Vanuatu: Difference between revisions
m Reverted edits by 2602:306:CD7E:D740:C0D:4FD0:4AE1:7772 (talk) to last version by Materialscientist |
Retention7 (talk | contribs) m HDI update |
||
| Line 49: | Line 49: | ||
|established_date1 = 30 July 1980 |
|established_date1 = 30 July 1980 |
||
|Gini_year = 2010 |Gini_change = <!--increase/decrease/steady--> |Gini = 37.2 <!--number only--> |Gini_ref = <ref name="wb-gini">{{cite web |url=http://data.worldbank.org/indicator/SI.POV.GINI/ |title=Gini Index |publisher=World Bank |accessdate=2 March 2011}}</ref> |Gini_rank = |
|Gini_year = 2010 |Gini_change = <!--increase/decrease/steady--> |Gini = 37.2 <!--number only--> |Gini_ref = <ref name="wb-gini">{{cite web |url=http://data.worldbank.org/indicator/SI.POV.GINI/ |title=Gini Index |publisher=World Bank |accessdate=2 March 2011}}</ref> |Gini_rank = |
||
|HDI_year = |
|HDI_year = 2014<!-- Please use the year to which the data refers, not the publication year--> |
||
|HDI_change = |
|HDI_change = increase<!--increase/decrease/steady--> |
||
|HDI = 0. |
|HDI = 0.594 <!--number only--> |
||
|HDI_ref = <ref name="HDI">{{cite web |url=http://hdr.undp.org/sites/default/files/ |
|HDI_ref = <ref name="HDI">{{cite web |url=http://hdr.undp.org/sites/default/files/hdr_2015_statistical_annex.pdf |title=2015 Human Development Report |year=2015 |accessdate=15 December 2015 |publisher=United Nations Development Programme | }}</ref> |
||
|HDI_rank = |
|HDI_rank = 134th |
||
|currency = [[Vanuatu vatu]] |
|currency = [[Vanuatu vatu]] |
||
|currency_code = VUV |
|currency_code = VUV |
||
Revision as of 15:54, 15 December 2015
Republic of Vanuatu | |
|---|---|
| Motto: "Long God yumi stanap" (Bislama) "In God we stand"[1][2][3] | |
| Anthem: Yumi, Yumi, Yumi (Bislama) We, We, We | |
 | |
| Capital and largest city | Port Vila |
| Official languages | |
| Ethnic groups (1999) |
|
| Demonym(s) | Ni-Vanuatu |
| Government | Unitary parliamentary republic |
| Baldwin Lonsdale | |
| Sato Kilman | |
| Legislature | Parliament |
| Independence | |
• from France and the United Kingdom | 30 July 1980 |
| Area | |
• Total | 12,190 km2 (4,710 sq mi) (161st) |
| Population | |
• July 2015[5] estimate | 272,264 |
• 2009 census | 243,304[4] |
• Density | 19.7/km2 (51.0/sq mi) (188th) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2011 estimate |
• Total | $1.204 billion[6] |
• Per capita | $4,916[6] |
| GDP (nominal) | 2011 estimate |
• Total | $743 million[6] |
• Per capita | $3,036[6] |
| Gini (2010) | 37.2[7] medium inequality |
| HDI (2014) | medium (134th) |
| Currency | Vanuatu vatu (VUV) |
| Time zone | UTC+11 (VUT (Vanuatu Time)) |
| Drives on | right |
| Calling code | +678 |
| ISO 3166 code | VU |
| Internet TLD | .vu |
Vanuatu (English: /ˌvɑːnuːˈɑːtuː/ vah-noo-AH-too or /vænˈwɑːtuː/ van-WAH-too; Bislama IPA: [vanuaˈtu]), officially the Republic of Vanuatu (Template:Lang-fr, Bislama: Ripablik blong Vanuatu), is an Oceanian island nation located in the South Pacific Ocean. The archipelago, which is of volcanic origin, is some 1,750 kilometres (1,090 mi) east of northern Australia, 500 kilometres (310 mi) northeast of New Caledonia, east of New Guinea, southeast of the Solomon Islands, and west of Fiji.
Vanuatu was first inhabited by Melanesian people. The first Europeans to visit the islands were a Spanish expedition led by Portuguese navigator Fernandes de Queirós, who arrived on the largest island in 1606. He then claimed the archipelago for Spain, as part of the colonial Spanish East Indies, and named it Austrialia del Espiritu Santo.
In the 1880s, France and Great Britain claimed parts of the archipelago, and in 1906 they agreed on a framework for jointly managing the archipelago as the New Hebrides through a British–French Condominium. An independence movement arose in the 1970s, and the Republic of Vanuatu was founded in 1980.
Etymology
Vanuatu's name is derived from the word vanua ("land" or "home"),[9] which occurs in several Austronesian languages,[10] and the word tu ("stand").[11] Together the two words indicated the independent status of the new country.[11]
History
The prehistory of Vanuatu is obscure; archaeological evidence supports the theory that people speaking Austronesian languages first came to the islands some 4,000 years ago. Pottery fragments have been found dating to 1300–1100 BC.[12]
The Vanuatu group of islands first had contact with Europeans in 1606, when the Portuguese explorer Pedro Fernandes de Queirós, sailing for the Spanish Crown, arrived on the largest island and called the group of islands La Austrialia del Espiritu Santo or "The Southern Land of the Holy Spirit", believing he had arrived in Terra Australis or Australia. The Spanish established a short-lived settlement at Big Bay on the north side of the island. The name Espiritu Santo remains to this day.
