Gregorian calendar: Difference between revisions
Undid revision 678401320 by Gherghel (talk) per WP:SEEALSO, this is linked above |
|||
| Line 302: | Line 302: | ||
*[[Old Calendarists]] |
*[[Old Calendarists]] |
||
**[[Greek Old Calendarists]] |
**[[Greek Old Calendarists]] |
||
*[[Tropical year]] |
|||
==Notes== |
==Notes== |
||
Revision as of 05:15, 29 August 2015
The Gregorian calendar, also called the Western calendar and the Christian calendar, is internationally the most widely used civil calendar.[1][2][3] It is named for Pope Gregory XIII, who introduced it in 1582.
The calendar was a refinement in 1582 to the Julian calendar[4] amounting to a 0.002% correction in the length of the year. The motivation for the reform was to bring the date for the celebration of Easter to the time of the year in which it was celebrated when it was introduced by the early Church. Because the celebration of Easter was tied to the spring equinox, the Roman Catholic Church considered the steady drift in the date of Easter caused by the year being slightly too long to be undesirable. The reform was adopted initially by the Catholic countries of Europe. Protestants and Eastern Orthodox countries continued to use the traditional Julian calendar and adopted the Gregorian reform after a time, for the sake of convenience in international trade. The last European country to adopt the reform was Greece, in 1923.
The Gregorian reform contained two parts: a reform of the Julian calendar as used prior to Pope Gregory XIII's time and a reform of the lunar cycle used by the Church, with the Julian calendar, to calculate the date of Easter. The reform was a modification of a proposal made by Aloysius Lilius.[5] His proposal included reducing the number of leap years in four centuries from 100 to 97, by making 3 out of 4 centurial years common instead of leap years. Lilius also produced an original and practical scheme for adjusting the epacts of the moon when calculating the annual date of Easter, solving a long-standing obstacle to calendar reform.
The Gregorian reform modified the Julian calendar's scheme of leap years as follows:
Every year that is exactly divisible by four is a leap year, except for years that are exactly divisible by 100, but these centurial years are leap years if they are exactly divisible by 400. For example, the years 1700, 1800, and 1900 are not leap years, but the year 2000 is.[6]
In addition to the change in the mean length of the calendar year from 365.25 days (365 days 6 hours) to 365.2425 days (365 days 5 hours 49 minutes 12 seconds), a reduction of 10 minutes 48 seconds per year, the Gregorian calendar reform also dealt with the accumulated difference between these lengths. The canonical Easter tables were devised at the end of the third century, when the vernal equinox fell either on 20 March or 21 March depending on the year's position in the leap year cycle. As the rule was that the full moon preceding Easter was not to precede the equinox the equinox was fixed at 21 March for computational purposes and the earliest date for Easter was fixed at 22 March. The Gregorian calendar reproduced these conditions by removing ten days.[7]
To unambiguously specify the date, dual dating or Old Style (O.S.) and New Style (N.S.) are sometimes used with dates. Dual dating uses two consecutive years because of differences in the starting date of the year, or includes both the Julian and Gregorian dates. Old Style and New Style (N.S.) indicate either whether the start of the Julian year has been adjusted to start on 1 January (N.S.) even though documents written at the time use a different start of year (O.S.), or whether a date conforms to the Julian calendar (O.S.) rather than the Gregorian (N.S.).
The Gregorian calendar continued to use the previous calendar era (year-numbering system), which counts years from the traditional date of the nativity (Anno Domini), originally calculated in the 6th century by Dionysius Exiguus.[8] This year-numbering system, also known as Dionysian era or Common Era, is the predominant international standard today.[9]
Description
| No. | Name | Length in days |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | January | 31 |
| 2 | February | 28 or 29 |
| 3 | March | 31 |
| 4 | April | 30 |
| 5 | May | 31 |
| 6 | June | 30 |
| 7 | July | 31 |
| 8 | August | 31 |
| 9 | September | 30 |
| 10 | October | 31 |
| 11 | November | 30 |
| 12 | December | 31 |


The Gregorian calendar is a solar calendar. A regular Gregorian year consists of 365 days. As in the Julian calendar, in a leap year, a leap day is added to February. When the Julian calendar was introduced by order of Julius Caesar the leap day fell immediately after 23 February. Anniversaries in February keep to the same day of the month, whether the year is leap or not. Some churches, notably the Roman Catholic Church, delay February festivals after the 23rd by one day in leap year.[10] In the Julian calendar, a leap year occurs every 4 years, but the Gregorian calendar omits 3 leap days every 400 years.
Gregorian years are identified by consecutive year numbers.[11] The cycles repeat completely every 146,097 days, which equals 400 years, and which also happens to be 20,871 seven-day weeks.[12][13]
Of these 400 years, 303 are regular years of 365 days and 97 are leap years of 366 days. A calendar mean year is 365 days = 365.2425 days = 365 days, 5 hours, 49 minutes and 12 seconds. The same result is obtained by summing the fractional parts implied by the rule: 365 + 1⁄4 − 1⁄100 + 1⁄400 = 365 + 0.25 − 0.01 + 0.0025 = 365.2425
For patterns within the calendar consider Zeller's Congruence.
A calendar date is fully specified by the year (numbered by some scheme beyond the scope of the calendar itself), the month (identified by name or number), and the day of the month (numbered sequentially starting at 1).
