1,2-Bis(dimethylphosphino)ethane: Difference between revisions
m Chembox: rm/replace deprecated params. Fix unknown parameters (via AWB script) |
m corected authors list (CS1 maint) |
||
| Line 50: | Line 50: | ||
==Synthesis== |
==Synthesis== |
||
It is synthesised by the reaction of [[methylmagnesium iodide]] with 1,2-bis(dichlorophosphino)ethane:<ref>{{cite journal | |
It is synthesised by the reaction of [[methylmagnesium iodide]] with 1,2-bis(dichlorophosphino)ethane:<ref>{{cite journal |authors =R. J. Burt, J. Chatt, W. Hussain, G. J. Leigh |title=A convenient synthesis of 1,2-bis(dichlorophosphino)ethane, 1,2-bis(dimethylphosphino)ethane and 1,2-bis(diethylphosphino)ethane |journal=[[Journal of Organometallic Chemistry|J. Organomet. Chem.]] |volume=182 |issue=2 |year=1979 |pages=203–6 |doi=10.1016/S0022-328X(00)94383-3}}</ref> |
||
:Cl<sub>2</sub>PCH<sub>2</sub>CH<sub>2</sub>PCl<sub>2</sub> + 4 MeMgI → Me<sub>2</sub>PCH<sub>2</sub>CH<sub>2</sub>PMe<sub>2</sub> + 4 MgICl |
:Cl<sub>2</sub>PCH<sub>2</sub>CH<sub>2</sub>PCl<sub>2</sub> + 4 MeMgI → Me<sub>2</sub>PCH<sub>2</sub>CH<sub>2</sub>PMe<sub>2</sub> + 4 MgICl |
||
Alternatively but it can be generated by alkylation of sodium dimethylphosphide. |
Alternatively but it can be generated by alkylation of sodium dimethylphosphide. |
||
Revision as of 03:31, 14 May 2016

| |
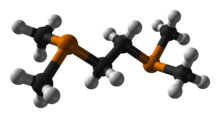
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Ethane-1,2-diylbis(dimethylphosphane)
| |
| Other names
DMPE
ethylenebis(dimethylphosphine) 1,2-Bis(dimethylphosphino)ethane | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.155.809 |
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H16P2 | |
| Molar mass | 150.14 g mol−1 |
| Density | 0.9 g/mL at 25 °C |
| Boiling point | 180 °C (356 °F; 453 K) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
  [1] [1]
| |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
1,2-Bis(dimethylphosphino)ethane (dmpe) is a diphosphine ligand in coordination chemistry. It is a colorless, air-sensitive liquid that is soluble in organic solvents. With the formula (CH2PMe2)2 is used as a compact strongly basic spectator ligand (Me = methyl), Representative complexes include V(dmpe)2(BH4)2, Mn(dmpe)2(AlH4)2, Tc(dmpe)2(CO)2Cl, and Ni(dmpe)Cl2.[2]
Synthesis
It is synthesised by the reaction of methylmagnesium iodide with 1,2-bis(dichlorophosphino)ethane:[3]
- Cl2PCH2CH2PCl2 + 4 MeMgI → Me2PCH2CH2PMe2 + 4 MgICl
Alternatively but it can be generated by alkylation of sodium dimethylphosphide.
The synthesis of dmpe from thiophosphoryl chloride has led to serious accidents and has been abandoned.[4]
Related ligands
Tetramethylethylenediamine is the diamine analogue of dmpe. Bis(dicyclohexylphosphino)ethane is a bulky analogue of dmpe, which offers the advantage of being a solid.
References
- ^ a b c Sigma-Aldrich Co., 1,2-Bis(dimethylphosphino)ethane. Retrieved on 2013-07-20.
- ^ Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. ISBN 978-0-08-037941-8.
- ^ "A convenient synthesis of 1,2-bis(dichlorophosphino)ethane, 1,2-bis(dimethylphosphino)ethane and 1,2-bis(diethylphosphino)ethane". J. Organomet. Chem. 182 (2): 203–6. 1979. doi:10.1016/S0022-328X(00)94383-3.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|authors=ignored (help) - ^ J. E. Bercaw, G. W. Parshall, "Preparation of Tetramethyldiphosphine Disulfide and Ethylenebis(dimethylphosphine) (dmpe)" Inorganic Syntheses 1985, vol. 23, Pages: 199–200. doi:10.1002/9780470132548.ch42
