Perchlorate: Health and Environmental Impacts of Unregulated Exposure". United States Congress. Retrieved 15 April 2012.
- ^ Perchlorate Levels in Pregnancy Linked to Low Childhood IQ, by Nancy A. Melville, October 22, 2013
- ^ National Research Council (2005). "Perchlorate and the thyroid". Health implications of perchlorate ingestion. Washington, D.C: National Academies Press. p. 7. ISBN 0-309-09568-9. Retrieved on April 3, 2009 through Google Book Search.
- ^ Clark, J. J. J. (2000). "Toxicology of perchlorate". In Urbansky ET (ed.) (ed.). Perchlorate in the environment. New York: Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishers. pp. 19–20. ISBN 978-0-306-46389-1.
{{cite book}}:|editor=has generic name (help) Retrieved on April 3, 2009 through Google Book Search. - ^ Committee to Assess the Health Implications of Perchlorate Ingestion, National Research Council (2005). Health Implications of Perchlorate Ingestion. Washington, DC: The National Academies Press. ISBN 0-309-09568-9.
- ^ McKee, Maggie. "Perchlorate found in breast milk across US". New Scientist. February 23, 2005
- ^ Perchlorate In Food
- ^ "CDC Scientists Find Rocket Fuel Chemical In Infant Formula". Anila Jacob, M.D., M.P.H.. Environmental Working Group. 2 April 2009.
External links
- NAS Report: The Health Effects of Perchlorate Ingestion
- NRDC's criticism of NAS report
- Environment California report (Executive Summary with link to full text)
- Macho Moms: Perchlorate pollutant masculinizes fish: Science News Online, Aug. 12, 2006
- New Scientist Space Blog: Phoenix discovery may be bad for Mars life
- "State Threatening To Sue Military Over Water Pollution", Associated Press, May 19, 2003.
- "Health Effects Of Perchlorate From Spent Rocket", SpaceDaily.com, July 11, 2002.
- = Dept of Defense, Dept of Energy, and US Environmental Protection Agency's Strategic Environmental Research and Development Program, Elimination of Perchlorate Oxidizers from Pyrotechnic Flare Compositions, 2009