Although the calendar year runs from 1 January to 31 December, at previous times year numbers were based on a different starting point within the calendar. (See the "beginning of the year" section below.)
Gregorian reform


The calendar was a reform in 1582 to the Julian calendar. It was introduced by Pope Gregory XIII, after whom the calendar was named, by papal bull Inter gravissimas dated 24 February 1582.[4] The motivation for the adjustment was to bring the date for the celebration of Easter to the time of year in which it was celebrated when it was introduced by the early Church. Although a recommendation of the First Council of Nicaea in 325 specified that all Christians should celebrate Easter on the same day, it took almost five centuries before virtually all Christians achieved that objective by adopting the rules of the Church of Alexandria (see Easter for the issues which arose).[14]
Background
Because the spring equinox was tied to the date of Easter, the Roman Catholic Church considered the seasonal drift in the date of Easter undesirable. The Church of Alexandria celebrated Easter on the Sunday after the 14th day of the moon (computed using the Metonic cycle) that falls on or after the vernal equinox, which they placed on 21 March. However, the Church of Rome still regarded 25 March as the equinox (until 342) and used a different cycle to compute the day of the moon.[15] In the Alexandrian system, since the 14th day of the Easter moon could fall at earliest on 21 March its first day could fall no earlier than 8 March and no later than 5 April. This meant that Easter varied between 22 March and 25 April. In Rome, Easter was not allowed to fall later than 21 April, that being the day of the Parilia or birthday of Rome and a pagan festival.The first day of the Easter moon could fall no earlier than 5 March and no later than 2 April.
Easter was the Sunday after the 15th day of this moon, whose 14th day was allowed to precede the equinox. Where the two systems produced different dates there was generally a compromise so that both churches were able to celebrate on the same day. By the 10th century all churches (except some on the eastern border of the Byzantine Empire) had adopted the Alexandrian Easter, which still placed the vernal equinox on 21 March, although Bede had already noted its drift in 725—it had drifted even further by the 16th century.[16]
Worse, the reckoned Moon that was used to compute Easter was fixed to the Julian year by a 19-year cycle. That approximation built up an error of one day every 310 years, so by the 16th century the lunar calendar was out of phase with the real Moon by four days.
Preparation
The Council of Trent approved a plan in 1563 for correcting the calendrical errors, requiring that the date of the vernal equinox be restored to that which it held at the time of the First Council of Nicaea in 325 and that an alteration to the calendar be designed to prevent future drift. This would allow for a more consistent and accurate scheduling of the feast of Easter. In 1577, a Compendium was sent to expert mathematicians outside the reform commission for comments. Some of these experts, including Giambattista Benedetti and Giuseppe Moleto, believed Easter should be computed from the true motions of the sun and moon, rather than using a tabular method, but these recommendations were not adopted.[17] The reform adopted was a modification of a proposal made by the Calabrian doctor Aloysius Lilius (or Lilio).[5]
Lilius's proposal included reducing the number of leap years in four centuries from 100 to 97, by making three out of four centurial years common instead of leap years. He also produced an original and practical scheme for adjusting the epacts of the moon when calculating the annual date of Easter, solving a long-standing obstacle to calendar reform.
Ancient tables provided the sun's mean longitude.[18][19] Christopher Clavius, the architect of the Gregorian calendar, noted that the tables agreed neither on the time when the sun passed through the vernal equinox nor on the length of the mean tropical year. Tycho Brahe also noticed discrepancies.[20][21] The Gregorian leap year rule (97 leap years in 400 years) was put forward by Petrus Pitatus of Verona in 1560. He noted that it is consistent with the tropical year of the Alfonsine tables and with the mean tropical year of Copernicus (De revolutionibus) and Reinhold (Prutenic tables). The three mean tropical years in Babylonian sexagesimals as the excess over 365 days (the way they would have been extracted from the tables of mean longitude) were 14,33,9,57 (Alphonsine), 14,33,11,12 (Copernicus) and 14,33,9,24 (Reinhold). All values are the same to two places (14:33) and this is also the mean length of the Gregorian year. Thus Pitatus' solution would have commended itself to the astronomers.
Lilius's proposals had two components. Firstly, he proposed a correction to the length of the year. The mean tropical year is 365.24219 days long.[22] As the average length of a Julian year is 365.25 days, the Julian year is almost 11 minutes longer than the mean tropical year. The discrepancy results in a drift of about three days every 400 years. Lilius's proposal resulted in an average year of 365.2425 days (see Accuracy). At the time of Gregory's reform there had already been a drift of 10 days since the Council of Nicaea, resulting in the vernal equinox falling on 10 or 11 March instead of the ecclesiastically fixed date of 21 March, and if unreformed it would drift further. Lilius proposed that the 10-day drift should be corrected by deleting the Julian leap day on each of its ten occurrences over a period of forty years, thereby providing for a gradual return of the equinox to 21 March.
Lilius's work was expanded upon by Christopher Clavius in a closely argued, 800-page volume. He would later defend his and Lilius's work against detractors. Clavius's opinion was that the correction should take place in one move, and it was this advice which prevailed with Gregory.