Europeans did not return until 1768, when Louis Antoine de Bougainville rediscovered the islands. In 1774, Captain Cook named the islands the New Hebrides, a name that would last until independence in 1980.[12]

In 1825, the trader Peter Dillon discovered sandalwood on the island of Erromango, which began a rush of immigrants that ended in 1830, after a clash between immigrants and Polynesian workers. During the 1860s, planters in Australia, Fiji, New Spain, and the Samoan Islands, in need of labourers, encouraged a long-term indentured labour trade called "blackbirding". At the height of the labour trade, more than one half of the adult male population of several of the islands worked abroad. Fragmentary evidence indicates that the current population of Vanuatu is greatly reduced compared to pre-contact times.[12]
In the 19th century, Catholic and Protestant missionaries from Europe and North America went to the islands to work with the people. For example, John Geddie (1815–1872), a Scots-Canadian Presbyterian missionary, arrived at the island of Aneityum in 1848; he spent the rest of his life there, working to convert the inhabitants to Christianity and western ways. John Gibson Paton was a Scottish missionary who devoted his life to the region.
Settlers came looking for land on which to establish cotton plantations. When international cotton prices collapsed, planters switched to coffee, cocoa, bananas, and, most successfully, coconuts. Initially, British subjects from Australia made up the majority of settlers, but the establishment of the Caledonian Company of the New Hebrides in 1882 attracted more French subjects. By the start of the 20th century, the French outnumbered the British two to one.[12]

The jumbling of French and British interests in the islands brought petitions for one or another of the two powers to annexe the territory. In 1906, France and the United Kingdom agreed to administer the islands jointly. Called the British-French Condominium, it was a unique form of government. The separate governmental systems came together only in a joint court. Melanesians were barred from acquiring the citizenship of either power.[12]
Challenges to this form of government began in the early 1940s. The arrival of Americans during World War II, with their informal habits and relative wealth, contributed to the rise of nationalism in the islands. The belief in a mythical messianic figure named John Frum was the basis for an indigenous cargo cult (a movement attempting to obtain industrial goods through magic) promising Melanesian deliverance. Today, John Frum is both a religion and a political party with a member in Parliament.[12]

The first political party, established in the early 1970s, was called the New Hebrides National Party. One of the founders was Father Walter Lini, who later became Prime Minister. Renamed the Vanua'aku Pati in 1974, the party pushed for independence, which was gained amidst the brief Coconut War.[13][14]
The independent Republic of Vanuatu was established in 1980.[12]
During the 1990s, Vanuatu experienced a period of political instability which resulted in a more decentralised government. The Vanuatu Mobile Force, a paramilitary group, attempted a coup in 1996 because of a pay dispute. There were allegations of corruption in the government of Maxime Carlot Korman. New elections have been called for several times since 1997, most recently in 2004.
Geography
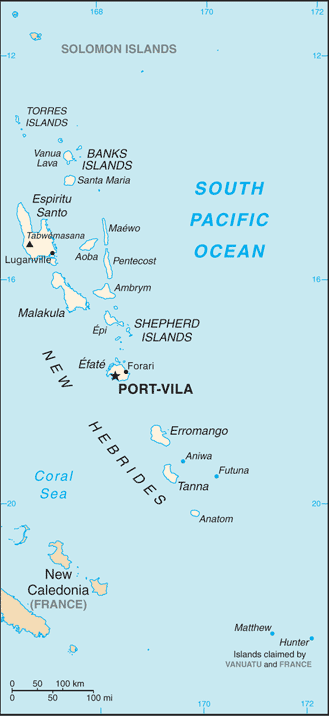


Vanuatu is a Y-shaped archipelago consisting of about 82 relatively small, geologically newer islands of volcanic origin (65 of them inhabited), with about 1,300 kilometres (810 mi) between the most northern and southern islands.[15] Two of these islands (Matthew and Hunter) are also claimed and controlled by France as part of the French collectivity of New Caledonia. The country lies between latitudes 13° and 21°S and longitudes 166° and 171°E.
The fourteen of Vanuatu's islands that have surface areas of more than 100 square kilometres (39 sq mi) are, from largest to smallest: Espiritu Santo, Malakula, Efate, Erromango, Ambrym, Tanna, Pentecost, Epi, Ambae or Aoba, Gaua, Vanua Lava, Maewo, Malo, and Aneityum or Anatom. The nation's largest towns are the capital Port Vila, on Efate, and Luganville on Espiritu Santo.[16] The highest point in Vanuatu is Mount Tabwemasana, at 1,879 metres (6,165 ft), on the island of Espiritu Santo.
Vanuatu's total area is roughly 12,274 square kilometres (4,739 sq mi),[17] of which its land surface is very limited (roughly 4,700 square kilometres (1,800 sq mi)). Most of the islands are steep, with unstable soils and little permanent fresh water.[15] One estimate, made in 2005, is that only 9% of land is used for agriculture (7% with permanent crops, plus 2% considered arable).[18] The shoreline is mostly rocky with fringing reefs and no continental shelf, dropping rapidly into the ocean depths.[15]
There are several active volcanoes in Vanuatu, including Lopevi, Mount Yasur, and several underwater volcanoes. Volcanic activity is common, with an ever-present danger of a major eruption; a nearby undersea eruption of 6.4 magnitude occurred in November 2008 with no casualties, and an eruption occurred in 1945.[19] Vanuatu is recognised as a distinct terrestrial ecoregion, known as the Vanuatu rain forests. It is part of the Australasia ecozone, which includes New Caledonia, the Solomon Islands, Australia, New Guinea, and New Zealand.
