Submandibular lymph nodes: Difference between revisions
m cleanup (wikitables, html markup, layout, etc.) |
Billinghurst (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
One gland, the ''middle gland of Stahr'', which lies on the [[external maxillary artery]] as it turns over the mandible, is the most constant of the series; small lymph glands are sometimes found on the deep surface of the [[submandibular gland]]. |
One gland, the ''middle gland of Stahr'', which lies on the [[external maxillary artery]] as it turns over the mandible, is the most constant of the series; small lymph glands are sometimes found on the deep surface of the [[submandibular gland]]. |
||
The '' |
The ''afferents'' of the submandibular glands drain the [[medial palpebral commissure]], the [[cheek]], the side of the [[Human nose|nose]], the [[upper lip]], the lateral part of the [[lower lip]], the [[gums]], and the anterior part of the margin of the [[tongue]]. |
||
''[[Efferent]]'' vessels from the facial and submental glands also enter the submaxillary glands. Their efferent vessels pass to the [[superior deep cervical glands]]. |
''[[Efferent]]'' vessels from the facial and submental glands also enter the submaxillary glands. Their efferent vessels pass to the [[superior deep cervical glands]]. |
||
Revision as of 11:34, 7 February 2015
| Submandibular lymph nodes | |
|---|---|
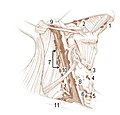
 1: Submental lymph nodes 2: Submandibular lymph nodes 3: Supraclavicular lymph nodes 4: Retropharyngeal lymph nodes 5: Buccinator lymph node 6: Superficial cervical lymph nodes 7: Jugular lymph nodes 8: Parotid lymph nodes 9: Retroauricular lymph nodes & occipital lymph nodes | |
 Superficial lymph glands and lymphatic vessels of head and neck. (Submaxillary glands labeled at center right.) | |
| Details | |
| System | Lymphatic system |
| Source | Mandibular lymph node |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Nodi lymphoidei submandibulares |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The submandibular lymph nodes (submaxillary glands in older texts), three to six in number, are placed beneath the body of the mandible in the submaxillary triangle, and rest on the superficial surface of the submandibular gland.
One gland, the middle gland of Stahr, which lies on the external maxillary artery as it turns over the mandible, is the most constant of the series; small lymph glands are sometimes found on the deep surface of the submandibular gland.
The afferents of the submandibular glands drain the medial palpebral commissure, the cheek, the side of the nose, the upper lip, the lateral part of the lower lip, the gums, and the anterior part of the margin of the tongue.
Efferent vessels from the facial and submental glands also enter the submaxillary glands. Their efferent vessels pass to the superior deep cervical glands.
Additional images
-
Deep Lymph Nodes
References
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 697 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 697 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
External links
- Diagram at umich.edu - rollover to see labels
- http://www.med.mun.ca/anatomyts/head/hnl3a.htm
- Diagram at Baylor College of Medicine
- http://www.patient.co.uk/showdoc/27000835/
- http://www.aafp.org/afp/20021201/2103.html
- http://www.emedicine.com/ent/topic306.htm#section~anatomy_of_the_cervical_lymphatics