The second component consisted of an approximation which would provide an accurate yet simple, rule-based calendar. Lilius's formula was a 10-day correction to revert the drift since the Council of Nicaea, and the imposition of a leap day in only 97 years in 400 rather than in 1 year in 4. The proposed rule was that years divisible by 100 would be leap years only if they were divisible by 400 as well.
The 19-year cycle used for the lunar calendar was also to be corrected by one day every 300 or 400 years (8 times in 2500 years) along with corrections for the years that are no longer leap years (i.e., 1700, 1800, 1900, 2100, etc.). In fact, a new method for computing the date of Easter was introduced.
When the new calendar was put in use, the error accumulated in the 13 centuries since the Council of Nicaea was corrected by a deletion of 10 days. The Julian calendar day Thursday, 4 October 1582 was followed by the first day of the Gregorian calendar, Friday, 15 October 1582 (the cycle of weekdays was not affected).
Adoption
Although Gregory's reform was enacted in the most solemn of forms available to the Church, the bull had no authority beyond the Catholic Church and the Papal States. The changes that he was proposing were changes to the civil calendar, over which he had no authority. They required adoption by the civil authorities in each country to have legal effect.
The bull Inter gravissimas became the law of the Catholic Church in 1582, but it was not recognised by Protestant Churches, Orthodox Churches, and a few others. Consequently, the days on which Easter and related holidays were celebrated by different Christian Churches again diverged.
A month after having decreed the reform, the pope with a brief of 3 April 1582 granted to Antonio Lilio, the brother of Luigi Lilio, the exclusive right to publish the calendar for a period of ten years. The Lunario Novo secondo la nuova riforma printed by Vincenzo Accolti, one of the first calendars printed in Rome after the reform, notes at the bottom that it was signed with papal authorization and by Lilio (Con licentia delli Superiori... et permissu Ant(onii) Lilij). The papal brief was later revoked, on 20 September 1582, because Antonio Lilio proved unable to keep up with the demand for copies.[23]
Philip II of Spain decreed the change from the Julian to the Gregorian calendar, which affected much of Roman Catholic Europe, as Philip was at the time ruler over Spain and Portugal as well as much of Italy. In these territories, as well as in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth (ruled by Anna Jagiellon) and in the Papal States, the new calendar was implemented on the date specified by the bull, with Julian Thursday, 4 October 1582, being followed by Gregorian Friday, 15 October 1582. The Spanish and Portuguese colonies followed somewhat later de facto because of delay in communication.[24]
Many Protestant countries initially objected to adopting a Catholic innovation; some Protestants feared the new calendar was part of a plot to return them to the Catholic fold.
Britain and the British Empire (including the eastern part of what is now the United States) adopted the Gregorian calendar in 1752, followed by Sweden in 1753.
Prior to 1917, Turkey used the lunar Islamic calendar with the Hegira era for general purposes and the Julian calendar for fiscal purposes. The start of the fiscal year was eventually fixed at 1 March and the year number was roughly equivalent to the Hegira year (see Rumi calendar). As the solar year is longer than the lunar year this originally entailed the use of "escape years" every so often when the number of the fiscal year would jump. From 1 March 1917 the fiscal year became Gregorian, rather than Julian. On 1 January 1926 the use of the Gregorian calendar was extended to include use for general purposes and the number of the year became the same as in other countries.
Difference between Gregorian and Julian calendar dates
| Gregorian range | Julian range | Difference |
|---|---|---|
| From 15 October 1582 to 28 February 1700 |
From 5 October 1582 to 18 February 1700 |
10 days |
| From 1 March 1700 to 28 February 1800 |
From 19 February 1700 to 17 February 1800 |
11 days |
| From 1 March 1800 to 28 February 1900 |
From 18 February 1800 to 16 February 1900 |
12 days |
| From 1 March 1900 to 28 February 2100 |
From 17 February 1900 to 15 February 2100 |
13 days |
| From 1 March 2100 to 28 February 2200 |
From 16 February 2100 to 14 February 2200 |
14 days |
Since the introduction of the Gregorian calendar, the difference between Gregorian and Julian calendar dates has increased by three days every four centuries (all date ranges are inclusive):
This section always places the intercalary day on 29 February even though it was always obtained by doubling 24 February (the bissextum (twice sixth) or bissextile day) until the late Middle Ages. The Gregorian calendar is proleptic before 1582 (assumed to exist before 1582).
The following equation gives the number of days (actually, dates) that the Gregorian calendar is ahead of the Julian calendar, called the secular difference between the two calendars. A negative difference means the Julian calendar is ahead of the Gregorian calendar.[26]
where is the secular difference and is the year using astronomical year numbering, that is, use (year BC) − 1 for BC years. means that if the result of the division is not an integer it is rounded down to the nearest integer. Thus during the 1900s, 1900/400 = 4, while during the −500s, −500/400 = −2.