Vanuatu's population (estimated in 2008 as growing 2.4% annually)[20] is placing increasing pressure on land and resources for agriculture, grazing, hunting, and fishing.[15] Some 90% of Vanuatu households fish and consume fish, which has caused intense fishing pressure near villages and the depletion of near-shore fish species.[15] While well-vegetated, most islands show signs of deforestation.[15] The islands have been logged, particularly of high-value timber, subjected to wide-scale slash-and-burn agriculture, and converted to coconut plantations and cattle ranches, and now show evidence of increased soil erosion and landslides.[15]
Many upland watersheds are being deforested and degraded, and fresh water is becoming increasingly scarce.[15] Proper waste disposal, as well as water and air pollution, are becoming troublesome issues around urban areas and large villages.[15] Additionally, the lack of employment opportunities in industry and inaccessibility to markets have combined to lock rural families into a subsistence or self-reliance mode, putting tremendous pressure on local ecosystems.[15]
Flora and fauna
Despite its tropical forests, Vanuatu has a limited number of plant and animal species. It has an indigenous flying fox, Pteropus anetianus. Flying foxes are important rainforest and timber regenerators. They pollinate and seed disperse a wide variety of native trees. Their diet is nectar, pollen and fruit and they are commonly called "fruit bats". They are in decline across their South Pacific range. However, governments are increasingly aware of the economic and ecological value of flying foxes and there are calls to increase their protection. There are no indigenous large mammals. The nineteen species of native reptiles include the flowerpot snake, found only on Efate. The Fiji Banded Iguana (Brachylophus fasciatus) was introduced as a feral animal in the 1960s.[21][22] There are eleven species of bats (three unique to Vanuatu) and sixty-one species of land and water birds. While the small Polynesian rat is thought to be indigenous, the large species arrived with Europeans, as did domesticated hogs, dogs, and cattle. The ant species of some of the islands of Vanuatu were catalogued by E. O. Wilson.[23]
The region is rich in sea life, with more than 4,000 species of marine molluscs and a large diversity of marine fishes. Coneshell and stonefish carry poison fatal to humans. The Giant East African land snail arrived only in the 1970s, but already has spread from the Port-Vila region to Luganville.
There are three or possibly four adult saltwater crocodiles living in Vanuatu's mangroves and no current breeding population.[22] It is said the crocodiles reached the northern part of the islands after cyclones, given the island chain's proximity to the Solomon Islands and New Guinea where crocodiles are very common.[24]
Climate
The climate is tropical, with about nine months of warm to hot rainy weather and the possibility of cyclones and three to four months of cooler, drier weather characterised by winds from the southeast.[15] The water temperature ranges from 72 °F (22 °C) in winter to 82 °F (28 °C) in the summer.[15] Cool between April and September, the days become hotter and more humid starting in October.[15] The daily temperature ranges from 68 to 90 °F (20 to 32 °C).[15] South easterly trade winds occur from May to October.[15]
Vanuatu has a long rainy season, with significant rainfall almost every month.[15] The wettest and hottest months are December through April, which also constitute the cyclone season.[15] The driest months are June through November.[15] Rainfall averages about 2,360 millimetres (93 in) per year but can be as high as 4,000 millimetres (160 in) in the northern islands.[18]
- Tropical cyclones
In March 2015, Cyclone Pam devastated much of Vanuatu, caused extensive damage to all the islands and deaths. As of 17 March 2015[update] the United Nations said the official death toll was 11 (six from Efate and five from Tanna), and 30 were reported injured; these numbers are expected to rise as more remote islands are reached.[25][26]
Cyclone Pam is possibly the worst natural disaster in Vanuatu's history. Vanuatu lands minister, Ralph Regenvanu said, "This is the worst disaster to affect Vanuatu ever as far as we know."[27]
Earthquakes
Vanuatu has relatively frequent earthquakes. Seven earthquakes were recorded in 2011, all of which were at least a 6.0 magnitude.
Government
Politics

The Republic of Vanuatu is a parliamentary democracy with a written constitution, which declares that the "head of the Republic shall be known as the President and shall symbolise the unity of the nation." The powers of the President of Vanuatu, who is elected for a five-year term by a two-thirds majority of an electoral college, are primarily ceremonial.[28] The electoral college consists of members of Parliament and the presidents of Regional Councils. The President may be removed by the electoral college for gross misconduct or incapacity.
The Prime Minister, who is the head of government, is elected by a majority vote of a three-quarters quorum of the Parliament. The Prime Minister, in turn, appoints the Council of Ministers, whose number may not exceed a quarter of the number of parliamentary representatives. The Prime Minister and the Council of Ministers constitute the executive government.
The Parliament of Vanuatu is unicameral and has 52 members,[29] who are elected by popular vote every four years unless earlier dissolved by a majority vote of a three-quarters quorum or by a directive from the President on the advice of the Prime Minister. The national Council of Chiefs, called the Malvatu Mauri and elected by district councils of chiefs, advises the government on all matters concerning ni-Vanuatu culture and language.
Besides national authorities and figures, Vanuatu also has high-placed people at the village level. Chiefs were and are still the leading figures on village level. It has been reported that even politicians need to oblige them.[30] One becomes such a figure by holding a number of lavish feasts (each feast allowing them a higher ceremonial grade) or alternatively through inheritance (the latter only in Polynesian-influenced villages). In northern Vanuatu, feasts are graded through the nimangki-system.
Government and society in Vanuatu tend to divide along linguistic French and English lines. Forming coalition governments, however, has proved problematic at times due to differences between English and French speakers. Francophone politicians like those of the Union of Moderate Parties tend to be conservative and support neo-liberal policies, as well as closer relations with France and the West. The anglophone Vanua'aku Pati identifies as socialist and anti-colonial.
The Supreme Court consists of a chief justice and up to three other judges. Two or more members of this court may constitute a Court of Appeal. Magistrate courts handle most routine legal matters. The legal system is based on British common law and French civil law. The constitution also provides for the establishment of village or island courts presided over by chiefs to deal with questions of customary law.
Foreign relations
Vanuatu has joined the Asian Development Bank, the World Bank, the International Monetary Fund, the Agence de Coopération Culturelle et Technique, la Francophonie and the Commonwealth of Nations.
