Black hole information paradox: Difference between revisions
Chaosdruid (talk | contribs) →Postulated solutions: headers to list. There is no information for them to be headings for - Unless each postulation is expanded and fleshed out - as stood it was an information paradox of its own! |
|||
| Line 58: | Line 58: | ||
:Advantage: [[Semiclassical gravity]] is sufficient, i.e., the solution does not depend on details of (still not well understood) [[quantum gravity]]. |
:Advantage: [[Semiclassical gravity]] is sufficient, i.e., the solution does not depend on details of (still not well understood) [[quantum gravity]]. |
||
:Disadvantage: Contradicts the intuitive view of nature as an entity that evolves with time. |
:Disadvantage: Contradicts the intuitive view of nature as an entity that evolves with time. |
||
* The de Broglie wavelength of particles falling into the Black Hole causes permanent bias in the vacuum energy |
|||
Vacuum particle-antiparticle pairs with wavelengths close to or much less than the de Broglie wavelength of the infalling particle are suppressed in favour of higher wavelength particle-antiparticle pairs and this suppression is recorded |
|||
in space-time like a memory of the particle's energy. |
|||
:Advantage:Explains information loss paradox-particles emitted from suppressed zone will have total energy of original infalling particle. |
|||
:Disadvantage:exact mechanism unknown .May be caused by rapid change of space-time curvature just before and beyond event horizon and de Broglie wavelength of infalling particle being made of sum of many different wavelengths that split like |
|||
light passing through a prism. |
|||
== Recent developments == |
== Recent developments == |
||
Revision as of 16:29, 1 May 2016

The black hole information paradox[1] is an observational phenomenon that results from the combination of quantum mechanics and general relativity which suggests that physical information could permanently disappear in a black hole, allowing many physical states to devolve into the same state. This is controversial because it violates a commonly assumed tenet of science—that in principle complete information about a physical system at one point in time should determine its state at any other time.[2][3] A fundamental postulate of quantum mechanics is that complete information about a system is encoded in its wave function up to when the wave function collapses. The evolution of the wave function is determined by a unitary operator, and unitarity implies that information is conserved in the quantum sense. This is the strictest form of determinism.
Principles in action
There are two main principles in play:[citation needed]
- Quantum determinism means that given a present wave function, its future changes are uniquely determined by the evolution operator.
- Reversibility refers to the fact that the evolution operator has an inverse, meaning that the past wave functions are similarly unique.
The combination of the two means that information must always be preserved.
Starting in the mid-1970s, Stephen Hawking and Jacob Bekenstein put forward theoretical arguments based on general relativity and quantum field theory that not only appeared to be inconsistent with information conservation but were not accounting for the information loss and state no reason for it. Specifically, Hawking's calculations[4] indicated that black hole evaporation via Hawking radiation does not preserve information. Today, many physicists believe that the holographic principle (specifically the AdS/CFT duality) demonstrates that Hawking's conclusion was incorrect, and that information is in fact preserved.[5] In 2004 Hawking himself conceded a bet he had made, agreeing that black hole evaporation does in fact preserve information.