The general rule, in years which are leap years in the Julian calendar but not the Gregorian, is as follows:
Up to February 28 in the calendar you are converting from add one day less or subtract one day more than the calculated value. Remember to give February the appropriate number of days for the calendar you are converting into. When you are subtracting days to move from Julian to Gregorian be careful, when calculating the Gregorian equivalent of February 29 (Julian), to remember that February 29 is discounted. Thus if the calculated value is -4 the Gregorian equivalent of this date is February 24.[27][28]
Beginning of the year
| Country | Start numbered year on 1 January |
Adoption of Gregorian calendar |
|---|---|---|
| Denmark | Gradual change from 13th to 16th centuries[29] |
1700 |
| Venice | 1522 | 1582 |
| Holy Roman Empire (Catholic states) | 1544 | 1583 |
| Spain, Poland, Portugal | 1556 | 1582 |
| Holy Roman Empire (Protestant states) | 1559 | 1700 |
| Sweden | 1559 | 1753 |
| France | 1564[30] | 1582[n 1] |
| Southern Netherlands | 1576[31] | 1582 |
| Lorraine | 1579 | 1682 |
| Dutch Republic | 1583 | 1582 |
| Scotland | 1600[32][33] | 1752 |
| Russia | 1700[34] | 1918 |
| Tuscany | 1721 | 1750 |
| Great Britain and the British Empire except Scotland |
1752[32] | 1752 |
The year used in dates during the Roman Republic and the Roman Empire was the consular year, which began on the day when consuls first entered office—probably 1 May before 222 BC, 15 March from 222 BC and 1 January from 153 BC.[35] The Julian calendar, which began in 45 BC, continued to use 1 January as the first day of the new year. Even though the year used for dates changed, the civil year always displayed its months in the order January to December from the Roman Republican period until the present.
During the Middle Ages, under the influence of the Catholic Church, many Western European countries moved the start of the year to one of several important Christian festivals—25 December (supposed Nativity of Jesus), 25 March (Annunciation), or Easter (France),[36] while the Byzantine Empire began its year on 1 September and Russia did so on 1 March until 1492 when the new year was moved to 1 September.[37]
In common usage, 1 January was regarded as New Year's Day and celebrated as such,[38] but from the 12th century until 1751 the legal year in England began on 25 March (Lady Day).[39] So, for example, the Parliamentary record lists the execution of Charles I on 30 January as occurring in 1648 (as the year did not end until 24 March),[40] although modern histories adjust the start of the year to 1 January and record the execution as occurring in 1649.[41]
Most Western European countries changed the start of the year to 1 January before they adopted the Gregorian calendar. For example, Scotland changed the start of the Scottish New Year to 1 January in 1600 (this means that 1599 was a short year). England, Ireland and the British colonies changed the start of the year to 1 January in 1752 (so 1751 was a short year with only 282 days) though in England the start of the tax year remained at 25 March (O.S.), 5 April (N.S.) till 1800, when it moved to 6 April. Later in 1752 in September the Gregorian calendar was introduced throughout Britain and the British colonies (see the section Adoption). These two reforms were implemented by the Calendar (New Style) Act 1750.[42]
In some countries, an official decree or law specified that the start of the year should be 1 January. For such countries a specific year when a 1 January-year became the norm can be identified. In other countries the customs varied, and the start of the year moved back and forth as fashion and influence from other countries dictated various customs.
Neither the papal bull nor its attached canons explicitly fix such a date, though it is implied by two tables of saint's days, one labelled 1582 which ends on 31 December, and another for any full year that begins on 1 January. It also specifies its epact relative to 1 January, in contrast with the Julian calendar, which specified it relative to 22 March. The old date was derived from the Greek system: the earlier Supputatio Romana specified it relative to 1 January.
- ^ In 1793 France abandoned the Gregorian calendar in favour of the French Republican Calendar. This change was reverted in 1805.
Dual dating
During the period between 1582, when the first countries adopted the Gregorian calendar, and 1923, when the last European country adopted it, it was often necessary to indicate the date of some event in both the Julian calendar and in the Gregorian calendar, for example, "10/21 February 1750/51", where the dual year accounts for some countries already beginning their numbered year on 1 January while others were still using some other date. Even before 1582, the year sometimes had to be double dated because of the different beginnings of the year in various countries. Woolley, writing in his biography of John Dee (1527–1608/9), notes that immediately after 1582 English letter writers "customarily" used "two dates" on their letters, one OS and one NS.[43]
Old Style and New Style dates
"Old Style" (OS) and "New Style" (NS) are sometimes added to dates to identify which system is used in the British Empire and other countries that did not immediately change. Because the Calendar Act of 1750 altered the start of the year,[44] and also aligned the British calendar with the Gregorian calendar, there is some confusion as to what these terms mean. They can indicate that the start of the Julian year has been adjusted to start on 1 January (NS) even though contemporary documents use a different start of year (OS); or to indicate that a date conforms to the Julian calendar (OS), formerly in use in many countries, rather than the Gregorian calendar (NS).[41][45][46][47]
Proleptic Gregorian calendar
Extending the Gregorian calendar backwards to dates preceding its official introduction produces a proleptic calendar, which should be used with some caution. For ordinary purposes, the dates of events occurring prior to 15 October 1582 are generally shown as they appeared in the Julian calendar, with the year starting on 1 January, and no conversion to their Gregorian equivalents. The Battle of Agincourt is universally known to have been fought on 25 October 1415 which is Saint Crispin's Day.
Usually, the mapping of new dates onto old dates with a start of year adjustment works well with little confusion for events that happened before the introduction of the Gregorian calendar. But for the period between the first introduction of the Gregorian calendar on 15 October 1582 and its introduction in Britain on 14 September 1752, there can be considerable confusion between events in continental western Europe and in British domains in English language histories.