Since 1980, Australia, the United Kingdom (UK), France, and New Zealand have provided the bulk of Vanuatu's development aid. Direct aid from the UK to Vanuatu ceased in 2005 following the decision by the UK to no longer focus on the Pacific. However, more recently new donors such as the Millennium Challenge Account (MCA) and the People's Republic of China have been providing increased amounts of aid funding. In 2005 the MCA announced that Vanuatu was one of the first 15 countries in the world selected to receive support—an amount of US$65 million was given for the provision and upgrading of key pieces of public infrastructure.
Vanuatu retains strong economic and cultural ties to Australia, the European Union (in particular France and UK) and New Zealand. Australia now provides the bulk of external assistance, including the police force, which has a paramilitary wing.[31]
There is no Vanuatu High Commission or other Vanuatu Government office in Britain, but the British Friends of Vanuatu,[32] based in London, provides support for Vanuatu visitors to the UK, and can often offer advice and contacts to persons seeking information about Vanuatu or wishing to visit, and welcomes new members (not necessarily resident in the UK) interested in Vanuatu. The association's Charitable Trust funds small scale assistance in the education and training sector.
Vanuatu is not a member of Interpol, along with 11 other countries mainly in Oceania.
Military
There are two police wings: the Vanuatu Police Force (VPF) and the paramilitary wing, the Vanuatu Mobile Force (VMF).[33] Altogether there were 547 police officers organised into two main police commands: one in Port Vila and one in Luganville.[33] In addition to the two command stations there were four secondary police stations and eight police posts. This means that there are many islands with no police presence, and many parts of islands where getting to a police post can take several days.[34][35] There is no purely military expenditure.[36]
Administrative divisions

Vanuatu has been divided into six provinces since 1994. The names in English of all provinces are derived from the initial letters of their constituent islands:
- Malampa (Malakula, Ambrym, Paama)
- Penama (Pentecost, Ambae, Maewo – in French: Pénama)
- Sanma (Santo, Malo)
- Shefa (Shepherds group, Efate – in French: Shéfa)
- Tafea (Tanna, Aniwa, Futuna, Erromango, Aneityum – in French: Taféa)
- Torba (Torres Islands, Banks Islands)
Provinces are autonomous units with their own popularly elected local parliaments known officially as provincial councils. They collect local taxes and make by-laws in local matters like tourism, the provincial budget or the provision of some basic services. They are headed by a chairman elected from among the members of the local parliaments and assisted by a secretary appointed by the Public Service Commission.
Their executive arm consists of a provincial government headed by an executive officer who is appointed by the Prime Minister with the advice of the minister of local government. The provincial government is usually formed by the party that has the majority in the provincial council and, like the national government, is advised in Ni-Vanuatu culture and language by the local council of chiefs. The provincial president is constitutionally a member of the electoral college that elects the President of Vanuatu.
The provinces are in turn divided into municipalities (usually consisting of an individual island) headed by a council and a mayor elected from among the members of the council.
Economy


The four mainstays of the economy are agriculture, tourism, offshore financial services, and raising cattle. There is substantial fishing activity, although this industry does not bring in much foreign exchange. Exports include copra, kava, beef, cocoa, and timber, and imports include machinery and equipment, foodstuffs, and fuels. In contrast, mining activity is unsubstantial.
While manganese mining halted in 1978, there was an agreement in 2006 to export manganese already mined but not yet exported. The country has no known petroleum deposits. A small light-industry sector caters to the local market. Tax revenues come mainly from import duties and a 12.5% VAT on goods and services. Economic development is hindered by dependence on relatively few commodity exports, vulnerability to natural disasters, and long distances between constituent islands and from main markets.
Agriculture is used for consumption as well as for export. It provides a living for 65% of the population. In particular, production of copra and kava create substantial revenue. Many farmers have been abandoning cultivation of food crops, and use earnings from kava cultivation to buy food.[30] Kava has also been used in ceremonial exchanges between clans and villages.[37] Cocoa is also grown for foreign exchange.[38]
In 2007, the number of households engaged in fishing was 15,758, mainly for consumption (99%), and the average number of weekly fishing trips was 3.[39] The tropical climate enables growing of a wide range of fruits and vegetables and spices, including banana, garlic, cabbage, peanuts, pineapples, sugarcane, taro, yams, watermelons, leaf spices, carrots, radishes, eggplants, vanilla (both green and cured), pepper, cucumber, and many others.[40] In 2007, the value (in terms of millions of vatu – the official currency of Vanuatu), for agricultural products, was estimated for different products: kava (341 million vatu), copra (195), cattle (135), crop gardens (93), cocoa (59), forestry (56), fishing (24), coffee (12).[41]
Tourism brings in much-needed foreign exchange. Vanuatu is widely recognised as one of the premier vacation destinations for scuba divers wishing to explore coral reefs of the South Pacific region.[42] A further significant attraction to scuba divers is the wreck of the luxury cruise liner and converted troop carrier SS President Coolidge on Espiritu Santo island. Sunk during the Second World War, it is one of the largest shipwrecks in the world that is accessible for recreational diving. Tourism increased 17% from 2007 to 2008 to reach 196,134 arrivals, according to one estimate.[43] The 2008 total is a sharp increase from 2000, in which there were only 57,000 visitors (of these, 37,000 were from Australia, 8,000 from New Zealand, 6,000 from New Caledonia, 3,000 from Europe, 1,000 from North America, 1,000 from Japan. (Note: figures rounded to the nearest thousand)).[44] Tourism has been promoted, in part, by Vanuatu being the site of several reality-TV shows. The ninth season of the reality TV series Survivor was filmed on Vanuatu, entitled Survivor: Vanuatu—Islands of Fire. Two years later, Australia's Celebrity Survivor was filmed at the same location used by the US version. In mid-2002, the government stepped up efforts to boost tourism.
