Distal radioulnar articulation: Difference between revisions
Mannanan51 (talk | contribs) |
Luis Goslin (talk | contribs) m fixed link to radius |
||
| Line 36: | Line 36: | ||
==Function== |
==Function== |
||
The function of the radioulnar joint is to lift and maneuver weight load from the distal radioulnar joint to be distributed across the forearm’s [[radius]] and [[ulna]] as a [[load-bearing joint]].<ref>Lees, V. (2013). Functional anatomy of the distal radioulnar joint in health and disease. Annals of The Royal College of Surgeons of England, 95(3), 163–170. doi:10.1308/003588413X13511609957452</ref> [[Supination]] of the radioulnar joint can move from 0 [[Range of Motion|degrees]] neutral to approximately 80-90 degrees where [[Pronation]] of the Radioulnar Joint can move from 0 degrees neutral to approximately 70-90 degrees.<ref>Thomas, B. P., & Sreekanth, R. (2012). Distal radioulnar joint injuries. Indian Journal of Orthopaedics, 46(5), 493–504. doi:10.4103/0019-5413.101031</ref> Supination (palms facing up) vs. pronation (palms facing down). Muscles that contribute to function are all supinator ([[Biceps Brachii]], [[Brachioradialis]], and [[Supinator]]) and pronator muscles ([[Brachioradialis]], [[Pronator Quadratus]], and [[Pronator Teres]]). |
The function of the radioulnar joint is to lift and maneuver weight load from the distal radioulnar joint to be distributed across the forearm’s [[Radius_(bone)|radius]] and [[ulna]] as a [[load-bearing joint]].<ref>Lees, V. (2013). Functional anatomy of the distal radioulnar joint in health and disease. Annals of The Royal College of Surgeons of England, 95(3), 163–170. doi:10.1308/003588413X13511609957452</ref> [[Supination]] of the radioulnar joint can move from 0 [[Range of Motion|degrees]] neutral to approximately 80-90 degrees where [[Pronation]] of the Radioulnar Joint can move from 0 degrees neutral to approximately 70-90 degrees.<ref>Thomas, B. P., & Sreekanth, R. (2012). Distal radioulnar joint injuries. Indian Journal of Orthopaedics, 46(5), 493–504. doi:10.4103/0019-5413.101031</ref> Supination (palms facing up) vs. pronation (palms facing down). Muscles that contribute to function are all supinator ([[Biceps Brachii]], [[Brachioradialis]], and [[Supinator]]) and pronator muscles ([[Brachioradialis]], [[Pronator Quadratus]], and [[Pronator Teres]]). |
||
==Injuries== |
==Injuries== |
||
Revision as of 12:25, 15 September 2016
| Distal radioulnar articulation | |
|---|---|
 | |
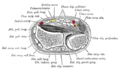
 Vertical section through the articulations at the wrist, showing the synovial cavities | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Articulatio radioulnaris distalis |
| TA98 | A03.5.10.001 |
| TA2 | 1781 |
| FMA | 35290 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The distal radioulnar articulation (inferior radioulnar joint) is a joint between the two bones in the forearm; the radius and ulna. It is one of two joints between the radius and ulna, the other being the proximal radioulnar articulation. The distal radioulnar articulation is the one of the two closest to the wrist and hand.
The distal radioulnar articulation pivot-joint formed between the head of ulna and the ulnar notch on the lower extremity of radius.
Ligaments
The articular surfaces are connected together by the following ligaments:
Function
The function of the radioulnar joint is to lift and maneuver weight load from the distal radioulnar joint to be distributed across the forearm’s radius and ulna as a load-bearing joint.[1] Supination of the radioulnar joint can move from 0 degrees neutral to approximately 80-90 degrees where Pronation of the Radioulnar Joint can move from 0 degrees neutral to approximately 70-90 degrees.[2] Supination (palms facing up) vs. pronation (palms facing down). Muscles that contribute to function are all supinator (Biceps Brachii, Brachioradialis, and Supinator) and pronator muscles (Brachioradialis, Pronator Quadratus, and Pronator Teres).
Injuries
Injuries to the distal radioulnar articulation often result from falls onto an outstretched hand. Injury can occur with concurrent fracture of the distal radius, the ulna, or can be isolated. A classification system has been proposed by Estaminet and colleagues.[3]
Estaminet Classification
Estaminet classified injuries of the distal radioulnar articulation into four categories with two subclasses: purely ligamentous (subclass A) and those with associated boney injury (subclass B).
- Estaminet I - Attenuation on MRI only
- Estaminet II - Volar distal radioulnar ligament is involved. Unstable in supination. Fixation should be in pronation.
- Estaminet III - Dorsal distal radioulnar ligament is involved. Unstable in pronation. Fixation should be in supination.
- Estaminet IV - Both ligaments are involved. Unstable in both supination and pronation. Fixation is in neutral.
Additional images
-
Transverse section across distal ends of radius and ulna.
See also
References
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 325 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 325 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- ^ Lees, V. (2013). Functional anatomy of the distal radioulnar joint in health and disease. Annals of The Royal College of Surgeons of England, 95(3), 163–170. doi:10.1308/003588413X13511609957452
- ^ Thomas, B. P., & Sreekanth, R. (2012). Distal radioulnar joint injuries. Indian Journal of Orthopaedics, 46(5), 493–504. doi:10.4103/0019-5413.101031
- ^ Estaminet et al. Estaminet-Klassifikation von distal radioulnar Aussprache-Trauma. 20. Jahresversammlung der europäischen Orthopädischen Forschungsgesellschaft (EORS 2012), am 26–28 September, Amsterdam, Die Niederlande