Events in continental western Europe are usually reported in English language histories as happening under the Gregorian calendar. For example the Battle of Blenheim is always given as 13 August 1704. Confusion occurs when an event affects both. For example William III of England arrived at Brixham in England on 5 November 1688 (Julian calendar), after setting sail from the Netherlands on 11 November 1688 (Gregorian calendar).
Shakespeare and Cervantes seemingly died on exactly the same date (23 April 1616), but Cervantes predeceased Shakespeare by ten days in real time (as Spain used the Gregorian calendar, but Britain used the Julian calendar). This coincidence encouraged UNESCO to make 23 April the World Book and Copyright Day.
Astronomers avoid this ambiguity by the use of the Julian day number.
For dates before the year 1, unlike the proleptic Gregorian calendar used in the international standard ISO 8601, the traditional proleptic Gregorian calendar (like the Julian calendar) does not have a year 0 and instead uses the ordinal numbers 1, 2, … both for years AD and BC. Thus the traditional time line is 2 BC, 1 BC, AD 1, and AD 2. ISO 8601 uses astronomical year numbering which includes a year 0 and negative numbers before it. Thus the ISO 8601 time line is −0001, 0000, 0001, and 0002.
Months of the year
English speakers sometimes remember the number of days in each month by memorising a traditional mnemonic verse:
Thirty days hath September,
April, June, and November.
All the rest have thirty-one,
Excepting February alone,
Which hath but twenty-eight days clear,
And twenty-nine in each leap year.
For variations and alternate endings, see Thirty days hath September.

A language-independent alternative used in many countries is to hold up one's two fists with the index knuckle of the left hand against the index knuckle of the right hand. Then, starting with January from the little knuckle of the left hand, count knuckle, space, knuckle, space through the months. A knuckle represents a month of 31 days, and a space represents a short month (a 28- or 29-day February or any 30-day month). The junction between the hands is not counted, so the two index knuckles represent July and August.
This method also works by starting the sequence on the right hand's little knuckle, then continuing towards the left. It can also be done using just one hand: after counting the fourth knuckle as July, start again counting the first knuckle as August. A similar mnemonic can be found on a piano keyboard: starting on the key F for January, moving up the keyboard in semitones, the black notes give the short months, the white notes the long ones.
The origins of English naming used by the Gregorian calendar:
- January: Janus (Roman god of gates, doorways, beginnings and endings)
- February: Februus (Etruscan god of death) Februarius (mensis) (Latin for "month of purification (rituals)" it is said to be a Sabine word, the last month of ancient pre-450 BC Roman calendar). It is related to fever.[48][49][50]
- March: Mars (Roman god of war)
- April: The Romans thought that the name Aprilis derived from aperio, aperire, apertus, a verb meaning "to open". Varro and Cincius both reject the connection of the name to Aphrodite, and the common Roman derivation from aperio may be the correct one.[51]
- May: Maia Maiestas (Roman goddess of springtime, warmth, and increase)[52]
- June: Juno (Roman goddess, wife of Jupiter)
- July: Julius Caesar (Roman dictator) (month was formerly named Quintilis, the fifth month of the calendar of Romulus)
- August: Augustus (first Roman emperor) (month was formerly named Sextilis, the sixth month of Romulus)
- September: septem (Latin for seven, the seventh month of Romulus)
- October: octo (Latin for eight, the eighth month of Romulus)
- November: novem (Latin for nine, the ninth month of Romulus)
- December: decem (Latin for ten, the tenth month of Romulus)
Week
In conjunction with the system of months there is a system of weeks. A physical or electronic calendar provides conversion from a given date to the weekday, and shows multiple dates for a given weekday and month. Calculating the day of the week is not very simple, because of the irregularities in the Gregorian system. When the Gregorian calendar was adopted by each country, the weekly cycle continued uninterrupted. For example, in the case of the few countries that adopted the reformed calendar on the date proposed by Gregory XIII for the calendar's adoption, Friday, 15 October 1582, the preceding date was Thursday, 4 October 1582 (Julian calendar).
Opinions vary about the numbering of the days of the week. ISO 8601, in common use worldwide, starts with Monday=1; printed monthly calendar grids list Mondays in the first (left) column of dates and Sundays in the last. Software often starts with Sunday=0, which places Sundays in the left column of a monthly calendar page.
Accuracy
The Gregorian calendar improves the approximation made by the Julian calendar by skipping three Julian leap days in every 400 years, giving an average year of 365.2425 mean solar days long.[53] This approximation has an error of about one day per 3,300 years with respect to the mean tropical year. However, because of the precession of the equinoxes, the error with respect to the vernal equinox (which occurs, on average, 365.24237 days apart near 2000[54]) is 1 day every 7,700 years. By any criterion, the Gregorian calendar is substantially more accurate than the 1 day in 128 years error of the Julian calendar (average year 365.25 days).
In the 19th century, Sir John Herschel proposed a modification to the Gregorian calendar with 969 leap days every 4000 years, instead of 970 leap days that the Gregorian calendar would insert over the same period.[55] This would reduce the average year to 365.24225 days. Herschel's proposal would make the year 4000, and multiples thereof, common instead of leap. While this modification has often been proposed since, it has never been officially adopted.[56]
On time scales of thousands of years, the Gregorian calendar falls behind the astronomical seasons because the slowing down of the Earth's rotation makes each day slightly longer over time (see tidal acceleration and leap second) while the year maintains a more uniform duration.