Financial services are an important part of the economy. Vanuatu is a tax haven that until 2008 did not release account information to other governments or law-enforcement agencies. International pressure, mainly from Australia, influenced the Vanuatu government to begin adhering to international norms to improve transparency. In Vanuatu, there is no income tax, withholding tax, capital gains tax, inheritance tax, or exchange control. Many international ship-management companies choose to flag their ships under the Vanuatu flag, because of the tax benefits and favourable labour laws (Vanuatu is a full member of the International Maritime Organization and applies its international conventions). Vanuatu is recognised as a "flag of convenience" country.[45] Several file-sharing groups, such as the providers of the KaZaA network of Sharman Networks and the developers of WinMX, have chosen to incorporate in Vanuatu to avoid regulation and legal challenges. In response to foreign concerns the government has promised to tighten regulation of its offshore financial centre. Vanuatu receives foreign aid mainly from Australia and New Zealand.

Raising cattle leads to beef production for export. One estimate in 2007 for the total value of cattle heads sold was 135 million vatu; cattle were first introduced into the area from Australia by British planter James Paddon.[46] On average, each household has 5 pigs and 16 chickens, and while cattle are the "most important livestock", pigs and chickens are important for subsistence agriculture as well as playing a significant role in ceremonies and customs (especially pigs).[47] There are 30 commercial farms (sole proprietorships (37%), partnerships (23%), corporations (17%)), with revenues of 533 million vatu and expenses of 329 million vatu in 2007.[48]
Earthquakes can negatively affect economic activity on the island nation. A severe earthquake in November 1999, followed by a tsunami, caused extensive damage to the northern island of Pentecost, leaving thousands homeless. Another powerful earthquake in January 2002 caused extensive damage in the capital, Port Vila, and surrounding areas, and was also followed by a tsunami. Another earthquake of 7.2 struck on 2 August 2007.[49]
The Vanuatu National Statistics Office (VNSO) released their 2007 agricultural census in 2008. According to the study, agricultural exports make up about three-quarters (73%) of all exports; 80% of the population lives in rural areas where "agriculture is the main source of their livelihood"; and of these households, almost all (99%) engaged in agriculture, fisheries and forestry.[50] Total annual household income was 1,803 million vatu. Of this income, agriculture grown for their own household use was valued at 683 million vatu, agriculture for sale at 561, gifts received at 38, handicrafts at 33, and fisheries (for sale) at 18.[50]
The largest expenditure by households was food (300 million vatu), followed by household appliances and other necessities (79 million vatu), transportation (59), education and services (56), housing (50), alcohol and tobacco (39), clothing and footwear (17).[51] Exports were valued at 3,038 million vatu, and included copra (485), kava (442), cocoa (221), beef (fresh and chilled) (180), timber (80), and fish (live fish, aquarium, shell, button) (28).[52] Total imports of 20,472 million vatu included industrial materials (4,261), food and drink (3,984), machinery (3,087), consumer goods (2,767), transport equipment (2,125), fuels and lubricants (187) and other imports (4,060).[53] There are substantial numbers of crop gardens – 97,888 in 2007 – many on flat land (62%), slightly hilly slope (31%), and even on steep slopes (7%); there were 33,570 households with at least one crop garden, and of these, 10,788 households sold some of these crops over a twelve-month period.[54]
The economy grew about 6% in the early 2000s.[55] This is higher than in the 1990s, when GDP rose less than 3%, on average.
One report from the Manila-based Asian Development Bank about Vanuatu's economy gave mixed reviews. It noted the economy was "expanding", noting that the economy grew at an impressive 5.9% rate from 2003 to 2007, and lauded "positive signals regarding reform initiatives from the government in some areas" but described certain binding constraints such as "poor infrastructure services". Since a private monopoly generates power, "electricity costs are among the highest in the Pacific" among developing countries. The report also cited "weak governance and intrusive interventions by the State" which reduced productivity.[55]
Vanuatu was ranked the 173rd safest investment destination in the world in the March 2011 Euromoney Country Risk rankings.[56]
Communications
Mobile phone service in the islands is provided by TVL and Digicel. Internet access is provided by TVL, Telsat Broadband, Digicel and Wantok using a variety of connection technologies. A newly installed submarine optical fibre cable now connects Vanuatu to Fiji. A government broadband network has been constructed, to provide email, telephone, internet and video conferencing facilities to government offices throughout the country.[57] Vanuatu became the 185th member of the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) in December 2011.[58]
Society
Demographics

Vanuatu has a population of 221,506.[16] Males outnumber females; in 1999, according to the Vanuatu Statistics Office, there were 95,682 males and 90,996 females. The population is predominantly rural, although Port Vila and Luganville have populations in the tens of thousands.
The inhabitants of Vanuatu are called Ni-Vanuatu in English, using a recent coinage. The Ni-Vanuatu are primarily (98.5%) of Melanesian descent, with the remainder made up of a mix of Europeans, Asians and other Pacific islanders. Three islands were historically colonised by Polynesians. About 2,000 Ni-Vanuatu live and work in New Caledonia. In 2006 the New Economics Foundation and Friends of the Earth environmentalist group published the Happy Planet Index which analysed data on levels of reported happiness, life expectancy and Ecological Footprint and estimated Vanuatu to be the most ecologically efficient country in the world in achieving high well-being.[59]
Languages
The national language of the Republic of Vanuatu is Bislama. The official languages are Bislama, French and English. The principal languages of education are French and English. The use of English or French as the formal language is split along political lines.
Bislama is a pidgin language, and now a creole in urban areas. Essentially combining a typically Melanesian grammar with a mostly English vocabulary, Bislama is the only language that can be understood and spoken by the majority of Vanuatu's population as a second language.