Hawking radiation
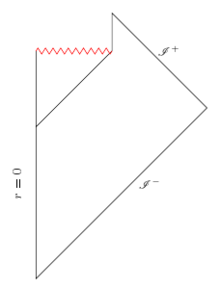
In 1975, Stephen Hawking and Jacob Bekenstein showed that black holes should slowly radiate away energy, which poses a problem. From the no-hair theorem, one would expect the Hawking radiation to be completely independent of the material entering the black hole. Nevertheless, if the material entering the black hole were a pure quantum state, the transformation of that state into the mixed state of Hawking radiation would destroy information about the original quantum state. This violates Liouville's theorem and presents a physical paradox.[citation needed]
More precisely, if there is an entangled pure state, and one part of the entangled system is thrown into the black hole while keeping the other part outside, the result is a mixed state after the partial trace is taken into the interior of the black hole. But since everything within the interior of the black hole will hit the singularity within a finite time, the part which is traced over partially might disappear completely from the physical system.[citation needed]
Hawking remained convinced that the equations of black-hole thermodynamics together with the no-hair theorem led to the conclusion that quantum information may be destroyed. This annoyed many physicists, notably John Preskill, who bet Hawking and Kip Thorne in 1997 that information was not lost in black holes. The implications that Hawking had opened led to a "battle" where Leonard Susskind and Gerard 't Hooft publicly 'declared war' on Hawking's solution, with Susskind publishing a popular book, The Black Hole War, about the debate in 2008. (The book carefully notes that the 'war' was purely a scientific one, and that at a personal level, the participants remained friends.[6]) The solution to the problem that concluded the battle is the holographic principle, which was first proposed by 't Hooft but was given a precise string theory interpretation by Susskind. With this, "Susskind quashes Hawking in [the] quarrel over quantum quandary".[7]
There are various ideas about how the paradox is solved. Since the 1997 proposal of the AdS/CFT correspondence, the predominant belief among physicists is that information is preserved and that Hawking radiation is not precisely thermal but receives quantum corrections.[clarification needed] Other possibilities include the information being contained in a Planckian remnant left over at the end of Hawking radiation or a modification of the laws of quantum mechanics to allow for non-unitary time evolution.[citation needed]
In July 2004, Stephen Hawking published a paper presenting a theory that quantum perturbations of the event horizon could allow information to escape from a black hole, which would resolve the information paradox.[8] His argument assumes the unitarity of the AdS/CFT correspondence which implies that an AdS black hole that is dual to a thermal conformal field theory. When announcing his result, Hawking also conceded the 1997 bet, paying Preskill with a baseball encyclopedia "from which information can be retrieved at will." [citation needed]
According to Roger Penrose, loss of unitarity in quantum systems is not a problem: quantum measurements are by themselves already non-unitary. Penrose claims that quantum systems will in fact no longer evolve unitarily as soon as gravitation comes into play, precisely as in black holes. The Conformal Cyclic Cosmology advocated by Penrose critically depends on the condition that information is in fact lost in black holes. This new cosmological model might in future be tested experimentally by detailed analysis of the cosmic microwave background radiation (CMB): if true the CMB should exhibit circular patterns with slightly lower or slightly higher temperatures. In November 2010, Penrose and V. G. Gurzadyan announced they had found evidence of such circular patterns, in data from the Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe (WMAP) corroborated by data from the BOOMERanG experiment.[9] The significance of the findings was subsequently debated by others.[clarification needed]
Postulated solutions
- Advantage: Seems to be a direct consequence of relatively non-controversial calculation based on semiclassical gravity.
- Disadvantage: Violates unitarity. (Banks, Susskind and Peskin argued that it also violates energy-momentum conservation or locality, but the argument does not seem to be correct for systems with a large number of degrees of freedom [12]).
- Advantage: Intuitively appealing because it qualitatively resembles information recovery in a classical process of burning.
- Disadvantage: Requires a large deviation from classical and semiclassical gravity (which do not allow information to leak out from the black hole) even for macroscopic black holes for which classical and semiclassical approximations are expected to be good approximations.
- Advantage: A significant deviation from classical and semiclassical gravity is needed only in the regime in which the effects of quantum gravity are expected to dominate.
- Disadvantage: Just before the sudden escape of information, a very small black hole must be able to store an arbitrary amount of information, which violates the Bekenstein bound.
- Advantage: No mechanism for information escape is needed.
- Disadvantage: To contain the information from any evaporated black hole, the remnants would need to have an infinite number of internal states. It has been argued that it would be possible to produce an infinite amount of pairs of these remnants since they are small and indistinguishable from the perspective of the low-energy effective theory.[13]
- Advantage: The size of remnant increases with the size of the initial black hole, so there is no need for an infinite number of internal states.
- Disadvantage: Hawking radiation must stop before the black hole reaches the Planck size, which requires a violation of semi-classical gravity at a macroscopic scale.