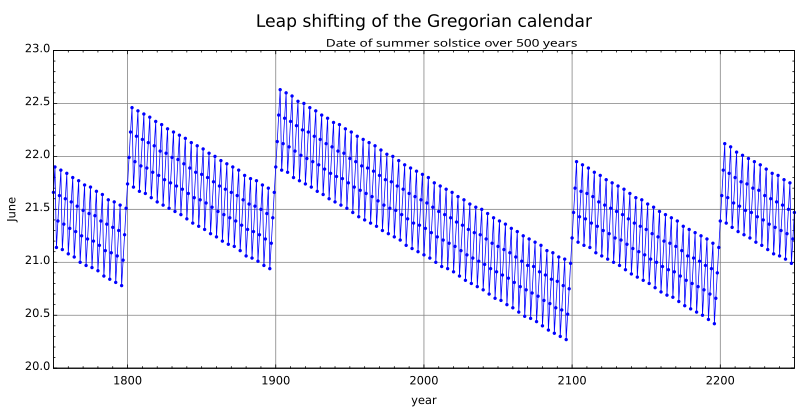
Calendar seasonal error
This image shows the difference between the Gregorian calendar and the astronomical seasons.
The y-axis is the date in June and the x-axis is Gregorian calendar years.
Each point is the date and time of the June solstice in that particular year. The error shifts by about a quarter of a day per year. Centurial years are ordinary years, unless they are divisible by 400, in which case they are leap years. This causes a correction in the years 1700, 1800, 1900, 2100, 2200, and 2300.
For instance, these corrections cause 23 December 1903 to be the latest December solstice, and 20 December 2096 to be the earliest solstice—2.25 days of variation compared with the seasonal event.
Proposed reforms
The following are proposed reforms of the Gregorian calendar:
- Holocene calendar
- International Fixed Calendar (also called the International Perpetual calendar)
- World Calendar
- World Season Calendar
- Leap week calendars
See also
- Calendar reform
- Conversion between Julian and Gregorian calendars
- Computus — Gregorian lunar calendar
- Doomsday rule
- Dual dating
- Inter gravissimas in English — Wikisource
- Julian day calculation
- History of calendars
- list of calendars
- Old Style and New Style dates
- Old Calendarists
- Tropical year
Notes
- ^ Introduction to Calendars. United States Naval Observatory. Retrieved 15 January 2009.
- ^ Calendars by L. E. Doggett. Section 2.
- ^ The international standard for the representation of dates and times, ISO 8601, uses the Gregorian calendar. Section 3.2.1.
- ^ a b See Wikisource English translation of the (Latin) 1582 papal bull Inter gravissimas.
- ^ a b Moyer (1983).
- ^ Introduction to Calendars. (15 May 2013). United States Naval Observatory.
- ^ Ziggelaar (1983), p. 223.
- ^ Nineteen-Year Cycle of Dionysius. Introduction and first [argumentum] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help).
- ^ The first known occurrence of Common Era in English dates to 1708. Years before the beginning of the era are abbreviated in English as either BC for "Before Christ", or as BCE for "Before the Common Era" Two era names occur within the bull Inter gravissimas itself, [anno Incarnationis dominicæ] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help) ("in the year of the Incarnation of the Lord") for the year it was signed, and [anno à Nativitate Domini nostri Jesu Christi] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help) ("in the year from the Nativity of our Lord Jesus Christ") for the year it was printed. Les canons of Les textes fondateurs du calendrier grégorien Template:La icon Template:Fr icon
- ^ Richards, p. 101
- ^ Clause 3.2.1 ISO 8601
- ^ The cycle described applies to the solar, or civil, calendar. If the ecclesiastical lunar rules are also considered, the lunisolar Easter computus cycle repeats only after 5,700,000 years of 2,081,882,250 days in 70,499,183 lunar months, based on an assumed mean lunar month of 29 days 12 hours 44 minutes 2 seconds. (Seidelmann (1992), p. 582) [To properly function as an Easter computus, this lunisolar cycle must have the same mean year as the Gregorian solar cycle, and indeed that is exactly the case.]
- ^ The extreme length of the Gregorian Easter computus is due to its being the product of the 19-year Metonic cycle, the thirty different possible values of the epact, and the least common multiple (10,000) of the 400 - year and 2,500 - year solar and lunar correction cycles. (Walker 1945, 218)
- ^ The last major Christian region to accept the Alexandrian rules was the Carolingian Empire (most of Western Europe) during 780–800. The last monastery in England to accept the Alexandrian rules did so in 931, and a few churches in southwest Asia beyond the eastern border of the Byzantine Empire continued to use rules that differed slightly, causing four dates for Easter to differ every 532 years.
- ^ Pedersen (1983), pp. 42–43.
- ^ For example, in the Julian calendar, at Rome in 1550, the March equinox occurred at 11 Mar 6:51 AM local mean time. "Seasons calculator", Time and Date AS, 2014.
- ^ Ziggelaar (1983), pp. 211, 214.