In addition to this lingua franca, 113 indigenous languages are still actively spoken in Vanuatu.[60] The density of languages, per capita, is the highest of any nation in the world[61] with an average of only 2,000 speakers per language. All vernacular languages of Vanuatu (i.e., excluding Bislama) belong to the Oceanic branch of the Austronesian family.
In recent years, the use of Bislama as a first language has considerably encroached on indigenous languages, whose use in the population has receded from 73.1 to 63.2 percent between 1999 and 2009.[62]
Religion
Christianity is the predominant religion in Vanuatu, consisting of several denominations. The Presbyterian Church in Vanuatu, adhered to by about one-third of the population, is the largest of them. Roman Catholic and Anglican are other common denominations, each claiming about 15% of the population. Others are the Seventh-day Adventist Church, the Church of Christ,[63] Neil Thomas Ministries (NTM), Jehovah's Witnesses, as well as many other religious groups and denominations.
Because of the modern goods that the military in World War II brought with them when they came to the islands, several cargo cults developed. Many died out, but the John Frum cult on Tanna is still large, and has adherents in the parliament.[citation needed] Also on Tanna is the Prince Philip Movement, which reveres the United Kingdom's Prince Philip.[64] Villagers of the Yaohnanen tribe believed in an ancient story about the pale-skinned son of a mountain spirit venturing across the seas to look for a powerful woman to marry. Prince Philip, having visited the island with his new wife Queen Elizabeth, fitted the description exactly and is therefore revered as a god around the isle of Tanna.[65][66]
Health
Vanuatu has a tropical climate and over 80% of the population lives in rural, isolated villages with access to their own gardens and food supplies. These geographically isolated communities have minimal access to basic health and education services. Churches and non-government organisations provide a minimal level of support to many rural villages. Vanuatu government health and education services are hard pressed to deal with the rapid increase of urban and peri-urban populations in informal and squatter settlements around Port Vila and to a lesser extent in Luganville.[67] Health services in Port Vila and Luganville provide reasonable health care, often supported and enhanced by visiting doctors.[42]
Official statistics show infant mortality declined during the last half of the twentieth century, from 123 deaths per 1,000 population in 1967 to 25 per 1,000 in 1999.[68] There were 46.85 infant deaths per 1,000 live births in 2011.[5]
Education
Education is not compulsory, and school enrolments and attendance are among the lowest in the Pacific. A 1999 estimate for the literacy rate of people aged 15–24 years was about 87% and a 2006 estimate for adult literacy was 78%, although the actual figures are likely to be much lower. The rate of primary school enrolment rose from 74.5% in 1989 to 78.2% in 1999 and then to 93.0% in 2004 but then fell to 85.4% in 2007. The proportion of pupils completing a primary education fell from 90% in 1991 to 72% in 2004[67] and up to 78% in 2012.
Port Vila and three other centres have campuses of the University of the South Pacific, an educational institution co-owned by twelve Pacific countries. The campus in Port Vila, known as the Emalus Campus, houses the University's law school.
Culture

Vanuatu culture retains a strong diversity through local regional variations and through foreign influence. Vanuatu may be divided into three major cultural regions. In the north, wealth is established by how much one can give away, through a grade-taking system. Pigs, particularly those with rounded tusks, are considered a symbol of wealth throughout Vanuatu. In the centre, more traditional Melanesian cultural systems dominate. In the south, a system involving grants of title with associated privileges has developed.[60]
Young men undergo various coming-of-age ceremonies and rituals[69] to initiate them into manhood, usually including circumcision.
Most villages have a nakamal or village clubhouse which serves as a meeting point for men and as a place to drink kava. Villages also have male- and female-only sections. These sections are situated all over the villages; in nakamals, special spaces are provided for females when they are in their menstruation period.
There are few prominent ni-Vanuatu authors. Women's rights activist Grace Mera Molisa, who died in 2002, achieved international notability as a descriptive poet.
Music

The traditional music of Vanuatu is still thriving in the rural areas of Vanuatu. Musical instruments consist mostly of idiophones: drums of various shape and size, slit gongs, stamping tubes, as well as rattles, among others. Another musical genre that has become widely popular during the 20th century in all areas of Vanuatu, is known as string band music. It combines guitars, ukulele, and popular songs.
More recently the music of Vanuatu, as an industry, grew rapidly in the 1990s and several bands have forged a distinctive ni-Vanuatu identity. Popular genres of modern commercial music, which are currently being played in the urban areas include zouk music and reggaeton. Reggaeton, a variation of rap/hip-hop spoken in the Spanish language, played alongside its own distinctive beat, is especially played in the local nightclubs of Port Vila with, mostly, an audience of Westerners and tourists.
Cuisine
The cuisine of Vanuatu (aelan kakae) incorporates fish, root vegetables such as taro and yams, fruits, and vegetables.[15] Most island families grow food in their gardens, and food shortages are rare.[15] Papayas, pineapples, mangoes, plantains, and sweet potatoes are abundant through much of the year.[15] Coconut milk and cream are used to flavour many dishes.[15] Most food is cooked using hot stones or through boiling and steaming; very little food is fried.[15]
The national dish of Vanuatu is the lap lap.[70]
Sports
See also
References
- ^ Selmen, Harrison (17 July 2011). "Santo chiefs concerned over slow pace of development in Sanma". Vanuatu Daily Post. Retrieved 29 August 2011.
- ^ John Lynch and Fa'afo Pat (eds), Proceedings of the first International Conference on Oceanic Linguistics, Australian National University, 1993, p. 319.
- ^ G. W. Trompf, The Gospel Is Not Western: Black Theologies from the Southwest Pacific, Orbis Books, 1987, p. 184.
- ^ "2009 Census Household Listing Counts" (PDF). Vanuatu National Statistics Office. 2009. Archived from the original (PDF) on 5 December 2010. Retrieved 6 January 2010.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ a b Central Intelligence Agency. "Vanuatu". The World Factbook. Retrieved 6 January 2010.