- Advantage: This scenario is predicted by the Einstein–Cartan theory of gravity which extends general relativity to matter with intrinsic angular momentum (spin). No violation of known general principles of physics is needed.
- Disadvantage: It is difficult to test the Einstein–Cartan theory because its predictions are significantly different from general-relativistic ones only at extremely high densities.
- Advantage: Semiclassical gravity is sufficient, i.e., the solution does not depend on details of (still not well understood) quantum gravity.
- Disadvantage: Contradicts the intuitive view of nature as an entity that evolves with time.
- The de Broglie wavelength of particles falling into the Black Hole causes permanent bias in the vacuum energy
Vacuum particle-antiparticle pairs with wavelengths close to or much less than the de Broglie wavelength of the infalling particle are suppressed in favour of higher wavelength particle-antiparticle pairs and this suppression is recorded in space-time like a memory of the particle's energy.
- Advantage:Explains information loss paradox-particles emitted from suppressed zone will have total energy of original infalling particle.
- Disadvantage:exact mechanism unknown .May be caused by rapid change of space-time curvature just before and beyond event horizon and de Broglie wavelength of infalling particle being made of sum of many different wavelengths that split like
light passing through a prism.
Recent developments
In 2014, Chris Adami, a physicist at the Michigan State University claimed to have solved the paradox.[19] Since absolute loss of information is not allowed by quantum physics, Adami argues that the "lost" information is contained in stimulated emission that accompanies the Hawking radiation emitted by blackholes.[20] His solution has not been confirmed.
Hawking et al. 5 Jan 2016 proposed new theories of information moving in and out of a black hole.[21][22] The 2016 work posits that the information is saved in "soft particles", low-energy versions of photons and other particles that exist in zero-energy empty space.[23]
See also
- AdS/CFT correspondence
- Beyond black holes
- Black hole complementarity
- Cosmic censorship hypothesis
- Firewall (physics)
- Fuzzball (string theory)
- Holographic principle
- List of paradoxes
- Maxwell's Demon
- No-hair theorem
- Thorne–Hawking–Preskill bet
References
- ^ The short form "ínformation paradox" is also used for the Arrow information paradox.
- ^ Hawking, Stephen (2006). The Hawking Paradox. Discovery Channel. Retrieved 13 August 2013.
- ^ Overbye, Dennis (12 August 2013). "A Black Hole Mystery Wrapped in a Firewall Paradox". New York Times. Retrieved 12 August 2013.
- ^ Hawking, Stephen (1 August 1975). "Particle Creation by Black Holes". Commun. Math. Phys. 43 (3): 199–220. Bibcode:1975CMaPh..43..199H. doi:10.1007/BF02345020. Retrieved 13 August 2013.
- ^ Barbón, J. L. F. "Black holes, information and holography" J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 171 01 (2009) doi:10.1088/1742-6596/171/1/012009 http://iopscience.iop.org/1742-6596/171/1/012009 p.1: "The most important departure from conventional thinking in recent years, the holographic principle...provides a definition of quantum gravity...[and] guarantees that the whole process is unitary."
- ^ Susskind, Leonard (2008-07-07). The Black Hole War: My Battle with Stephen Hawking to Make the World Safe for Quantum Mechanics. Little, Brown. p. 10. ISBN 9780316032698. Retrieved 2015-04-07.
It was not a war between angry enemies; indeed the main participants are all friends. But it was a fierce intellectual struggle of ideas between people who deeply respected each other but also profoundly disagreed.
- ^ "Susskind Quashes Hawking in Quarrel Over Quantum Quandary". CALIFORNIA LITERARY REVIEW. 2008-07-09. Archived from the original on 2012-04-02.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Baez, John. "This Week's Finds in Mathematical Physics (Week 207)". Retrieved 2011-09-25.
