Anatomical snuffbox: Difference between revisions
m Dating maintenance tags: {{Citation needed}} |
|||
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
=== Neurovascular anatomy === |
=== Neurovascular anatomy === |
||
Deep to the tendons which form the borders of the anatomical snuff box lies the [[radial artery]], which passes through the anatomical snuffbox on its course from the normal radial pulse detecting area, to the proximal space in between the first and second [[metacarpals]] to contribute to the superficial and deep palmar arches. The [[cephalic vein]] arises within the anatomical snuffbox, while the [[dorsal cutaneous branch]] of the [[radial nerve]] can be palpated by stroking along the extensor pollicis longus with the dorsal aspect of a fingernail. |
Deep to the tendons which form the borders of the anatomical snuff box lies the [[radial artery]], which passes through the anatomical snuffbox on its course from the normal radial pulse detecting area, to the proximal space in between the first and second [[metacarpals]] to contribute to the superficial and deep palmar arches. The [[cephalic vein]] arises within the anatomical snuffbox, while the [[Superficial branch of radial nerve|dorsal cutaneous branch]] of the [[radial nerve]] can be palpated by stroking along the extensor pollicis longus with the dorsal aspect of a fingernail. |
||
==Clinical significance== |
==Clinical significance== |
||
Revision as of 14:03, 22 August 2015
| Anatomical snuffbox | |
|---|---|
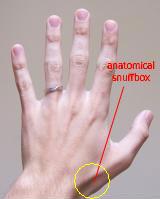 anatomical snuffbox | |
 The mucous sheaths of the tendons on the back of the wrist. (Anatomical snuffbox not labeled, but visible at right.) | |
| Details | |
| Artery | radial artery |
| Vein | cephalic vein |
| Nerve | radial nerve |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | fovea radialis |
| TA2 | 301 |
| FMA | 42329 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The anatomical snuff box or snuffbox is a triangular deepening on the radial, dorsal aspect of the hand—at the level of the carpal bones, specifically, the scaphoid and trapezium bones forming the floor. The name originates from the use of this surface for placing and then sniffing powdered tobacco, or "snuff." It is sometimes referred to by its French name tabatière.
Structure
Boundaries
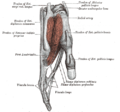
- The medial border of the snuffbox is the tendon of the extensor pollicis longus.
- The lateral border (closest to the edge of the hand) is a pair of parallel and intimate tendons, of the extensor pollicis brevis and the abductor pollicis longus.[1] (Accordingly, the anatomical snuffbox is most visible, having a more pronounced concavity, during thumb extension.)
- The proximal border is formed by the styloid process of the radius
- The distal border is formed by the approximate apex of the schematic snuffbox isosceles triangle.
- The floor of the snuffbox varies depending on the position of the wrist, but both the trapezium and primarily the scaphoid can be palpated.
Neurovascular anatomy
Deep to the tendons which form the borders of the anatomical snuff box lies the radial artery, which passes through the anatomical snuffbox on its course from the normal radial pulse detecting area, to the proximal space in between the first and second metacarpals to contribute to the superficial and deep palmar arches. The cephalic vein arises within the anatomical snuffbox, while the dorsal cutaneous branch of the radial nerve can be palpated by stroking along the extensor pollicis longus with the dorsal aspect of a fingernail.
Clinical significance
The radius and scaphoid articulate deep to the snuffbox to form the basis of the wrist joint. In the event of a fall onto an outstretched hand (FOOSH), this is the area through which the brunt of the force will focus. This results in these two bones being the most often fractured of the wrist. In a case where there is localized tenderness within the snuffbox, knowledge of wrist anatomy leads to the speedy conclusion that the fracture is likely to be of the scaphoid. This is understandable as the scaphoid is a small, oddly shaped bone whose purpose is to facilitate mobility rather than confer stability to the wrist joint [citation needed]. In the event of inordinate application of force over the wrist, this small scaphoid is likely to be the weak link [citation needed]. Scaphoid fracture is one of the most frequent causes of medico-legal issues.
An anatomical anomaly in the vascular supply to the scaphoid is the area to which the blood supply is first delivered. Blood enters the scaphoid distally. Consequently, in the event of a fracture the proximal segment of the scaphoid will be devoid of a vascular supply, and will—if action is not taken—avascularly necrose within a sufferer's snuffbox. Due to the small size of the scaphoid and its shape, it is difficult to determine, early on, whether or not the scaphoid is indeed fractured with an x-ray. Further complications include; carpal instability (ligament disruption) and fracture-dislocations.
Additional images
-
Tendons of forefinger and vincula tendina.
-
The veins on the dorsum of the hand.
-
Palm of left hand, showing position of skin creases and bones, and surface markings for the volar arches.
-
A particularly cavernous anatomical snuff box.
References
- ^ "Chapter 10: THE FOREARM". Archived from the original on 9 December 2007. Retrieved 2008-01-05.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help)