- ^ a b c d "Vanuatu". International Monetary Fund. Retrieved 22 April 2012.
- ^ "Gini Index". World Bank. Retrieved 2 March 2011.
- ^ "2015 Human Development Report" (PDF). United Nations Development Programme. 2015. Retrieved 15 December 2015.
{{cite web}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|1=(help) - ^ Hess, Sabine C. (July 2009). Person and Place: Ideas, Ideals and the Practice of Sociality on Vanua Lava, Vanuatu. Berghahn Books. p. 115. ISBN 978-1-84545-599-6.
- ^ Vanua in turns comes from the Proto-Austronesian banua – see Thomas Anton Reuter, Custodians of the Sacred Mountains: Culture and Society in the Highlands of Bali, University of Hawaii Press, 2002, p. 29; and Thomas Anton Reuter, Sharing the Earth, Dividing the Land: Land and Territory in the Austronesian World, ANU E Press, 2006, p. 326.
- ^ a b Crowley, Terry (2004). Bislama reference grammar. University of Hawaii Press. p. 3. ISBN 978-0-8248-2880-6.
- ^ a b c d e f g "Background Note: Vanuatu". U.S. Department of State. Archived from the original on 13 May 2008. This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ Shears, Richard (1980). The coconut war: the crisis on Espiritu Santo. North Ryde, N.S.W. : Cassell Australia, 1980. pp. 1–210. ISBN 0-7269-7866-3. 1414896.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location (link) CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - ^ "Independence". Vanuatu.travel – Vanuatu Islands. 17 September 2009. Archived from the original on 18 April 2011. Retrieved 17 September 2009.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w The Peace Corps Welcomes You to Vanuatu. Peace Corps (May 2007). This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ a b "Background Note: Vanuatu". Bureau of East Asian and Pacific Affairs. U.S. Department of State. April 2007. Retrieved 16 July 2007.
- ^ "Oceania – Vanuatu Summary". SEDAC Socioeconomic Data and Applications Centre. 2000. Retrieved 26 July 2009.
- ^ a b "Water, Sanitation and Hygiene (Pacific Islands Applied Geoscience Commission)". SOPAC. Retrieved 26 July 2009.
- ^ "Major Earthquake Jolts Island Nation Vanuatu". indiaserver.com. 11 July 2008. Archived from the original on 13 July 2011. Retrieved 26 July 2009.
- ^ Asia Development Bank Vanuatu Economic Report 2009
- ^ Robert George Sprackland (1992). Giant lizards. Neptune, NJ: T.F.H. Publications. ISBN 0-86622-634-6.
- ^ a b Harewood, Jocelyn (2009). Vanuatu and New Caledonia. Lonely Planet. p. 47. ISBN 0-86622-634-6.
- ^ * E. O. Wilson, Naturalist, 1994, Shearwater Books, ISBN 1-55963-288-7
- ^ Bennett, Michelle; Jocelyn Harewood (2003). Vanuatu. Lonely Planet. p. 19. ISBN 978-1-74059-239-0.
- ^ Stephen Coates (17 March 2015). "Rescue teams reach cyclone-hit Vanuatu islands, official toll lowered". Reuters. Reuters. Retrieved 18 March 2015.
- ^ "Cyclone devastates South Pacific islands of Vanuatu". BBC News. 14 March 2015. Retrieved 14 March 2015.
- ^ Joshua Robertson (15 March 2015). "Cyclone Pam: Vanuatu awaits first wave of relief and news from worst-hit islands". The Guardian. Retrieved 18 March 2015.
- ^ "Constitution of the Republic of Vanuatu". Government of the Republic of Vanuatu. 1983. Archived from the original on 30 April 2009. Retrieved 26 July 2009.
- ^ Representation of the People (Parliamentary Constituencies and Seats).
- ^ a b Lonely Planet:Vanuatu
- ^ "Military statistics – How Vanuatu ranks". NationMaster. Retrieved 12 May 2012.
- ^ The British Friends of Vanuatu website
- ^ a b The Vanuatu Police Force. Epress.anu.edu.au. Retrieved 17 April 2012.
- ^ Vanuatu Military 2012. theodora.com
- ^ "Armed forces (Vanuatu) – Sentinel Security Assessment – Oceania". Articles.janes.com. 3 November 2011. Retrieved 12 May 2012.
- ^ Vanuatu Military Profile 2012. Indexmundi.com (12 July 2011). Retrieved 17 April 2012.
- ^ Census of Agriculture 2007 (page 33 – 5.2)
- ^ Census of Agriculture 2007 (page 49 – 7.2)
- ^ Census of Agriculture 2007 (page 77 – 13.1)
- ^ Census of Agriculture 2007 (page 114 – table 4.17)
- ^ Census of Agriculture 2007 (various pages)
- ^ a b Harris, Richard (2006). "Tales from the South Pacific – diving medicine in Vanuatu". South Pacific Underwater Medicine Society Journal. 36 (1). Retrieved 10 March 2013.
- ^ "Asian Development Bank & Vanuatu – Fact Sheet (pdf file)". Asian Development Bank. 31 December 2008. Retrieved 26 July 2009.
- ^ "Tourism and Migration Statistics – Visitor Arrivals by Usual Country of Residence (1995–2001)". Vanuatu Statistics Office. 2001. Archived from the original on 29 April 2009. Retrieved 26 July 2009.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "International Transport Workers' Federation: FOC Countries". Itfglobal.org. 6 June 2005. Retrieved 29 August 2011.