- ^ Gurzadyan, V. G.; Penrose, R. (2010). "Concentric circles in WMAP data may provide evidence of violent pre-Big-Bang activity". 1011: 3706. arXiv:1011.3706. Bibcode:2010arXiv1011.3706GTemplate:Inconsistent citations
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help)CS1 maint: postscript (link). - ^ a b c d Giddings, Steven B. (1995). "The black hole information paradox". Particles, Strings and Cosmology. Johns Hopkins Workshop on Current Problems in Particle Theory 19 and the PASCOS Interdisciplinary Symposium 5. arXiv:hep-th/9508151.
{{cite conference}}: Unknown parameter|booktitle=ignored (|book-title=suggested) (help) - ^ a b c d e Preskill, John (1992). Do Black Holes Destroy Information?. International Symposium on Black Holes, Membranes, Wormholes, and Superstrings. arXiv:hep-th/9209058.
- ^ Nikolic, Hrvoje (2015). "Violation of unitarity by Hawking radiation does not violate energy-momentum conservation". 04. JCAP: 002. arXiv:1502.04324.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ Giddings, Steven B. (1998). "Comments on information loss and remnants". Phys Rev D. arXiv:hep-th/9310101. Bibcode:1994PhRvD..49.4078G. doi:10.1103/PhysRevD.49.4078.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ Giddings, Steven (1992). "Black Holes and Massive Remnants". 46. Phys Rev D: 1347–1352. arXiv:hep-th/9203059.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ Nikolic, Hrvoje (2015). "Gravitational crystal inside the black hole". 30. Mod Phys. Lett A: 1550201. arXiv:1505.04088.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ Nikodem J. Popławski (2010). "Cosmology with torsion: An alternative to cosmic inflation". Physics Letters B. 694 (3): 181–185. arXiv:1007.0587. Bibcode:2010PhLB..694..181P. doi:10.1016/j.physletb.2010.09.056.
- ^ Hartle, James B. (1998). "Generalized Quantum Theory in Evaporating Black Hole Spacetimes". Black Holes and Relativistic Stars: 195. arXiv:gr-qc/9705022. Bibcode:1998bhrs.conf..195H.
- ^ Nikolic, Hrvoje (2009). "Resolving the black-hole information paradox by treating time on an equal footing with space". Physics Letters B. 678 (2). Phys. Lett.: 218–221. arXiv:0905.0538. Bibcode:2009PhLB..678..218N. doi:10.1016/j.physletb.2009.06.029.
- ^ Bradler, Kamil; Adami, Christoph. "The capacity of black holes to transmit quantum information". Journal of High Energy Physics. 2014 (5). doi:10.1007/JHEP05(2014)095. ISSN 1029-8479.
- ^ "Plugging the hole in Hawking's black hole theory". MSUToday. Retrieved 2015-12-26.
- ^ "Stephen Hawking's New Black-Hole Paper, Translated: An Interview with Co-Author Andrew Strominger". Scientific American Blog Network. Retrieved 2016-01-09.
- ^ Hawking, Stephen W.; Perry, Malcolm J.; Strominger, Andrew (2016-01-05). "Soft Hair on Black Holes". arXiv:1601.00921 [hep-th].
- ^ magazine, Davide Castelvecchi,Nature. "Hawking's Latest Black Hole Paper Splits Physicists". Scientific American. Retrieved 2016-01-27.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
External links
- Black Hole Information Loss Problem, a USENET physics FAQ page
- Preskill, John (1992). "Do black holes destroy information?". An international symposium on Black Holes: 22. arXiv:hep-th/9209058. Bibcode:1993bhmw.conf...22PTemplate:Inconsistent citations
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: postscript (link). Discusses methods of attack on the problem, and their apparent shortcomings. - Report on Hawking's 2004 theory at Nature
- Hawking, S. W. (July 2005), Information Loss in Black Holes, arxiv:hep-th/0507171. Stephen Hawking's purported solution to the black hole unitarity paradox.
- Hawking and unitarity: an up-to-date discussion of the information loss paradox and Stephen Hawking's role in it
- The Hawking Paradox - BBC Horizon documentary (2005)
- "Horizon" The Hawking Paradox at IMDb
- A Black Hole Mystery Wrapped in a Firewall Paradox