- ^ See, for example,Tabule illustrissimi principis regis alfonsii, Prague 1401 -4 (Latin). A full set of Alphonsine Tables (including tables for mean motions, conjunctions of sun and moon, equation of time, spherical astronomy, longitudes and latitudes of cities, star tables, eclipse tables).
- ^ For an example of the information provided see Jacques Cassini, Tables astronomiques du soleil, de la lune, des planetes, des etoiles fixes, et des satellites de Jupiter et de Saturne, Paris 1740, available at [1] (go forward ten pages to Table III on p. 10).
- ^ Dreyer, J L E (2014). Tycho Brahe. Cambridge. p. 52. ISBN 978-1-108-06871-0.
He remarks that both the Alphonsine and the Prutenic Tables are several hours wrong with regard to the time of the equinoxes and solstices.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - ^ North, J (1989). The Universal frame: historical essays in astronomy, natural philosophy and scientific method. London. p. 29. ISBN 0-907628-95-8.
"He noted on one occasion that the Alphonsine tables differed from the Prutenic by nineteen hours as to the time of the vernal equinox of 1588.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - ^ Meeus and Savoie (1992).
- ^ Mezzi, E., and Vizza, F., Luigi Lilio Medico Astronomo e Matematico di Cirò, Laruffa Editore, Reggio Calabria, 2010, p. 14; p. 52, citing as primary references: Biblioteca Nazionale Centrale die Firenze, Magl. 5.10.5/a, ASV A.A., Arm. I‑XVIII, 5506, f. 362r.
- ^ "Pragmatica" on the Ten Days of the Year World Digital Library, the first known South American imprint, produced in 1584 by Antonio Ricardo, of a four-page edict issued by King Philip II of Spain in 1582, decreeing the change from the Julian to the Gregorian calendar.
- ^ A more extensive list is available at Conversion between Julian and Gregorian calendars.
- ^ Blackburn & Holford-Strevens (1999), p. 788.
- ^ James Evans, The history and practice of ancient astronomy (Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1998) 169. ISBN 0-19-509539-1.
- ^ Explanatory Supplement to The Astronomical Ephemeris and The American Ephemeris and Nautical Almanac (London: Her Majesty's Stationery Office, 1961) 417.
- ^ Herluf Nielsen: Kronologi (2nd ed., Dansk Historisk Fællesforening, Copenhagen 1967), pp.48–50.
- ^ Le calendrier grégorien en France Template:Fr icon
- ^ Per decree of 16 June 1575. Hermann Grotefend, "Osteranfang" (Easter beginning), Zeitrechnung de Deutschen Mittelalters und der Neuzeit (Chronology of the German Middle Ages and modern times) (1891–1898)
- ^ a b Blackburn & Holford-Strevens (1999), p. 784.
- ^ John James Bond, Handy-book of rules and tables for verifying dates with the Christian era Scottish decree on pp. xvii–xviii.
- ^ Roscoe Lamont, The reform of the Julian calendar, Popular Astronomy 28 (1920) 18–32. Decree of Peter the Great is on pp.23–24.
- ^ "Roman Dates: Eponymous Years". Tyndalehouse.com. Retrieved 14 September 2010.
- ^ Mike Spathaky Old Style and New Style Dates and the change to the Gregorian Calendar: A summary for genealogists
- ^ S. I. Seleschnikow: Wieviel Monde hat ein Jahr? (Aulis-Verlag, Leipzig/Jena/Berlin 1981, p. 149), which is a German translation of С. И. Селешников: История календаря и хронология (Издательство «Наука», Moscow 1977). The relevant chapter is available online here: История календаря в России и в СССР (Calendar history in Russia and the USSR). Anno Mundi 7000 lasted from 1 March 1492 to 31 August 1492. Template:Ru icon
- ^ Tuesday 31 December 1661, The Diary of Samuel Pepys "I sat down to end my journell for this year, ..."
- ^ Nørby, Toke. The Perpetual Calendar: What about England Version 29 February 2000
- ^ "House of Commons Journal Volume 8, 9 June 1660 (Regicides)". British History Online. Retrieved 18 March 2007.
- ^ a b Death warrant of Charles I web page of the UK National Archives. A demonstration of New Style meaning Julian calendar with a start of year adjustment.
- ^ Nørby, Toke. The Perpetual Calendar
- ^ Benjamin Woolley, The Queen's Conjurer: The science and magic of Dr. John Dee, adviser to Queen Elizabeth I (New York: Henry Holt, 2001) p.173
- ^ In Scotland the legal start of year had been moved to 1 January in 1600 (Mike Spathaky. Old Style New Style dates and the change to the Gregorian calendar); and as Ireland was not part of the union of Great Britain so separate legislation was needed for Ireland.
- ^ Spathaky, Mike Old Style New Style dates and the change to the Gregorian calendar. "increasingly parish registers, in addition to a new year heading after 24th March showing, for example '1733', had another heading at the end of the following December indicating '1733/4'. This showed where the New Style 1734 started even though the Old Style 1733 continued until 24th March. ... We as historians have no excuse for creating ambiguity and must keep to the notation described above in one of its forms. It is no good writing simply 20th January 1745, for a reader is left wondering whether we have used the Old or the New Style reckoning. The date should either be written 20th January 1745 OS (if indeed it was Old Style) or as 20th January 1745/6. The hyphen (1745-6) is best avoided as it can be interpreted as indicating a period of time."