- ^ Census of Agriculture 2007 (page 67 – 11.1)
- ^ Census of Agriculture 2007 (page 73 – 12.1)
- ^ Census of Agriculture 2007 (page 97 – 15.1)
- ^ "Magnitude 7.2 – Vanuatu". USGS Earthquake Hazards Program. Archived from the original on 10 August 2007. Retrieved 13 August 2007.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ a b Census of Agriculture 2007 (page 18)
- ^ Census of Agriculture 2007 (page 19 table 2.5)
- ^ Census of Agriculture 2007 (page 19 – table 2.6)
- ^ Census of Agriculture 2007 (page 20 – Table 2.7)
- ^ Census of Agriculture 2007 (page 27 – Table 4.1)
- ^ a b "Asian Development Bank & Vanuatu – Fact Sheet – Operational Challenges (pdf file)". Asian Development Bank. 31 December 2008. Retrieved 26 July 2009.
- ^ "Euromoney Country Risk". Euromoney country Risk. Euromoney Institutional Investor PLC. Retrieved 15 August 2011.
- ^ "e-Government – Opportunities and Threats, Daily Post, Article Archives". Dailypost.vu. 1 September 2009. Archived from the original on 13 September 2009. Retrieved 22 May 2010.
- ^ Garae, Len (22 December 2011). "Vanuatu is 185th member of WIPO | Vanuatu Daily Post". Vanuatu Daily Post. Retrieved 16 March 2012.
- ^ "Happiness doesn't cost the Earth". BBC News. 12 July 2006. Retrieved 16 July 2007.
- ^ a b "Culture of Vanuatu". Vanuatu Tourism Office. Archived from the original on 20 May 2007. Retrieved 16 July 2007.
- ^ Crowley, Terry. 2000. The language situation in Vanuatu. In Language Planning and Policy in the Pacific: Fiji, the Philippines and Vanuatu, ed. by Richard B. Baldauf,Robert B. Kaplan.
- ^ François, Alexandre (2012), "The dynamics of linguistic diversity: Egalitarian multilingualism and power imbalance among northern Vanuatu languages", International Journal of the Sociology of Language, 214: 85–110, doi:10.1515/ijsl-2012-0022, p.104.
- ^ "World Convention » Vanuatu". Retrieved 9 June 2012.
- ^ Fifty facts about the Duke of Edinburgh. royal.gov.uk (25 January 2002)
- ^ Shears, Richard. Is Prince Philip a god?, Mail on Sunday, 3 June 2006, downloaded 15 February 2007.
- ^ Squires, Nick (27 February 2007). "South Sea tribe prepares birthday feast for their favourite god, Prince Philip". The Daily Telegraph. London.
- ^ a b Asian Development Bank. Vanuatu economic report 2009: accelerating reform. Mandaluyong City, Philippines: Asian Development Bank, 2009.
- ^ "Population Statistics – Vanuatu Population Summary – Vital Statistics 1967–1999". Vanuatu Statistics Office. 1999. Archived from the original on 30 April 2009. Retrieved 26 July 2009.
- ^ Elisabeth Hurtel. "Customs dances and ceremonies in Vanuatu, photolibrary South-Images". South-images.com. Retrieved 22 May 2010.
- ^ The secrets of Vanuatu's national dish, the Lap Lap. Retrieved December 2013
Bibliography
- Census of Agriculture 2007 Vanuatu, Vanuatu National Statistics Office (2008)
Further reading
- Atlas du Vanouatou (Vanuatu), 2009, (1re édition), 392 p., by Patricia Siméoni, Port-Vila, Éditions Géo-consulte
- Arts of Vanuatu by Joël Bonnemaison et al.
- Birds of the Solomons, Vanuatu & New Caledonia by various
- Birds of Vanuatu by Heinrich L. Bregulla
- Cavorting With Cannibals: An Exploration of Vanuatu by Rick Williamson
- Diving and Snorkelling Guide to Vanuatu by various
- Ethnology of Vanuatu: An Early Twentieth Century Study by Felix Speiser
- Gender, Christianity and Change in Vanuatu: An Analysis of Social Movements in North Ambrym by Annelin Erikson
- Getting Stoned with Savages: A Trip Through the Islands of Fiji and Vanuatu by J. Maarten Troost
- House-girls Remember: Domestic Workers in Vanuatu by various
- Language Planning and Policy in the Pacific, vol. 1: Fiji, the Philippines, and Vanuatu by various
- Lonely Planet Guide: Vanuatu & New Caledonia by Jocelyn Harewood
- The Other Side: Ways of Being and Place in Vanuatu by John Patrick Taylor
- Pentecost: An island in Vanuatu by Genevieve Mescam
- Power of Perspective: Social Ontology and Agency on Ambrym Island, Vanuatu by Knut Mikjel Rio
- Unfolding the Moon: Enacting Women's Kastom in Vanuatu by Lissant Bolton
- Vanuatu Adventures: Kava and Chaos in the Sth Pacific by Jocelyn Harewood
- Women in Vanuatu: Analyzing Challenges to Economic Participation by various
- Women of the Place: Kastom, Colonialism and Gender in Vanuatu by Margaret Jolly
External links
- "Vanuatu". The World Factbook (2024 ed.). Central Intelligence Agency.
- Vanuatu from UCB Libraries GovPubs
- Template:Dmoz
 Wikimedia Atlas of Vanuatu
Wikimedia Atlas of Vanuatu- Government of Vanuatu
- Vanuatu Tourism Portal, the official website of the Vanuatu National Tourism Office
- Vanuaflora ; Flora database for Vanuatu (9000 plants on ligne from 20 000)
 Media related to Vanuatu at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Vanuatu at Wikimedia Commons
- Vanuatu
- Archipelagoes of the Pacific Ocean
- Island countries
- Countries in Oceania
- Commonwealth republics
- Republics
- English-speaking countries and territories
- French-speaking countries and territories
- Least developed countries
- Liberal democracies
- Melanesia
- Member states of the Commonwealth of Nations
- Member states of the United Nations
- Spanish East Indies
- States and territories established in 1980




