Wheatstone bridge: Difference between revisions
→Modifications of the fundamental bridge: Additional description. Kelvin-Varley divider not a modification (or indeed a bridge). |
→Modifications of the fundamental bridge: More direct link |
||
| Line 59: | Line 59: | ||
* [[Carey Foster bridge]], for measuring small resistances |
* [[Carey Foster bridge]], for measuring small resistances |
||
* [[Kelvin bridge]], for measuring small [[Four-terminal sensing|four terminal]] resistances |
* [[Kelvin bridge]], for measuring small [[Four-terminal sensing|four terminal]] resistances |
||
* [[Maxwell bridge]], for measuring [[reactance|reactive]] components. |
* [[Maxwell bridge]], for measuring [[Electrical reactance|reactive]] components. |
||
==See also== |
==See also== |
||
Revision as of 17:05, 11 November 2015
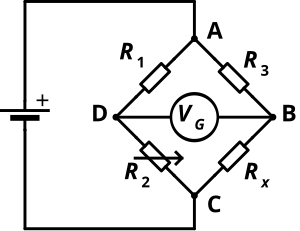
A Wheatstone bridge is an electrical circuit used to measure an unknown electrical resistance by balancing two legs of a bridge circuit, one leg of which includes the unknown component. The primary benefit of a wheatstone bridge is its ability to provide extremely accurate measurements (in contrast with something like a simple voltage divider).[1] Its operation is similar to the original potentiometer. It was invented by Samuel Hunter Christie in 1833 and improved and popularized by Sir Charles Wheatstone in 1843. One of the Wheatstone bridge's initial uses was for the purpose of soils analysis and comparison.[2]
Operation
In the figure, is the unknown resistance to be measured; , and are resistors of known resistance and the resistance of is adjustable. If the ratio of the two resistances in the known leg is equal to the ratio of the two in the unknown leg , then the voltage between the two midpoints (B and D) will be zero and no current will flow through the galvanometer . If the bridge is unbalanced, the direction of the current indicates whether is too high or too low. is varied until there is no current through the galvanometer, which then reads zero.
Detecting zero current with a galvanometer can be done to extremely high accuracy. Therefore, if , and are known to high precision, then can be measured to high precision. Very small changes in disrupt the balance and are readily detected.
At the point of balance, the ratio of
Alternatively, if , , and are known, but is not adjustable, the voltage difference across or current flow through the meter can be used to calculate the value of , using Kirchhoff's circuit laws (also known as Kirchhoff's rules). This setup is frequently used in strain gauge and resistance thermometer measurements, as it is usually faster to read a voltage level off a meter than to adjust a resistance to zero the voltage.
Derivation

First, Kirchhoff's first rule is used to find the currents in junctions B and D:
Then, Kirchhoff's second rule is used for finding the voltage in the loops ABD and BCD:
When the bridge is balanced, then IG = 0, so the second set of equations can be rewritten as:
Then, the equations are divided and rearranged, giving:
From the first rule, I3 = Ix and I1 = I2. The desired value of Rx is now known to be given as:
If all four resistor values and the supply voltage (VS) are known, and the resistance of the galvanometer is high enough that IG is negligible, the voltage across the bridge (VG) can be found by working out the voltage from each potential divider and subtracting one from the other. The equation for this is:
where VG is the voltage of node D relative to node B.
Significance
The Wheatstone bridge illustrates the concept of a difference measurement, which can be extremely accurate. Variations on the Wheatstone bridge can be used to measure capacitance, inductance, impedance and other quantities, such as the amount of combustible gases in a sample, with an explosimeter. The Kelvin bridge was specially adapted from the Wheatstone bridge for measuring very low resistances. In many cases, the significance of measuring the unknown resistance is related to measuring the impact of some physical phenomenon (such as force, temperature, pressure, etc.) which thereby allows the use of Wheatstone bridge in measuring those elements indirectly.
The concept was extended to alternating current measurements by James Clerk Maxwell in 1865 and further improved by Alan Blumlein around 1926.
Modifications of the fundamental bridge

The Wheatstone bridge is the fundamental bridge, but there are other modifications that can be made to measure various kinds of resistances when the fundamental Wheatstone bridge is not suitable. Some of the modifications are:
- Carey Foster bridge, for measuring small resistances
- Kelvin bridge, for measuring small four terminal resistances
- Maxwell bridge, for measuring reactive components.
See also
- Phantom circuit - a circuit using a balanced bridge
- Post Office Box
- Potentiometer
- Potential divider
- Ohmmeter
- Resistance thermometer
- Strain gauge
References
- ^ "Circuits in Practice: The Wheatstone Bridge, What It Does, and Why It Matters", as discussed in this MIT ES.333 class video
- ^ "The Genesis of the Wheatstone Bridge" by Stig Ekelof discusses Christie's and Wheatstone's contributions, and why the bridge carries Wheatstone's name. Published in "Engineering Science and Education Journal", volume 10, no 1, February 2001, pages 37–40.
External links
- Wheatstone Bridge - Interactive Tutorial National High Magnetic Field Laboratory