- ^ The October (November) Revolution Britannica encyclopaedia, A demonstration of New Style meaning the Gregorian calendar.
- ^ Stockton, J.R. Date Miscellany I: The Old and New Styles "The terms 'Old Style' and 'New Style' are now commonly used for both the 'Start of Year' and 'Leap Year' [(Gregorian calendar)] changes (England & Wales: both in 1752; Scotland: 1600, 1752). I believe that, properly and historically, the 'Styles' really refer only to the 'Start of Year' change (from March 25th to January 1st); and that the 'Leap Year' change should be described as the change from Julian to Gregorian."
- ^ Adriana Rosado-Bonewitz, "Whats in a word?" [dead link] (pdf, 1.3MB), Intercambios: Quarterly Newsletter of the Spanish Language Division of the American Translators, 9(1) (March 2005): 14–15, ISSN 1550-2945 (in Spanish)
- ^ Anatoly Liberman, "On A Self-Congratulatory Note, Or, All The Year Round: The Names of The Months" (filed in Oxford Etymologist, 7 March 2007)
- ^ Neuru(1996)
- ^ Scullard, Festivals and Ceremonies of the Roman Republic, p. 96; Forsythe, Time in Roman Religion, p. 10.
- ^ http://www.thaliatook.com/OGOD/maiamaiestas.html
- ^ Seidelmann (1992), pp. 580–581.
- ^ Meeus and Savoie (1992), p. 42
- ^ John Herschel, Outlines of Astronomy, 1849, p. 629.
- ^ Steel, Duncan (2000). Marking Time: The Epic Quest to Invent the Perfect Calendar. John Wiley & Sons. p. 185. ISBN 0-471-29827-1.
References
- Blackburn, B. & Holford-Strevens, L. (1999). The Oxford Companion to the Year. Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-214231-3.
- Blackburn, B. & Holford-Strevens, L. (2003). The Oxford Companion to the Year: An exploration of calendar customs and time-reckoning, Oxford University Press.
- Coyne, G. V., Hoskin, M. A., Pedersen, O. (Eds.) (1983). Gregorian Reform of the Calendar: Proceedings of the Vatican Conference to Commemorate its 400th Anniversary, 1582–1982. Vatican City: Pontifical Academy of Sciences, Vatican Observatory (Pontificia Academia Scientarum, Specola Vaticana).
- Borkowski, K. M., (1991). "The tropical calendar and solar year", J. Royal Astronomical Soc. of Canada 85(3): 121–130.
- Barsoum, Ignatius A. (2003). The Scattered Pearls. Piscataway: Georgias Press.
- Duncan, D. E. (1999). Calendar: Humanity's Epic Struggle To Determine A True And Accurate Year. HarperCollins. ISBN 9780380793242.
- Gregory XIII. (2002 [1582]). Inter Gravissimas (W. Spenser & R. T. Crowley, Trans.). International Organization for Standardization.
- Meeus, J. & Savoie, D. (1992). The history of the tropical year. Journal of the British Astronomical Association, 102(1): 40–42.
- Morrison, L. V. & Stephenson, F. R. (2004). Historical values of the Earth's clock error ΔT and the calculation of eclipses. Journal for the History of Astronomy Vol. 35, Part 3, No. 120, pp. 327–336.
- Moyer, Gordon (May 1982). "The Gregorian Calendar". Scientific American, pp. 144–152.
- Moyer, Gordon (1983). "Aloisius Lilius and the Compendium Novae Rationis Restituendi Kalendarium". In Coyne, Hoskin, Pedersen (1983), pp. 171–188.
- Pedersen, O. (1983). "The Ecclesiastical Calendar and the Life of the Church". In Coyne, Hoskin, Pedersen (eds), Gregorian Reform of the Calendar: Proceedings of the Vatican Conference to Commemorate its 400th Anniversary. Vatican City: Pontifical Academy of Sciences, Specolo Vaticano, pp. 17–74.
- Richards, E. G. (1998). Mapping Time: The Calendar and its History. Oxford U. Press.
- Seidelmann, P. K. (Ed.) (1992). Explanatory Supplement to the Astronomical Almanac. Sausalito, CA: University Science Books.
- Walker, G. W. Easter Intervals. Popular Astronomy June 1945, Vol. 53, pp. 162 –178, 218–232. Available at [2].
- Ziggelaar, A. (1983). "The Papal Bull of 1582 Promulgating a Reform of the Calendar". In Coyne, Hoskin, Pedersen (eds), Gregorian Reform of the Calendar: Proceedings of the Vatican Conference to Commemorate its 400th Anniversary. Vatican City: Pontifical Academy of Sciences, Specolo Vaticano, pp. 201–239.
External links
- Gregorian calendar on In Our Time at the BBC
- Calendar Converter
- Inter Gravissimas (Latin and French plus English)
- History of Gregorian Calendar
- The Perpetual Calendar Gregorian Calendar adoption dates for many countries.
- World records for mentally calculating the day of the week in the Gregorian Calendar
- The Calendar FAQ – Frequently Asked Questions about Calendars
- Today's date (Gregorian) in over 400 more-or-less obscure foreign languages